Calibrating Medical Pressure Sensors for Home-Use Accuracy
JUL 14, 2025 |
The rise of telemedicine and home health care has spotlighted the importance of accurate medical devices for home use, particularly pressure sensors. These devices play a crucial role in monitoring vital signs such as blood pressure, which means ensuring their accuracy is paramount for effective health management. Without proper calibration, the reliability of these sensors can be compromised, leading to potential health risks. This blog will explore the calibration process for medical pressure sensors, highlighting key strategies and best practices to ensure home-use accuracy.
Understanding Medical Pressure Sensors
Medical pressure sensors are devices that convert pressure measurements into an electrical signal, providing critical data for monitoring patient health. These sensors are commonly integrated into devices like blood pressure monitors, ventilators, and infusion pumps. In a home setting, their accuracy can be affected by various factors, including environmental conditions, sensor age, and user handling. Therefore, understanding how these sensors work and the importance of regular calibration is essential for maintaining their effectiveness.
Why Calibration is Essential
Calibration is the process of configuring a sensor to provide a result within an acceptable range. It involves comparing the output of the sensor to a known standard and adjusting it to minimize any deviation. For medical pressure sensors, calibration ensures that the readings are accurate and reliable. This is especially crucial in home settings, where users may not have immediate access to professional medical support to verify sensor accuracy. Regular calibration can prevent incorrect readings that might lead to inappropriate treatment or oversight of critical health issues.
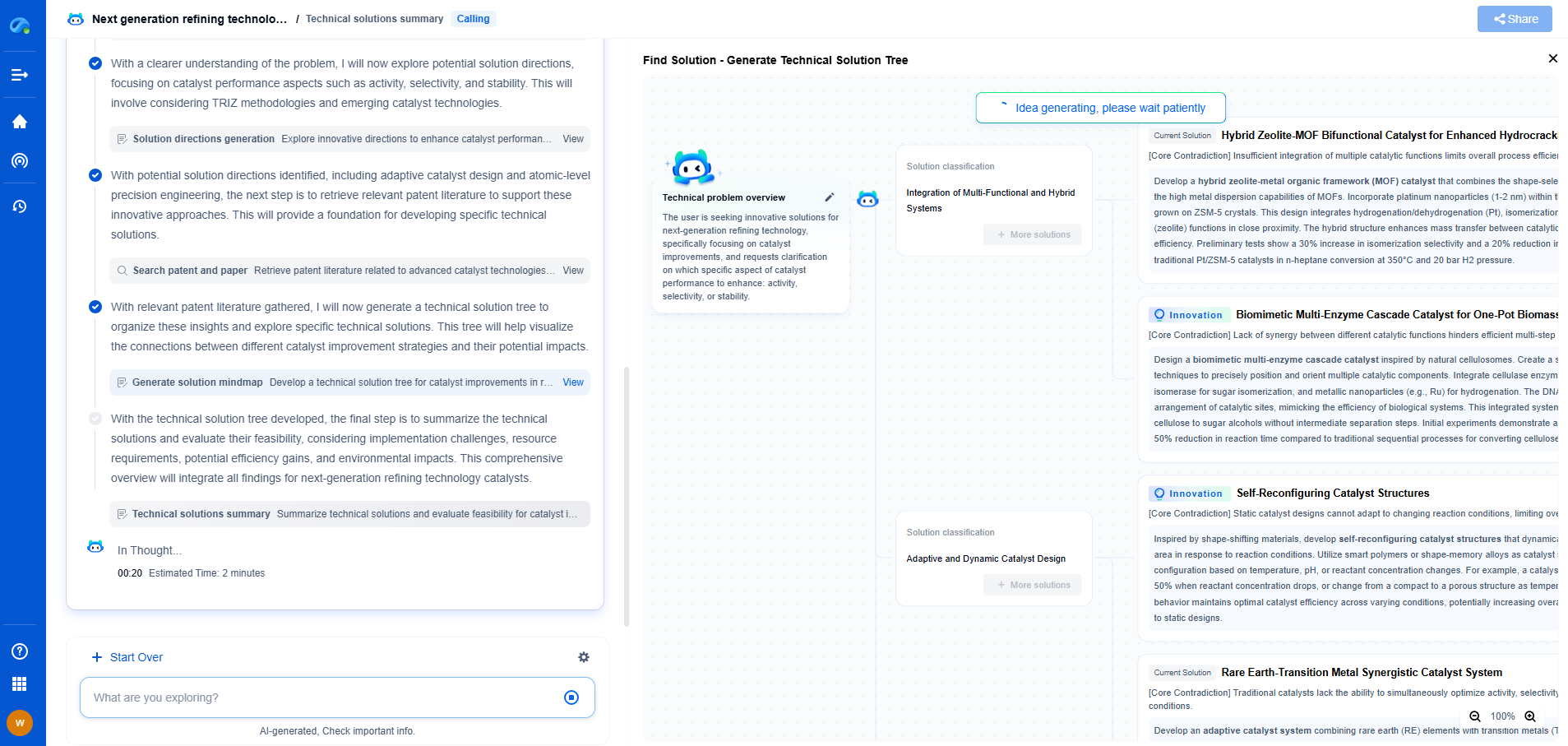
Steps in Calibrating Medical Pressure Sensors
1. Gathering Necessary Equipment
Before beginning the calibration process, it’s important to have all necessary equipment on hand. This typically includes a calibration device or reference sensor, which provides a known standard for comparison. Additionally, having a stable power source, connection cables, and any specific calibration software associated with the sensor is essential.
2. Setting Up the Environment
Calibration should ideally be conducted in a controlled environment to prevent external factors from affecting the sensor’s performance. This means a stable temperature and humidity level, as well as minimizing vibrations and electromagnetic interference. Setting up in a quiet, dedicated space can help achieve the most accurate results.
3. Performing the Calibration
The specific steps for calibration can vary depending on the sensor model and manufacturer instructions. Generally, it involves connecting the sensor to the calibration device and adjusting the sensor’s output to match the reference. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines closely to ensure the process is done correctly. This may involve entering specific codes or procedures in the device’s software.
4. Verifying the Results
After calibration, it’s crucial to verify that the sensor provides accurate readings within the acceptable range. This involves running tests to ensure consistency and reliability in the results. If discrepancies are found, the calibration process should be repeated or checked for errors.
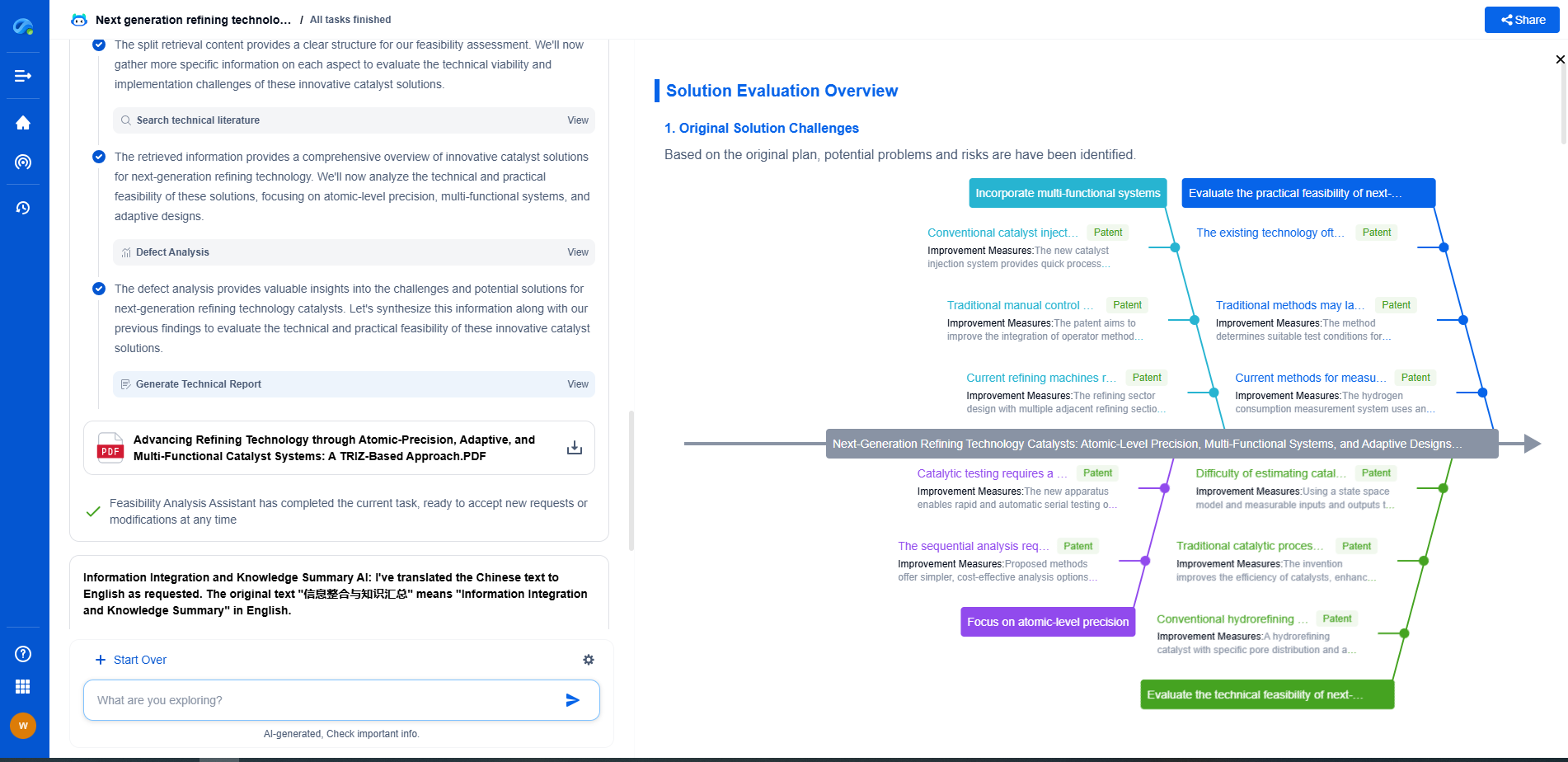
Maintaining Calibration Over Time
Calibration is not a one-time task. Over time, factors such as sensor wear and tear or environmental shifts can affect a sensor’s accuracy. It’s advisable to establish a regular calibration schedule based on the manufacturer’s recommendations or any signs of inaccurate readings. Keeping a log of calibration dates and results can also help track the sensor’s performance over time.
Challenges in Home-Use Calibration
While calibration is essential, it can present challenges in a home setting. Users may lack the technical knowledge or equipment needed for proper calibration, or the device may require professional attention. In such cases, seeking guidance from healthcare providers or manufacturers may be necessary. Additionally, some modern devices come with self-calibrating features or alerts when calibration is needed, which can aid in maintaining accuracy without the need for extensive user intervention.
Conclusion
Calibrating medical pressure sensors for home use is a critical component of ensuring accurate health monitoring. By understanding the calibration process and maintaining regular checks, users can rely on these devices to provide vital health information accurately. As home healthcare continues to grow, the importance of proper sensor calibration cannot be overstated, underscoring its role in effective and safe patient care.
From 5G NR to SDN and quantum-safe encryption, the digital communication landscape is evolving faster than ever. For R&D teams and IP professionals, tracking protocol shifts, understanding standards like 3GPP and IEEE 802, and monitoring the global patent race are now mission-critical.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
📡 Experience Patsnap Eureka today and unlock next-gen insights into digital communication infrastructure, before your competitors do.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com