Damping Foam vs. Viscoelastic Polymers: Which Is Better for Low-Frequency Vibration?
JUL 16, 2025 |
Understanding Low-Frequency Vibrations
Low-frequency vibrations typically refer to those in the range of 1 to 100 Hz. These vibrations can be challenging to manage as they often require materials that can absorb and dissipate energy efficiently without adding significant weight or bulk. Such vibrations are common in various applications, from industrial machinery to automotive systems, and can lead to structural fatigue, noise, and even failure if not properly managed.
Damping Foam: Characteristics and Applications
Damping foam is a lightweight material known for its ability to absorb vibrational energy. It is typically made from polyurethane or other polymeric materials and is characterized by its cell-like structure, which is effective at reducing noise and minimizing vibration transmission.
Advantages of Damping Foam:
1. Lightweight: Damping foam adds minimal weight, making it ideal for applications where weight is a concern.
2. Cost-Effective: Generally, damping foam is less expensive than some other vibration control materials.
3. Versatility: It can be easily shaped and cut to fit various applications, including automotive interiors and electronic enclosures.
However, damping foam can have limitations in its effectiveness at very low frequencies. While effective at reducing high-frequency noise and vibrations, its performance can start to wane as the frequency decreases.
Viscoelastic Polymers: Characteristics and Applications
Viscoelastic polymers are materials that exhibit both viscous and elastic characteristics when deformed. This unique property allows them to absorb and dissipate vibrational energy efficiently, making them highly effective for vibration control, especially at lower frequencies.
Advantages of Viscoelastic Polymers:
1. Superior Damping at Low Frequencies: These polymers are particularly effective at absorbing energy over a broad frequency range, including the challenging low-frequency spectrum.
2. Energy Dissipation: The viscoelastic nature enables them to convert mechanical energy into heat, reducing the amplitude of vibrations significantly.
3. Long-Term Durability: Viscoelastic materials often maintain their properties over time, providing consistent performance.
On the downside, viscoelastic polymers can be heavier and more expensive than damping foams. They may also require more precise application techniques to maximize effectiveness.
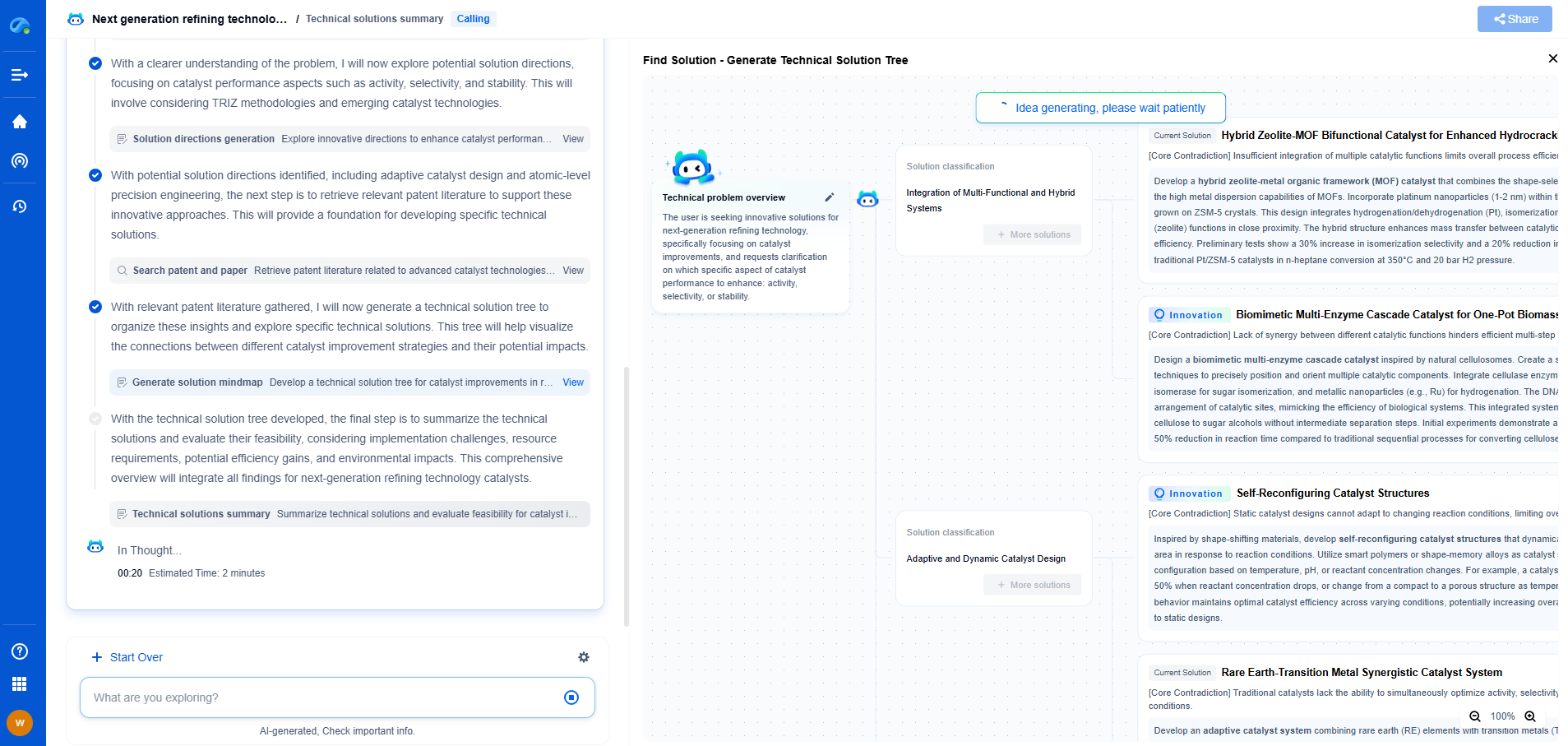
Comparative Analysis
When deciding between damping foam and viscoelastic polymers for low-frequency vibration control, it is essential to consider the specific requirements of the application.
Damping foam might be the right choice if the primary goals are cost savings, weight reduction, and ease of installation. Its effectiveness in controlling higher-frequency vibrations can also be a bonus in certain applications where a wide range of frequencies are present.
On the other hand, if the primary concern is controlling low-frequency vibrations with high efficiency, viscoelastic polymers would likely be a better fit. Although they may come with a higher cost and weight, their superior damping capabilities at low frequencies and long-term reliability can justify the investment.
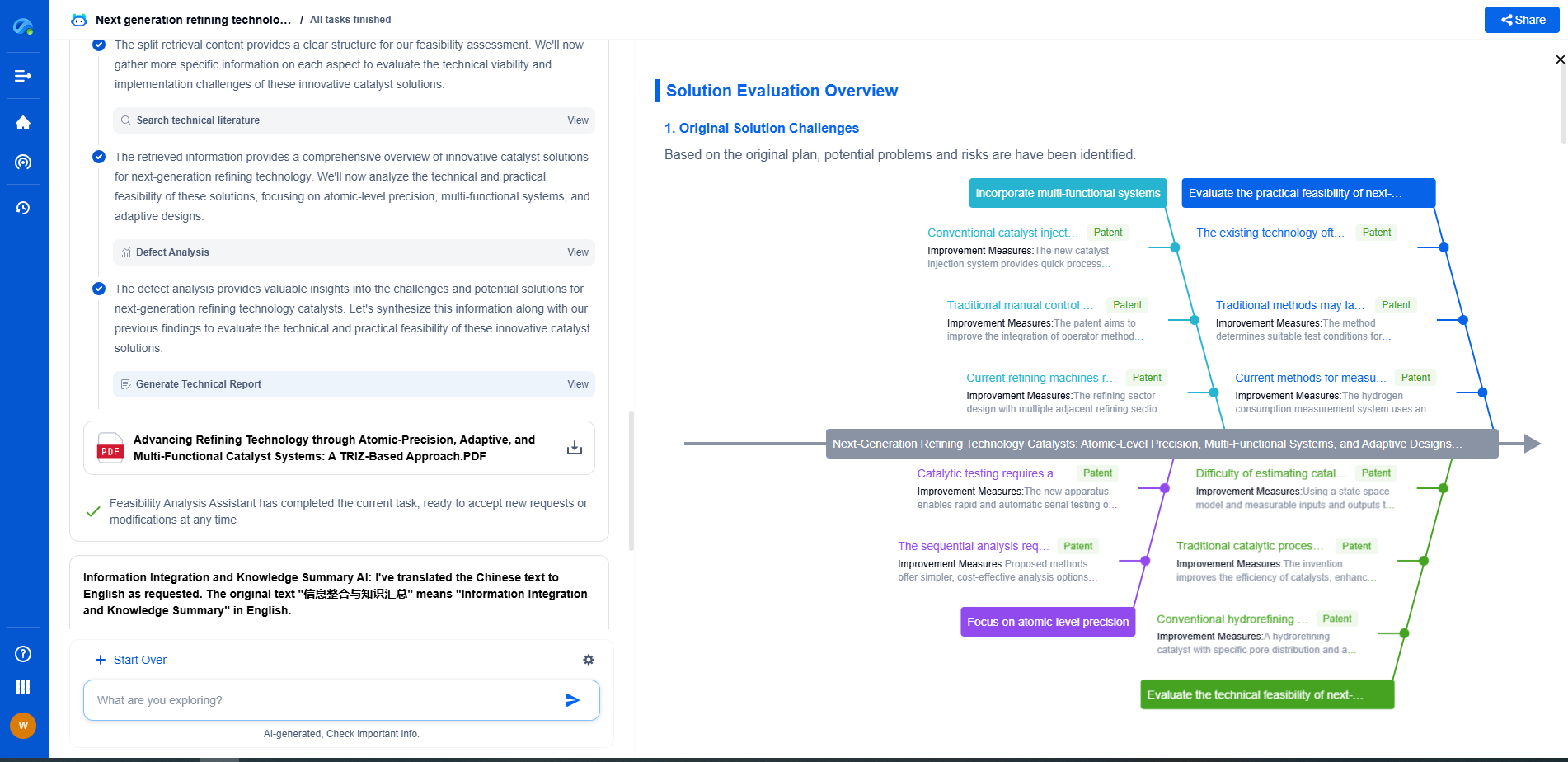
Conclusion
Both damping foam and viscoelastic polymers have their place in the realm of vibration control. The choice between them should be informed by the specific vibrational challenges at hand, budgetary constraints, and any additional performance requirements. For those dealing primarily with low-frequency vibrations, viscoelastic polymers might offer the edge needed to ensure effective vibration management. However, for applications where weight, cost, and versatility are paramount, damping foam remains a strong contender.
In the world of vibration damping, structural health monitoring, and acoustic noise suppression, staying ahead requires more than intuition—it demands constant awareness of material innovations, sensor architectures, and IP trends across mechanical, automotive, aerospace, and building acoustics.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚙️ Bring Eureka into your vibration intelligence workflow—and reduce guesswork in your R&D pipeline. Start your free experience today.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com