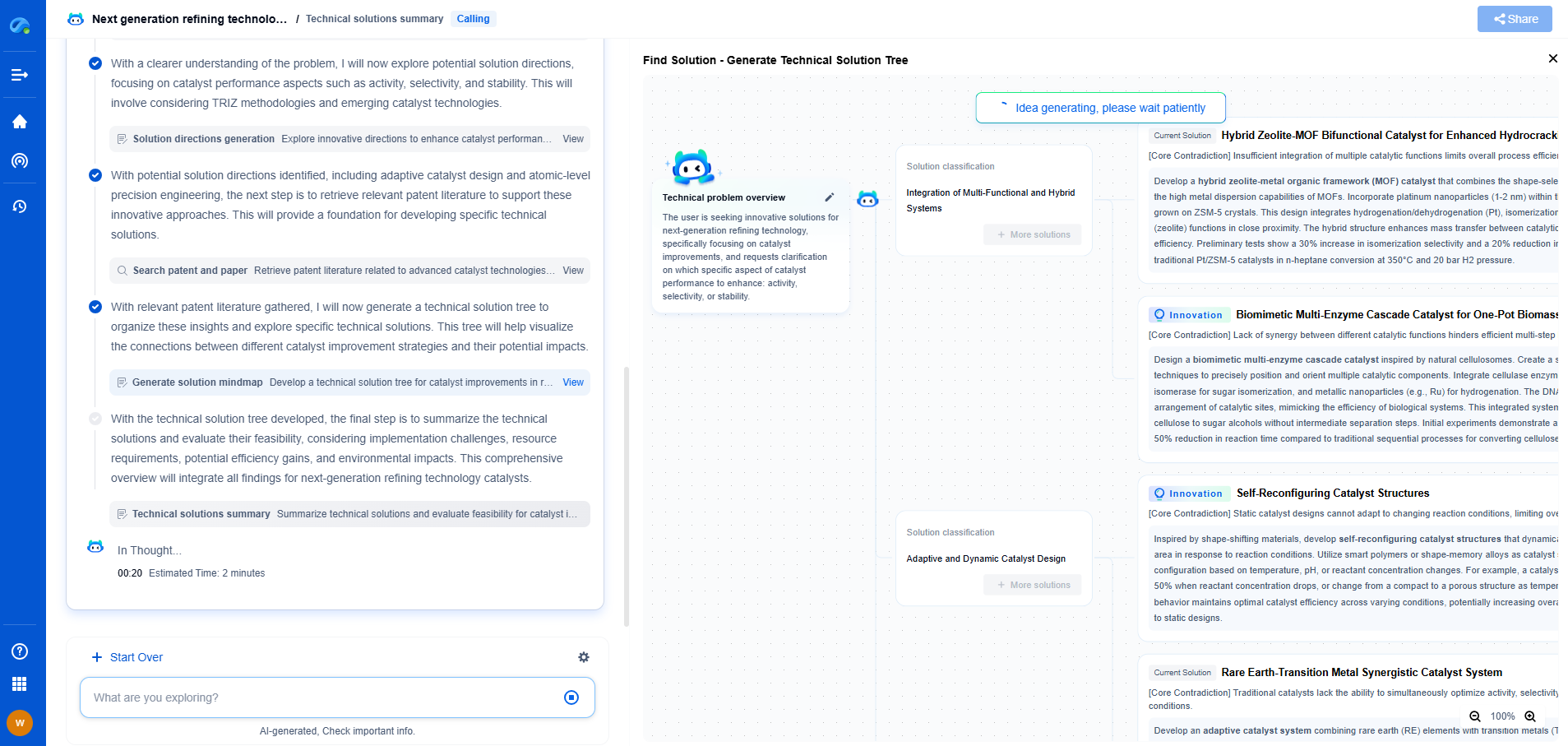
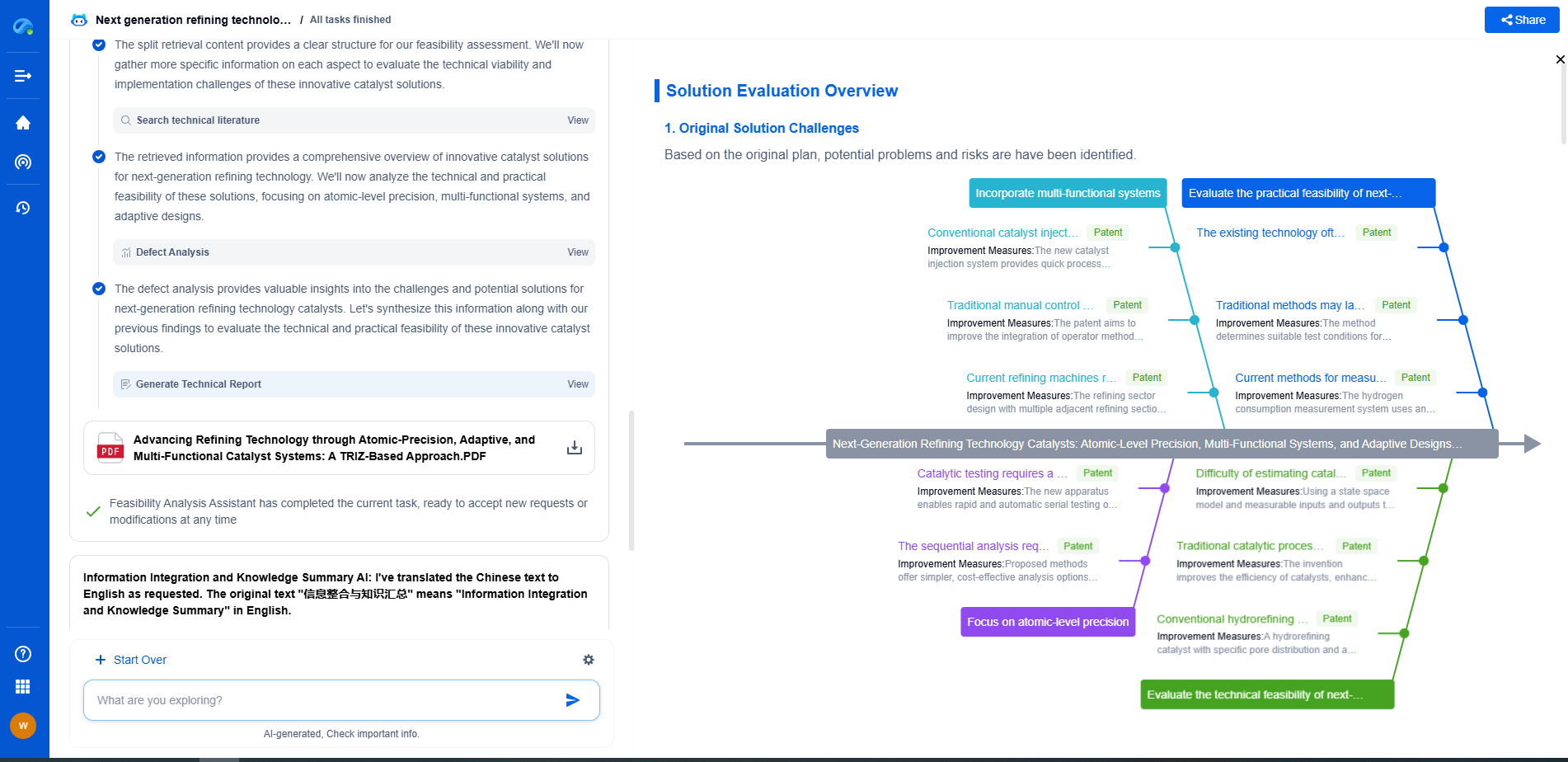
ASME B31.4 vs. B31.8: Key Differences Between Liquid & Gas Pipeline Design Rules
JUN 20, 2025 |
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) is a key organization in the development of standards and codes for engineering practices. Two of its essential standards for pipeline systems are ASME B31.4 and ASME B31.8, which respectively address the design, construction, and operation of liquid and gas pipelines. These standards ensure the safety, reliability, and efficiency of pipeline systems, each tailored to the specific characteristics of the media they transport. Understanding the differences between these codes is crucial for engineers and project managers who work in pipeline design and construction.
Purpose and Scope
ASME B31.4 is the code for liquid transportation systems for hydrocarbons, liquid petroleum gas, and anhydrous ammonia. It covers aspects such as the design, materials, construction, operation, and maintenance of these pipelines. ASME B31.8, on the other hand, is focused on gas transportation systems, including natural gas and other gaseous hydrocarbons. While both standards share a similar structure, their scopes are distinct, reflecting the different challenges and requirements associated with liquid and gas transport.
Design Considerations
One of the primary differences between B31.4 and B31.8 lies in the design considerations of pipelines. Liquid pipelines, governed by B31.4, must account for factors such as hydraulic design, pump station requirements, and surge pressures. The focus is often on maintaining a stable flow and preventing phenomena like water hammer, which can cause significant damage.
Gas pipelines, under B31.8, have unique considerations related to compressibility and the behavior of gases under pressure. This standard emphasizes the importance of pressure regulation, compressor stations, and the potential for leaks. The design must account for the varying physical properties of gases, including density and viscosity, which can affect pipeline flow dynamics.
Material Selection
Material selection is another area where B31.4 and B31.8 differ significantly. For liquid pipelines, the material must withstand the corrosive nature of the transported liquids, such as crude oil or ammonia. B31.4 provides guidance on selecting materials that can resist corrosion and maintain integrity under specific temperature and pressure conditions.
Gas pipelines face different challenges. ASME B31.8 requires materials that can handle high pressures and resist the potential for gas permeation, which could lead to leaks. The code emphasizes the use of materials that can endure the physical stress of gas transport, particularly at high velocities and pressures.
Construction and Welding
Construction and welding practices also vary between liquid and gas pipelines. B31.4 stipulates requirements for welding procedures and quality control measures specific to liquid transport systems. These include techniques for welding pipes that must withstand the chemical properties of the transported liquid and resist potential leaks.
In contrast, B31.8 outlines procedures that ensure the integrity of gas pipelines under pressure. It emphasizes the importance of weld quality and testing, given the risks associated with gas leaks and explosions. The code provides detailed specifications to ensure that welds can withstand the operational pressures of gas transport.
Operational and Maintenance Requirements
The operational and maintenance requirements for liquid and gas pipelines are tailored to their respective transport media. B31.4 requires regular inspection and maintenance to prevent leaks and ensure the efficient transport of liquids. This includes monitoring for corrosion, pressure anomalies, and potential blockages.
For gas pipelines, B31.8 emphasizes the importance of safety measures and leak detection systems. Regular inspections and maintenance are critical to prevent leaks that could lead to dangerous situations, such as fires or explosions. The code provides guidance on implementing safety protocols that minimize risk and ensure reliable operation.
Regulatory Compliance
Both ASME B31.4 and B31.8 are essential for ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. They provide frameworks that meet national and international guidelines for pipeline safety and efficiency. These standards aid in navigating the complex regulatory landscape and help companies avoid penalties associated with non-compliance.
Conclusion
In summary, while ASME B31.4 and B31.8 share common goals of safety and reliability, they are designed to address the unique challenges of liquid and gas pipelines. Understanding their differences is vital for engineers to design systems that are both efficient and compliant with industry standards. Whether designing pipelines for liquid or gas transport, adhering to these codes ensures the integrity and performance of pipeline systems across diverse environments.
Transform the Way You Innovate in Pipeline Technology—with AI-Powered Intelligence
From corrosion-resistant materials to smart monitoring systems and advanced flow control mechanisms, the pipeline industry is undergoing rapid technological transformation. Yet keeping up with evolving engineering solutions, regulatory landscapes, and competitive patents can be a major bottleneck for R&D and IP teams.
Patsnap Eureka is your AI-powered research companion—built specifically for professionals in high-tech and infrastructure domains like pipeline technology. Whether you're designing high-pressure transport systems, assessing trenchless installation innovations, or safeguarding proprietary flow assurance solutions, Eureka provides real-time insights into global patent trends, emerging technologies, and R&D intelligence—all in one intuitive interface.
Empower your team to innovate faster, reduce technical blind spots, and stay ahead of industry shifts. Discover Patsnap Eureka today and bring clarity and confidence to your pipeline technology decisions.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com