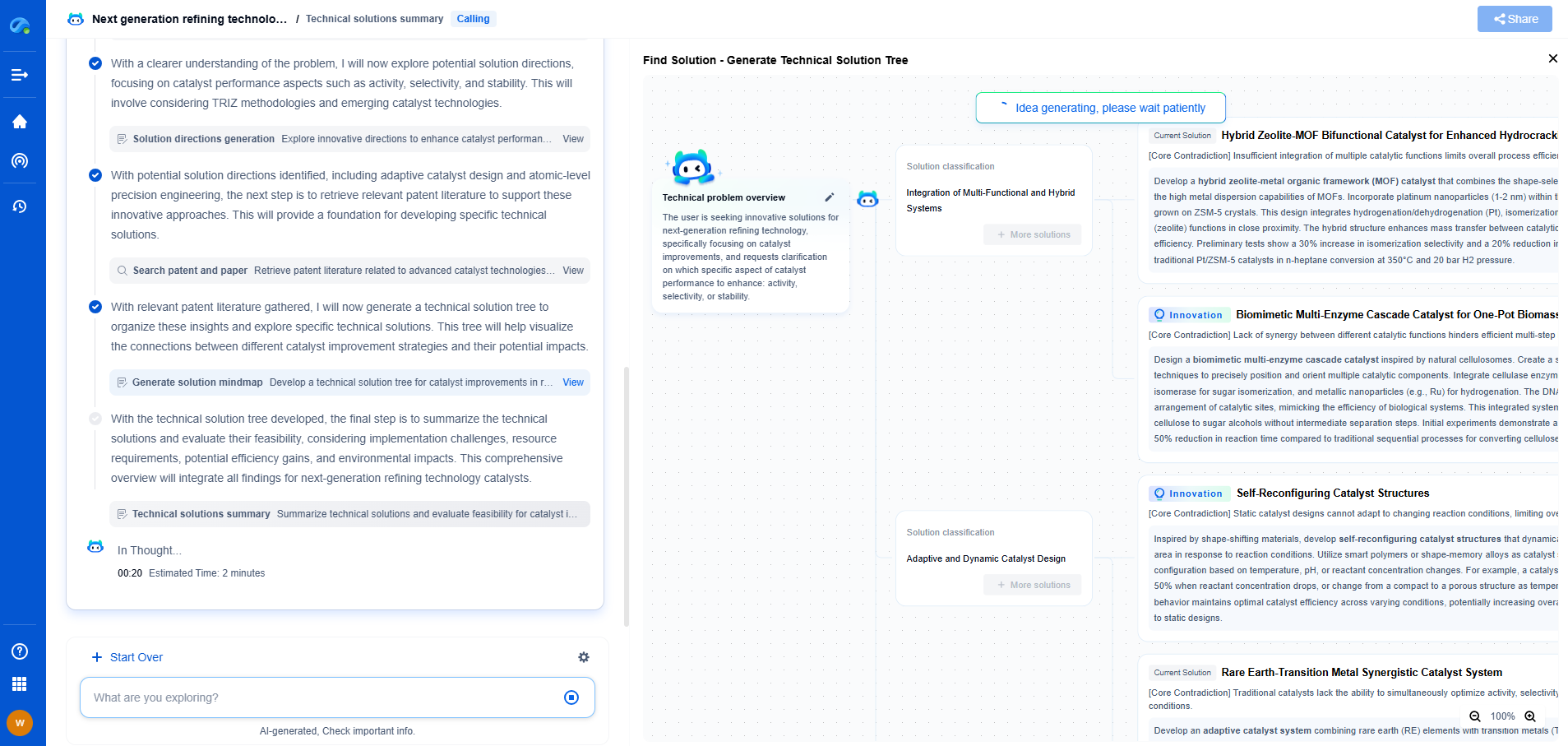
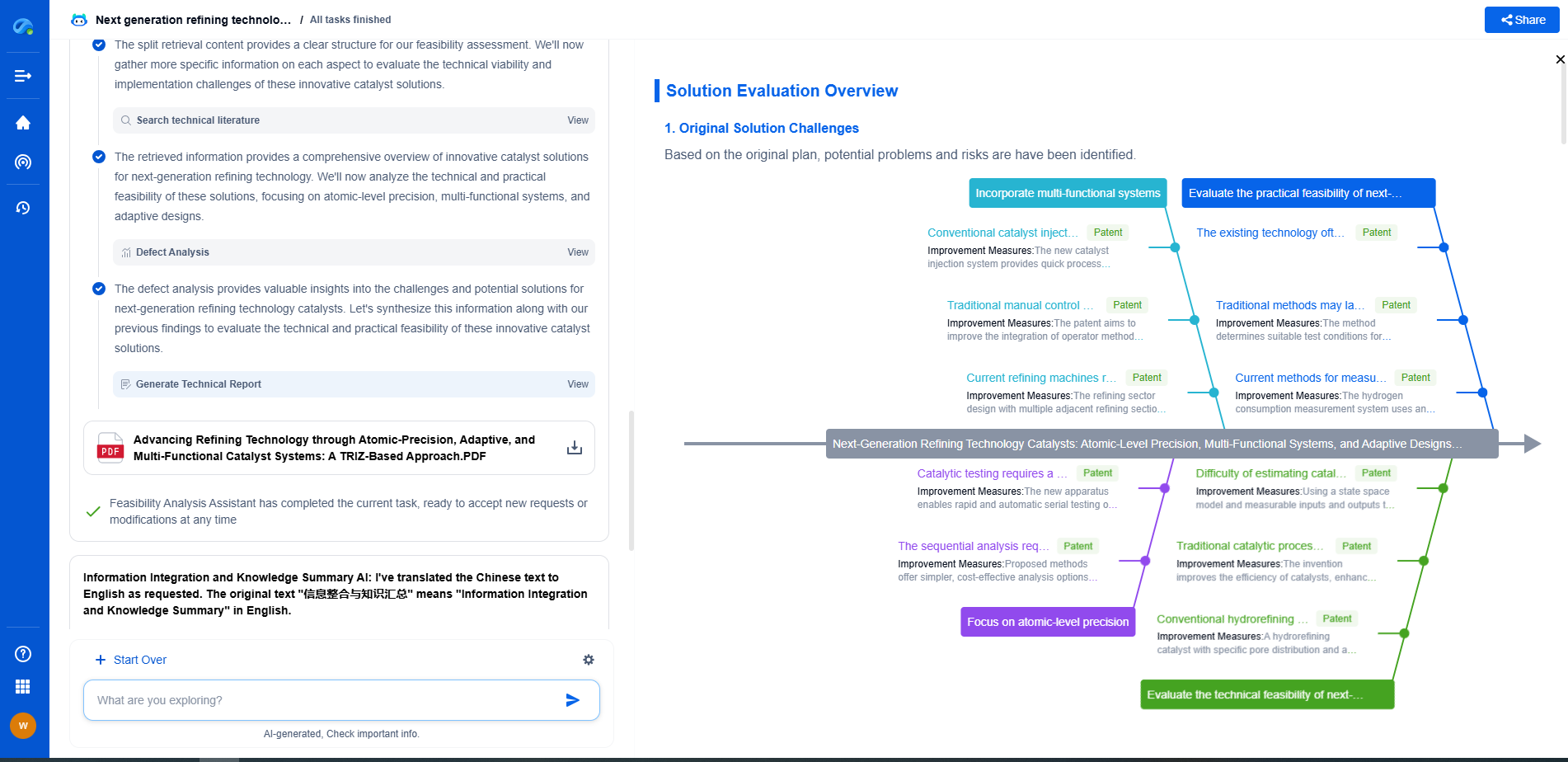
Capacitance Measurement Methods: LCR Meters vs. Bridge Circuits
JUL 9, 2025 |
Capacitance is a fundamental property of electronic components, especially capacitors, which store and release electrical energy. Measuring capacitance accurately is crucial in various applications, including designing circuits, quality control in manufacturing, and troubleshooting electronic systems. Two common tools employed for this task are LCR meters and bridge circuits. Each method offers distinct advantages and limitations, which can influence the choice of measurement approach in different scenarios.
LCR Meters: Simplicity Meets Precision
LCR meters are versatile instruments used to measure the inductance (L), capacitance (C), and resistance (R) of electronic components. These meters simplify the measurement process, offering ease of use and quick results. Modern LCR meters come equipped with advanced features such as automatic component recognition, multiple test frequencies, and digital displays that facilitate accurate and efficient measurements.
Advantages of LCR Meters
One of the primary advantages of using LCR meters is their user-friendly interface. Users can obtain measurements with minimal setup, making these meters ideal for both laboratory and field applications. The digital displays provide clear and immediate readings, reducing the likelihood of human error. Additionally, LCR meters can measure a range of frequencies, which is beneficial in applications requiring detailed analysis of a component's behavior across different operating conditions.
Another significant benefit is their portability. Many LCR meters are compact and battery-operated, allowing engineers and technicians to perform on-site capacitance measurements without the need for cumbersome equipment. This portability does not come at the cost of accuracy, as modern LCR meters maintain high precision, often comparable to more complex measurement setups.
Limitations of LCR Meters
Despite their advantages, LCR meters have limitations. They may not be suitable for measuring capacitance at very high frequencies beyond the device's specified range. Additionally, while they are excellent for general-purpose measurements, they may lack the precision required for specialized applications, such as those involving low-loss capacitors or very low capacitance values.
Bridge Circuits: The Classic Approach
Bridge circuits are one of the oldest methods for measuring capacitance, known for their high accuracy and reliability. These circuits typically involve a combination of resistors and capacitors arranged in a specific configuration, allowing the unknown capacitance to be determined by balancing the bridge.
Advantages of Bridge Circuits
Bridge circuits excel in precision, particularly in laboratory settings where measurement accuracy is paramount. They offer an excellent resolution for measuring small capacitances and can handle a wide range of values with minimal error. The use of a null-balance method in these circuits eliminates the influence of source impedance and other external factors, ensuring consistent and dependable results.
Bridge circuits are also beneficial for applications that require measurements at high frequencies. Unlike LCR meters, bridge circuits can be customized to suit specific measurement needs, making them versatile tools for specialized applications.
Limitations of Bridge Circuits
The primary drawback of bridge circuits is their complexity. Setting up bridge circuits requires a solid understanding of circuit theory and careful calibration to achieve accurate results. This makes them less suitable for casual or field use compared to LCR meters. Additionally, the need for manual adjustments can be time-consuming, especially when measuring multiple components or adjusting for environmental variations.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
When deciding between LCR meters and bridge circuits for capacitance measurement, it's essential to consider the specific requirements of your application. If ease of use, portability, and quick results are your priorities, an LCR meter may be the most appropriate choice. Conversely, if you require high precision and are working in a controlled laboratory environment, a bridge circuit could provide the accuracy you need.
Ultimately, understanding the strengths and limitations of each method will help you make an informed decision, ensuring that you achieve reliable and accurate capacitance measurements tailored to your specific needs.
Navigating the evolving world of electrical measurement—from high-precision signal integrity to advanced test protocols like BERT or TDR—demands more than just expertise; it demands smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka empowers you to keep up—by turning complex patent data, technical parameters, and industry signals into actionable insight. It’s your AI partner for exploring what’s next in test, measurement, and electrical diagnostics.
💡 Try Patsnap Eureka for free and see how it transforms the way you work with electrical measurement technologies.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com