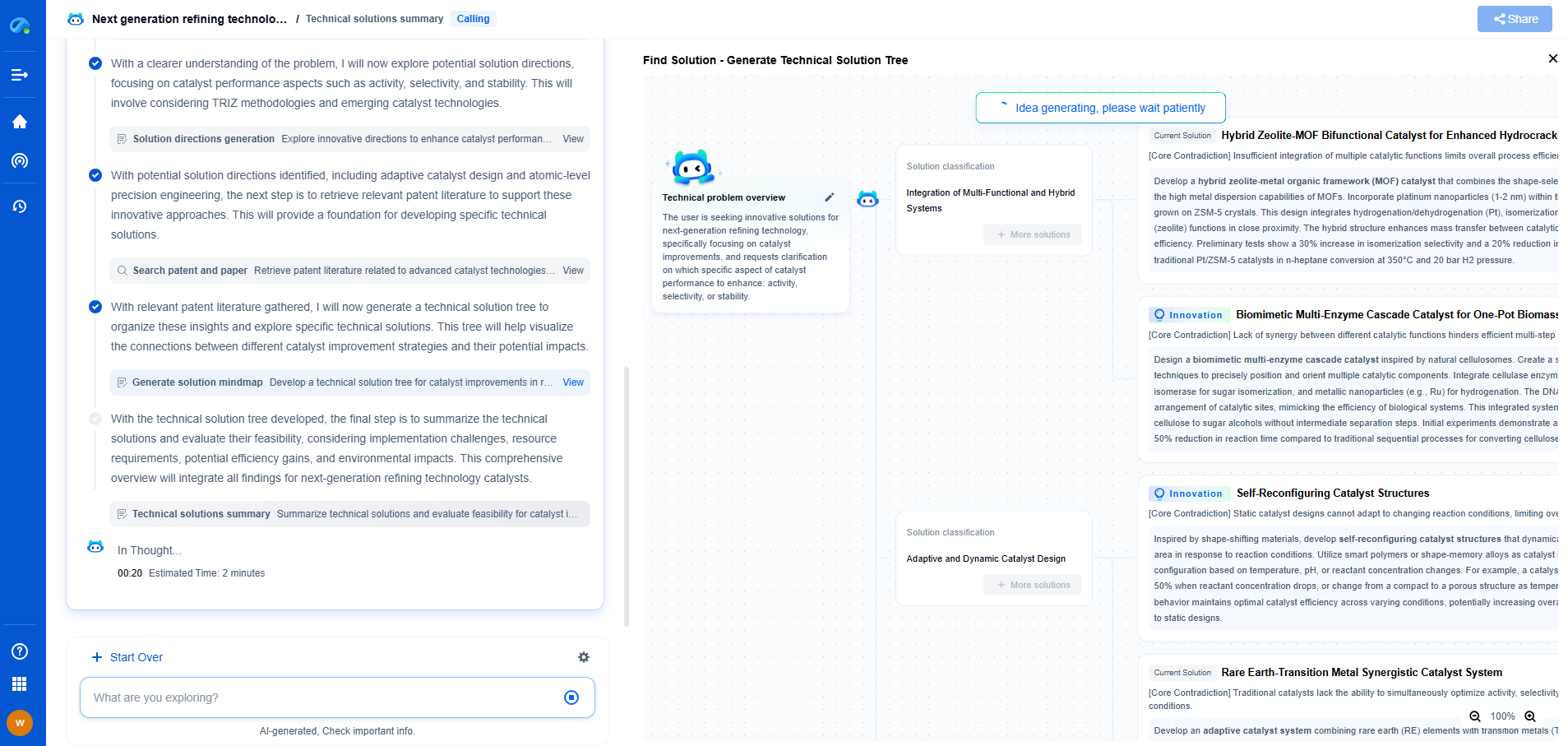
Belt drive vs. gear drive in agricultural machines: Which is better?
JUL 2, 2025 |
In the realm of agricultural machinery, the drive system is a crucial component that significantly impacts the efficiency, maintenance, and overall performance of equipment. Two predominant drive systems in agricultural machines are belt drives and gear drives. Each has its own set of advantages and drawbacks, and choosing the right one can make a considerable difference in the operation and longevity of agricultural equipment. This article delves into the characteristics of both belt drives and gear drives, aiming to provide a comprehensive comparison to determine which might be better suited for specific agricultural applications.
Understanding Belt Drives
Belt drives are one of the oldest forms of power transmission, using belts to transmit power between shafts. They are commonly utilized in various agricultural machines such as combine harvesters, tractors, and irrigation equipment.
Advantages of Belt Drives
One of the primary benefits of belt drives is their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. They are relatively easy to install and maintain, often requiring minimal downtime for repairs or replacements. Belt drives are known for their smooth and quiet operation, which can be beneficial in reducing noise pollution and vibrations in agricultural settings.
Furthermore, belt drives offer flexibility in terms of distance between drive and driven shafts, allowing for more versatile design options in machine construction. This flexibility is complemented by the ability of belt drives to absorb shock loads, thereby protecting the machinery from sudden impacts.
Limitations of Belt Drives
However, belt drives are not without their drawbacks. They can suffer from slippage, particularly under heavy loads or when the belts become worn or improperly tensioned. This slippage can lead to a loss of efficiency and power transmission, making belt drives less suitable for high-torque applications.
Belt drives also require more frequent maintenance compared to gear drives, as belts can wear out or break over time, especially in harsh agricultural environments where exposure to dirt, debris, and weather conditions is common.
Exploring Gear Drives
Gear drives, on the other hand, utilize interlocking gears to transmit power between shafts. They are often found in applications requiring high precision and torque, such as in the drivetrain of tractors or in high-power machinery.
Advantages of Gear Drives
The chief advantage of gear drives is their efficiency in power transmission. With minimal slippage, gear drives can reliably transmit power with high precision and consistency, making them ideal for heavy-duty applications. Gear drives are also known for their durability and longevity, often requiring less frequent replacements compared to belt drives.
Additionally, gear drives can handle higher loads and operate effectively in compact spaces, which is advantageous in machines where space is a premium. This robustness makes them well-suited for tasks that demand high torque and reliability.
Limitations of Gear Drives
Despite their strengths, gear drives come with their own set of challenges. They are generally more expensive to manufacture and repair, requiring specialized parts and skilled labor. Installation and maintenance can be more complex and time-consuming, leading to longer downtimes if issues arise.
Gear drives can also contribute to increased noise and vibration levels, which might be a concern in applications where operational quietness is desirable. Additionally, while they are less susceptible to environmental conditions than belt drives, they still require lubrication and protection from contaminants to function optimally.
Making the Right Choice
When choosing between belt drives and gear drives for agricultural machines, several factors must be considered. The specific application, required power and torque, environmental conditions, budget constraints, and maintenance capabilities all play a crucial role in determining the most suitable drive system.
For applications where cost-effectiveness, simplicity, and flexibility are prioritized, and where high precision is not critical, belt drives might be the preferable choice. On the other hand, for heavy-duty applications demanding high torque, efficiency, and durability, gear drives may be more appropriate.
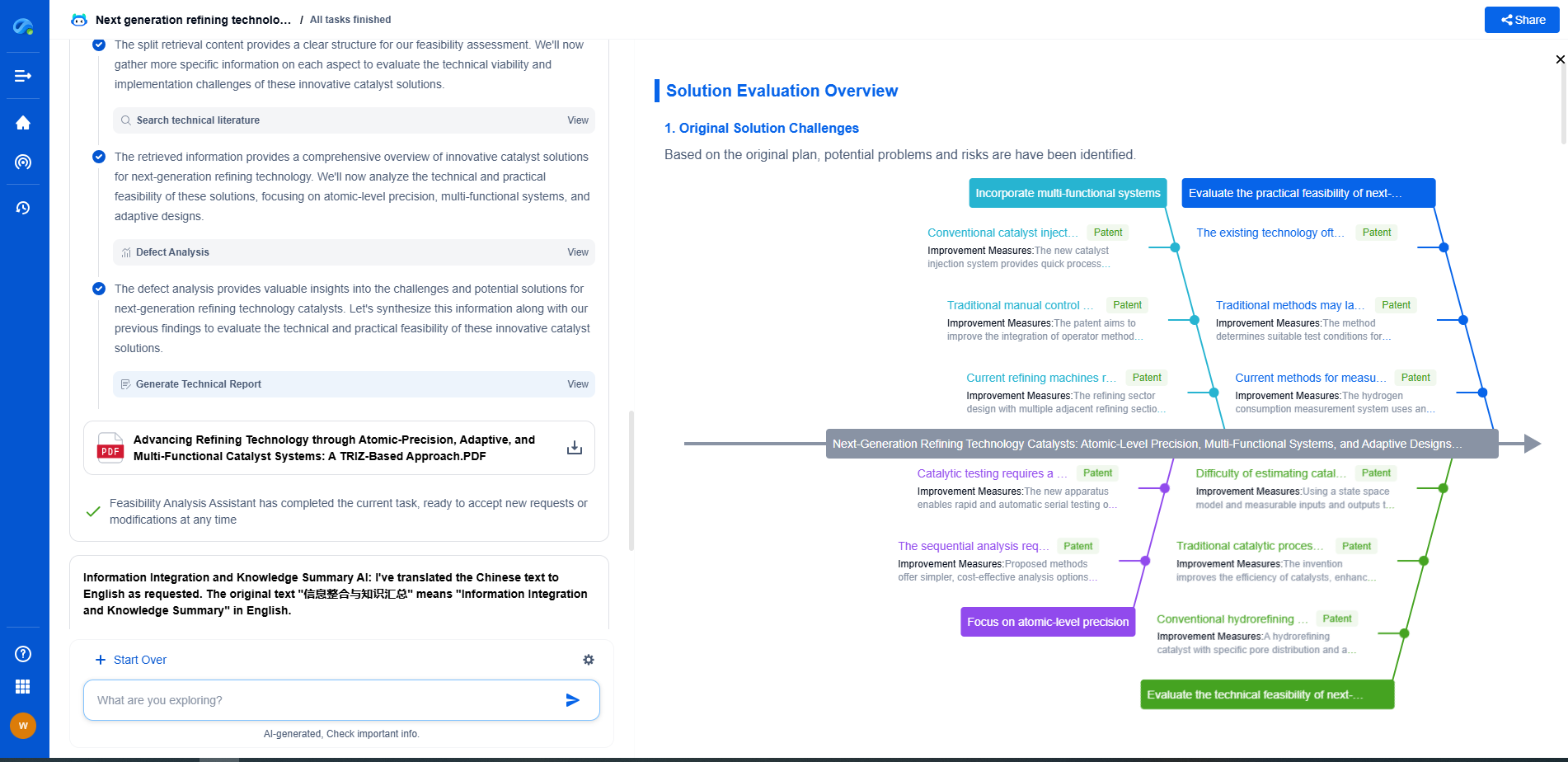
Conclusion
Both belt drives and gear drives have their unique advantages and limitations, and the decision ultimately depends on the specific needs and circumstances of the agricultural operation. By understanding the characteristics of each drive system, farmers and agricultural professionals can make informed choices that enhance the performance and longevity of their machinery. Whether opting for the flexibility and cost-effectiveness of belt drives or the precision and durability of gear drives, the key is to select a system that aligns with the operational demands and long-term goals of the agricultural enterprise.
Boost Innovation in Gears & Transmissions with Patsnap Eureka
Whether you're designing a next-gen planetary gearbox or optimizing gear tooth profiles for noise reduction, keeping up with the fast-evolving landscape of mechanical transmissions requires more than just experience—it takes insight, speed, and smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Whether you're streamlining a manual transmission system or exploring electromechanical actuation, Patsnap Eureka helps your team move from concept to novelty faster than ever.
👉 Experience Eureka in action—request a personalized demo today and see how AI can revolutionize your gear innovation workflows.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com