Causes of Pipe Buckling and How to Prevent It
JUN 20, 2025 |
Pipe buckling is a critical issue in various industries, especially in construction, oil, and gas sectors. It refers to the deformation or bending of pipes under excessive stress or pressure, leading to potential failure of the piping system. Understanding the causes of pipe buckling and implementing preventive measures can save industries from significant financial losses and safety hazards. This article explores the primary causes of pipe buckling and offers strategies to prevent it.
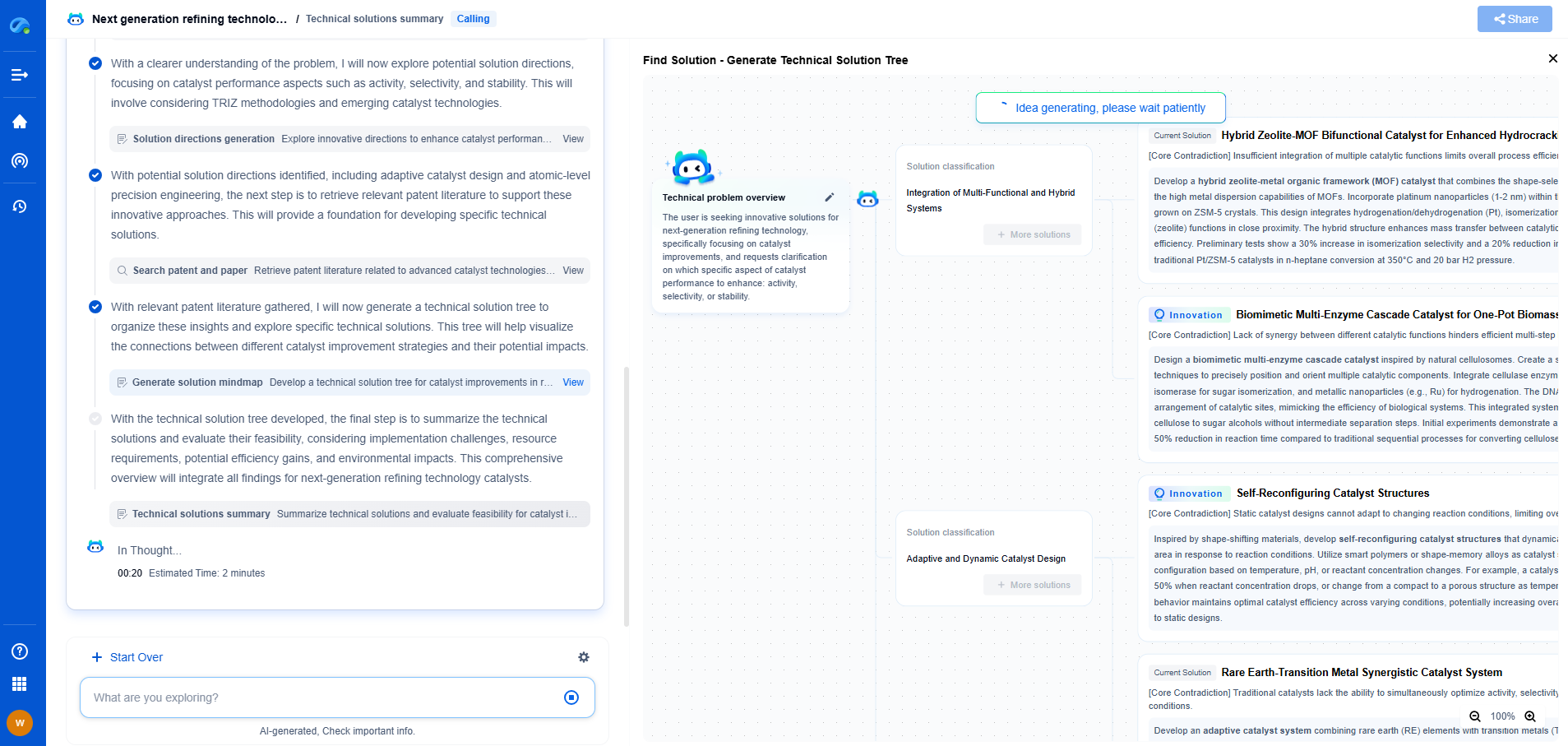
Causes of Pipe Buckling
1. **Excessive Loads**
One of the most common causes of pipe buckling is the application of excessive loads. This can happen when pipes are subjected to heavy external forces, such as soil pressure in buried pipelines or heavy equipment resting on pipes in construction sites. Overloading can push the pipe material beyond its elastic limit, causing permanent deformation.
2. **Thermal Expansion and Contraction**
Pipes can buckle due to thermal expansion and contraction. When pipes made of metals or thermoplastics are exposed to temperature fluctuations, they expand or contract. If there is no provision for this movement, it can lead to buckling. This is particularly prevalent in regions with extreme temperature variations.
3. **Improper Installation**
The incorrect installation of pipes can lead to buckling. This includes improper alignment, inadequate support, and incorrect joint connections. Such installation errors create weak points in the piping system, making the pipes more susceptible to buckling under stress.
4. **Material Deficiencies**
Quality of the pipe material is crucial in preventing buckling. Pipes made from inferior or unsuitable materials, or those with manufacturing defects, have a higher risk of buckling. Materials must be chosen based on the environment they will be exposed to, ensuring they can withstand the expected loads and stresses.
5. **Corrosion and Erosion**
Corrosion and erosion weaken the structural integrity of pipes over time. Corrosive environments, such as those containing chemicals or salts, can degrade the pipe material, making it more vulnerable to buckling. Similarly, erosion from the flow of abrasive materials inside the pipe can thin the pipe walls, reducing their ability to support loads.
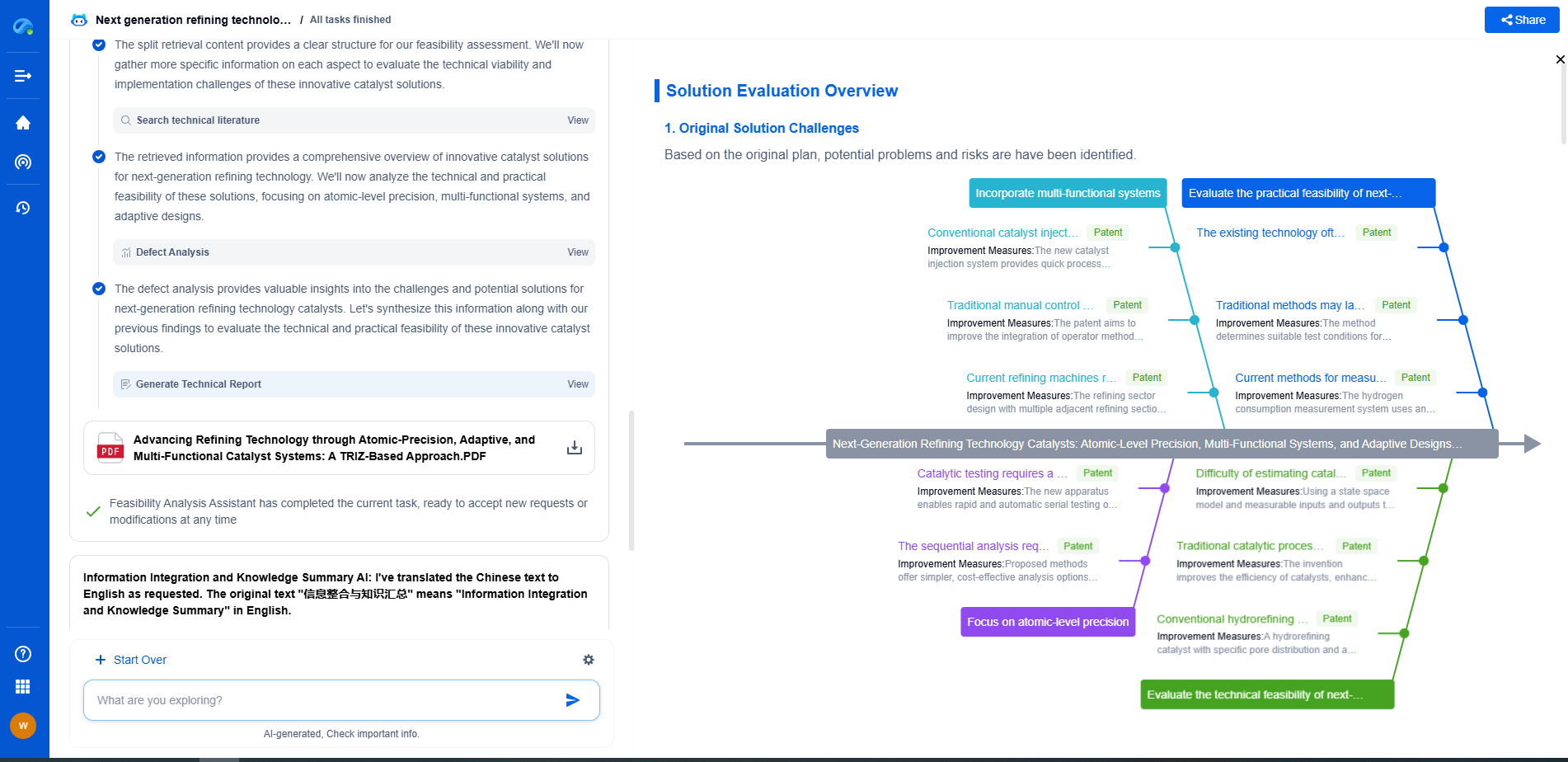
Preventive Measures
1. **Proper Design and Engineering**
Ensuring that pipes are designed to withstand the expected loads and environmental conditions is essential. This includes selecting the right materials, designing for thermal expansion, and incorporating adequate support and joint systems. Engineers should perform thorough stress analysis to predict and prevent potential buckling scenarios.
2. **Regular Maintenance and Inspection**
Routine inspection and maintenance are vital for identifying early signs of wear, corrosion, or misalignment that could lead to buckling. Regular checks can help detect issues before they escalate into significant problems. Maintenance schedules should be strictly followed, and any identified issues should be addressed promptly.
3. **Use of Expansion Joints**
Expansion joints or loops can be incorporated into piping systems to accommodate thermal expansion and contraction. These devices allow pipes to move without causing stress, significantly reducing the risk of buckling in systems subjected to temperature fluctuations.
4. **Quality Control in Material Selection**
Ensuring the use of high-quality materials free from defects is crucial. Materials should be carefully selected to suit the specific requirements of the project, and rigorous quality control measures should be in place during manufacturing and installation.
5. **Adequate Support and Anchoring**
Proper support and anchoring of pipes can prevent buckling by distributing loads evenly and providing stability. Supports should be spaced appropriately, and anchors should be installed to prevent excessive movement or sagging, especially in long pipe runs.
Conclusion
Pipe buckling can lead to severe operational disruptions and safety hazards. By understanding its causes—such as excessive loads, thermal effects, improper installation, material deficiencies, and corrosion—industries can implement effective preventive measures. Proper design, regular maintenance, and the use of quality materials play crucial roles in safeguarding piping systems against buckling. By taking these proactive steps, industries can ensure the longevity and reliability of their piping infrastructure.
Transform the Way You Innovate in Pipeline Technology—with AI-Powered Intelligence
From corrosion-resistant materials to smart monitoring systems and advanced flow control mechanisms, the pipeline industry is undergoing rapid technological transformation. Yet keeping up with evolving engineering solutions, regulatory landscapes, and competitive patents can be a major bottleneck for R&D and IP teams.
Patsnap Eureka is your AI-powered research companion—built specifically for professionals in high-tech and infrastructure domains like pipeline technology. Whether you're designing high-pressure transport systems, assessing trenchless installation innovations, or safeguarding proprietary flow assurance solutions, Eureka provides real-time insights into global patent trends, emerging technologies, and R&D intelligence—all in one intuitive interface.
Empower your team to innovate faster, reduce technical blind spots, and stay ahead of industry shifts. Discover Patsnap Eureka today and bring clarity and confidence to your pipeline technology decisions.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com