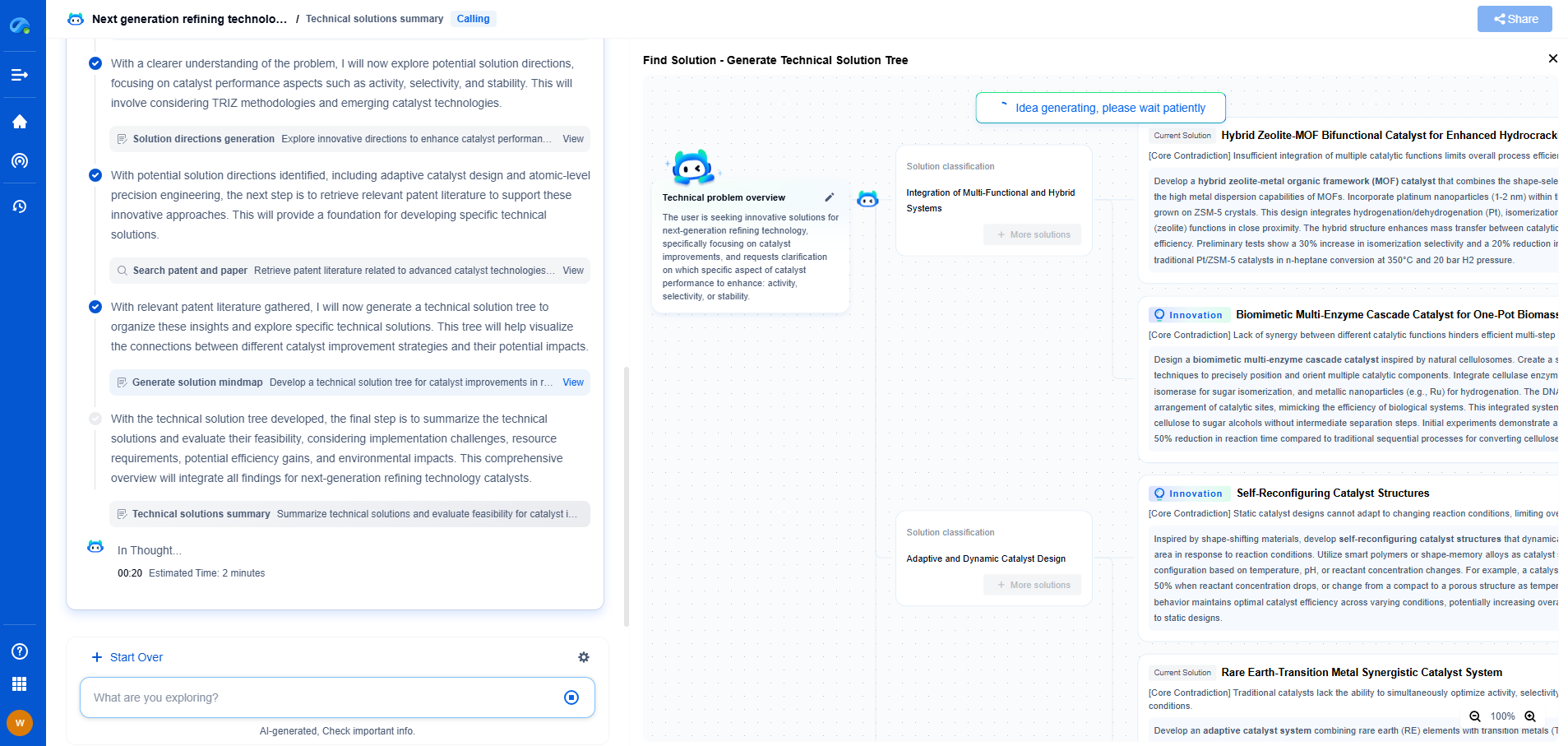
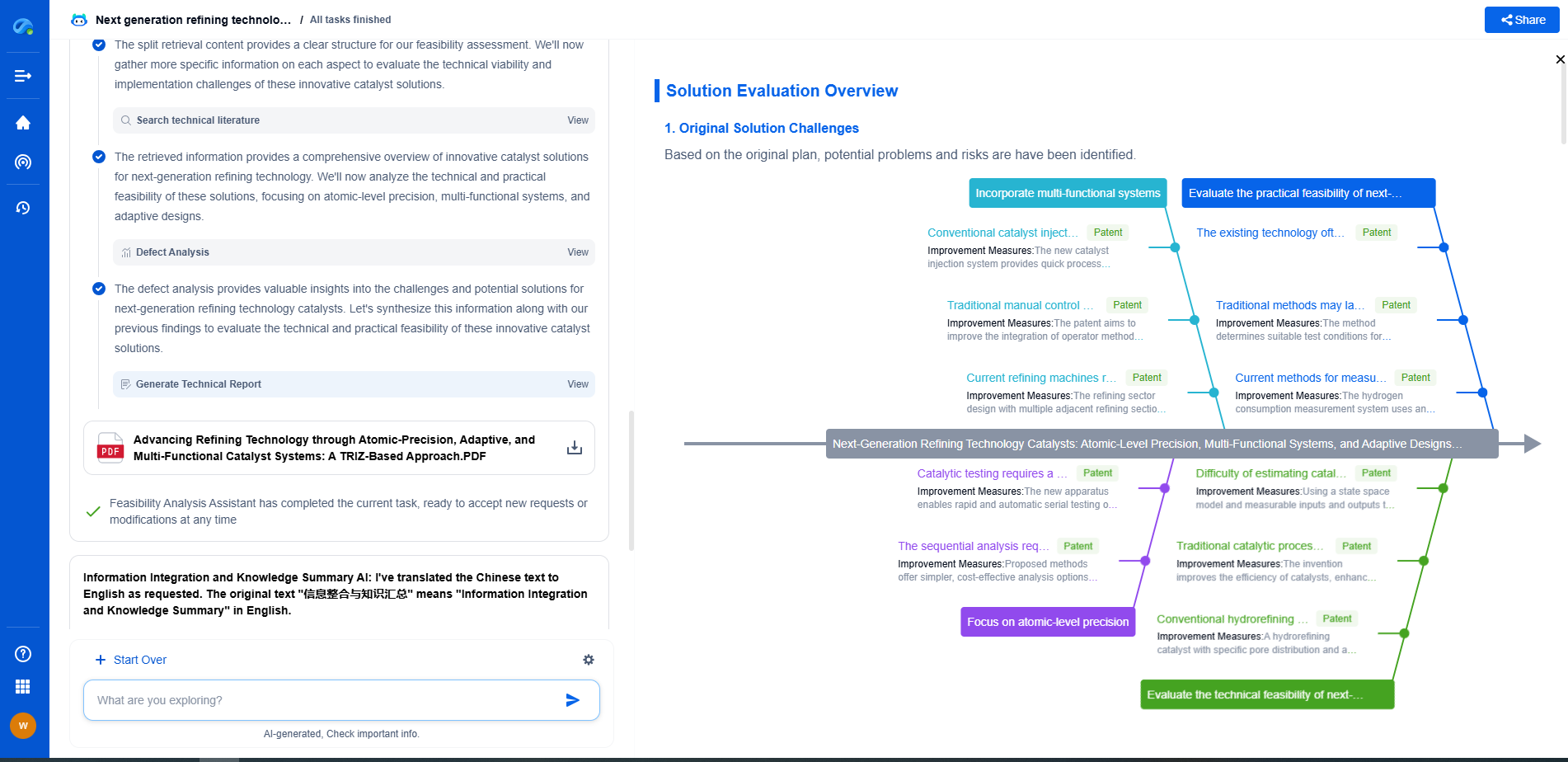
Comparison of wet vs dry resist stripping techniques
JUL 28, 2025 |
In the realm of semiconductor manufacturing and microfabrication, resist stripping is a crucial step. Photolithography, a process used to create intricate patterns on a substrate, relies heavily on photoresist materials. After these patterns are transferred to the substrate, removing the leftover photoresist becomes essential to ensure accuracy and quality in the final product. Two primary techniques dominate this cleaning process: wet and dry resist stripping. Each method has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, which this article will explore in detail.
Understanding Wet Resist Stripping
Wet resist stripping involves the use of liquid chemicals to dissolve and remove the photoresist material from the substrate surface. This technique is well-regarded for its efficiency and effectiveness in completely removing resist layers. Common chemicals used in wet stripping include organic solvents like acetone and N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP), as well as strong acids or bases depending on the resist type.
Advantages of Wet Resist Stripping
1. **Thoroughness**: Wet stripping can effectively remove thick and stubborn resist layers, making it suitable for heavily patterned substrates.
2. **Cost-Effectiveness**: The chemicals used are generally less expensive compared to the gases used in dry stripping, making wet stripping a more economical choice for many manufacturers.
3. **Simplicity**: The process is relatively straightforward, requiring less specialized equipment than dry stripping methods.
Disadvantages of Wet Resist Stripping
1. **Waste Management**: The use of chemicals generates waste that needs to be properly managed and disposed of, which can increase operational costs and environmental impact.
2. **Substrate Compatibility**: Some substrates may be sensitive to the chemicals used, risking damage to the underlying material.
3. **Residue Issues**: In some cases, wet stripping might leave behind residues that could interfere with subsequent manufacturing steps.
Exploring Dry Resist Stripping
Dry resist stripping, on the other hand, employs plasma or gas-phase chemistry to remove photoresist materials. This method is particularly useful in applications requiring high precision and minimal substrate interference. Plasma stripping involves the use of reactive gases like oxygen or fluorinated compounds, which are activated to form plasma that etches away the resist.
Advantages of Dry Resist Stripping
1. **Precision**: Dry stripping offers greater control over the removal process, making it ideal for delicate or complex patterns.
2. **Cleanliness**: The absence of liquid chemicals reduces the risk of residue, thus ensuring a cleaner substrate surface.
3. **Environmental Impact**: Generally, dry stripping generates less chemical waste, resulting in a more environmentally friendly process.
Disadvantages of Dry Resist Stripping
1. **Cost**: The equipment and gases required for dry stripping are often more expensive, leading to higher initial investment and operating costs.
2. **Complexity**: The process is more complex and requires specialized knowledge to operate and maintain the equipment.
3. **Potential Damage**: The high-energy plasma can potentially cause damage to sensitive substrate materials if not carefully controlled.
Choosing the Right Technique
The choice between wet and dry resist stripping largely depends on the specific requirements of the manufacturing process. Factors such as the type of substrate, the complexity of the pattern, budget constraints, and environmental considerations all play a role in determining the most suitable method.
For processes involving simple patterns and robust substrates, wet resist stripping may provide a cost-effective and efficient solution. Conversely, for applications demanding high precision and minimal substrate interference, dry resist stripping often emerges as the preferred choice despite its higher costs.
Conclusion
Both wet and dry resist stripping techniques offer valuable solutions in the field of semiconductor manufacturing and microfabrication. Understanding their unique advantages and disadvantages is key to selecting the appropriate method for specific applications. As technology continues to advance, innovation in resist stripping techniques promises to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of the microfabrication industry.
As photolithography continues to push the boundaries of nanoscale patterning, from EUV and DUV advancements to multi-patterning and maskless lithography, innovation cycles are accelerating—and the IP landscape is becoming more complex than ever.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Whether you're optimizing lithography depth of focus or exploring new materials for sub-3nm nodes, Patsnap Eureka empowers you to make smarter decisions, faster—combining AI efficiency with domain-specific insight.
💡 Start your free trial today and see how Eureka transforms how you discover, evaluate, and act on innovation in photolithography—from idea to impact.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com