Color Correction in Image Processing: Techniques and Use Cases
JUL 10, 2025 |
Color correction is an essential aspect of image processing, ensuring that the colors in digital images are true to life. This process involves adjusting the colors to achieve a realistic or aesthetically pleasing outcome. The need for color correction arises due to various factors, such as lighting conditions during photography, camera sensor limitations, or even the intended artistic style.
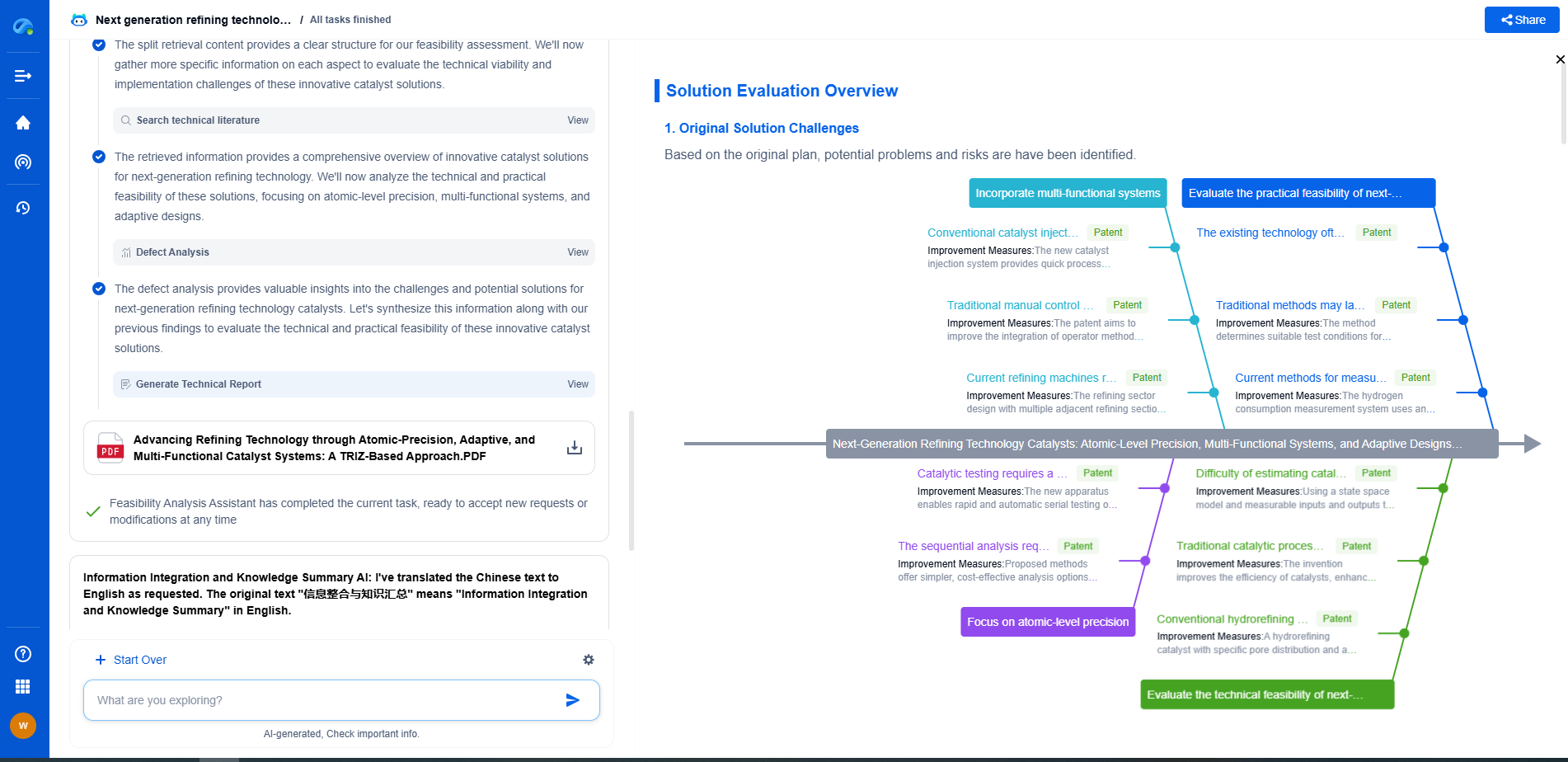
Basic Principles of Color Correction
At its core, color correction deals with manipulating the colors in an image to balance and harmonize them. The primary components often adjusted include hue, saturation, and luminance (HSL). Hue pertains to the color itself, saturation refers to the intensity of the color, and luminance deals with the brightness. By fine-tuning these elements, one can enhance the visual appeal of an image while ensuring it maintains a natural look.
Techniques in Color Correction
Several techniques are used in color correction, each serving different purposes and yielding unique results. Here are some common methods:
White Balance Adjustment
White balance correction aims to ensure that colors appear natural by setting the correct balance of red, green, and blue (RGB) in an image. It compensates for the color temperature of the light source, ensuring that white objects appear white rather than tinted with the color of the light source, such as a yellowish hue from incandescent lighting.
Histogram Equalization
Histogram equalization is a technique that enhances image contrast by spreading out the most frequent intensity values. By redistributing pixel intensity values, this method can reveal details in both the shadows and highlights, improving the overall dynamic range of an image.
Color Grading
Color grading is a stylistic approach that alters the visual tone and mood of an image. It goes beyond color correction by intentionally applying color changes that evoke certain emotions or aesthetics. This technique is prevalent in filmmaking and photography for storytelling purposes.
Selective Color Adjustment
Selective color adjustment allows for fine-tuning specific colors within an image without affecting others. By isolating colors, one can enhance or diminish particular hues, which is useful in emphasizing certain elements or correcting color imbalances.
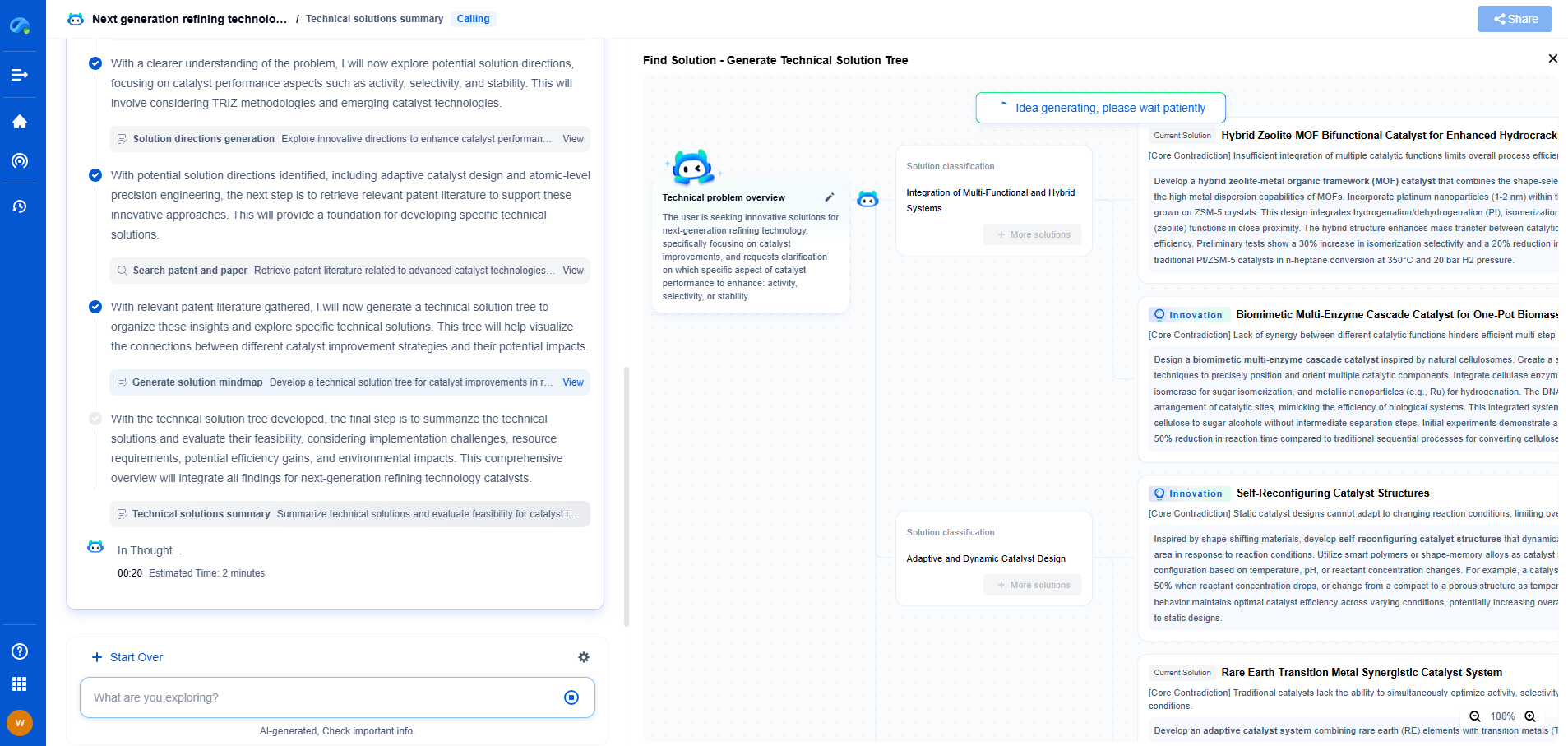
Use Cases of Color Correction
Photography
In photography, color correction is crucial for producing accurate and vibrant images. Photographers often deal with varying lighting conditions, which can introduce color casts. Correcting these casts ensures that the colors in the photograph appear as intended, enhancing the overall quality of the image.
Film and Video Production
In film and video production, color correction is part of the post-production process. It ensures consistency across scenes, especially when filmed in different lighting conditions or using multiple cameras. This consistency is vital for maintaining the visual continuity of the narrative.
Digital Art and Design
For digital artists and designers, color correction allows for precise control over the color palette. It enables them to maintain color consistency across different media and devices, ensuring that their work appears as intended regardless of the viewing platform.
Printing and Publishing
In the printing and publishing industries, color correction is essential to ensure that printed materials match the digital versions. This process involves compensating for the differences in how colors are produced on screen versus in print, maintaining color fidelity across formats.
Conclusion
Color correction is a fundamental aspect of image processing that ensures the accuracy and visual appeal of digital images. By employing various techniques, professionals across multiple industries can achieve desired results, whether it be for artistic expression or technical precision. Understanding and mastering these techniques allows for the creation of stunning and true-to-life visuals that resonate with viewers.
Image processing technologies—from semantic segmentation to photorealistic rendering—are driving the next generation of intelligent systems. For IP analysts and innovation scouts, identifying novel ideas before they go mainstream is essential.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
🎯 Try Patsnap Eureka now to explore the next wave of breakthroughs in image processing, before anyone else does.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com