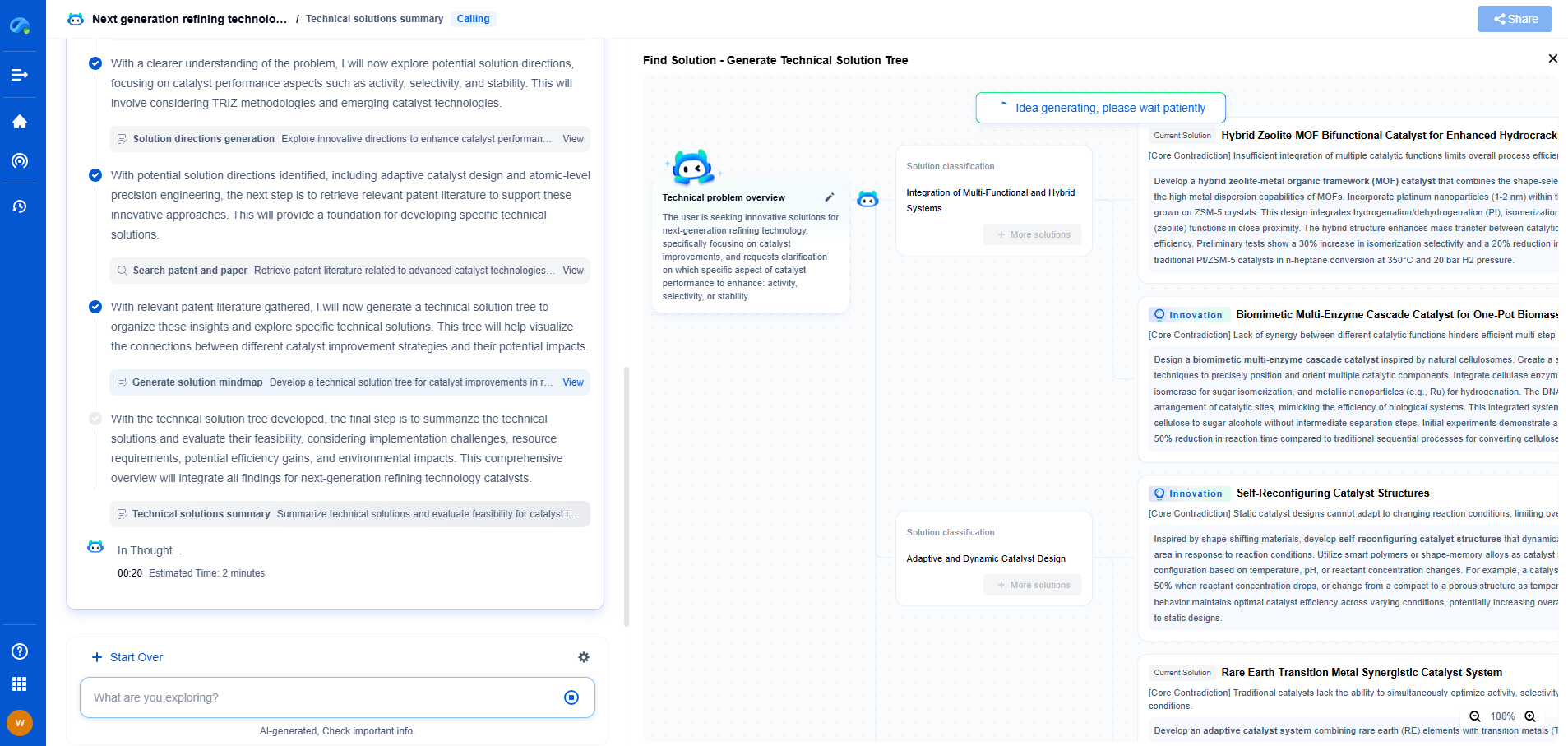
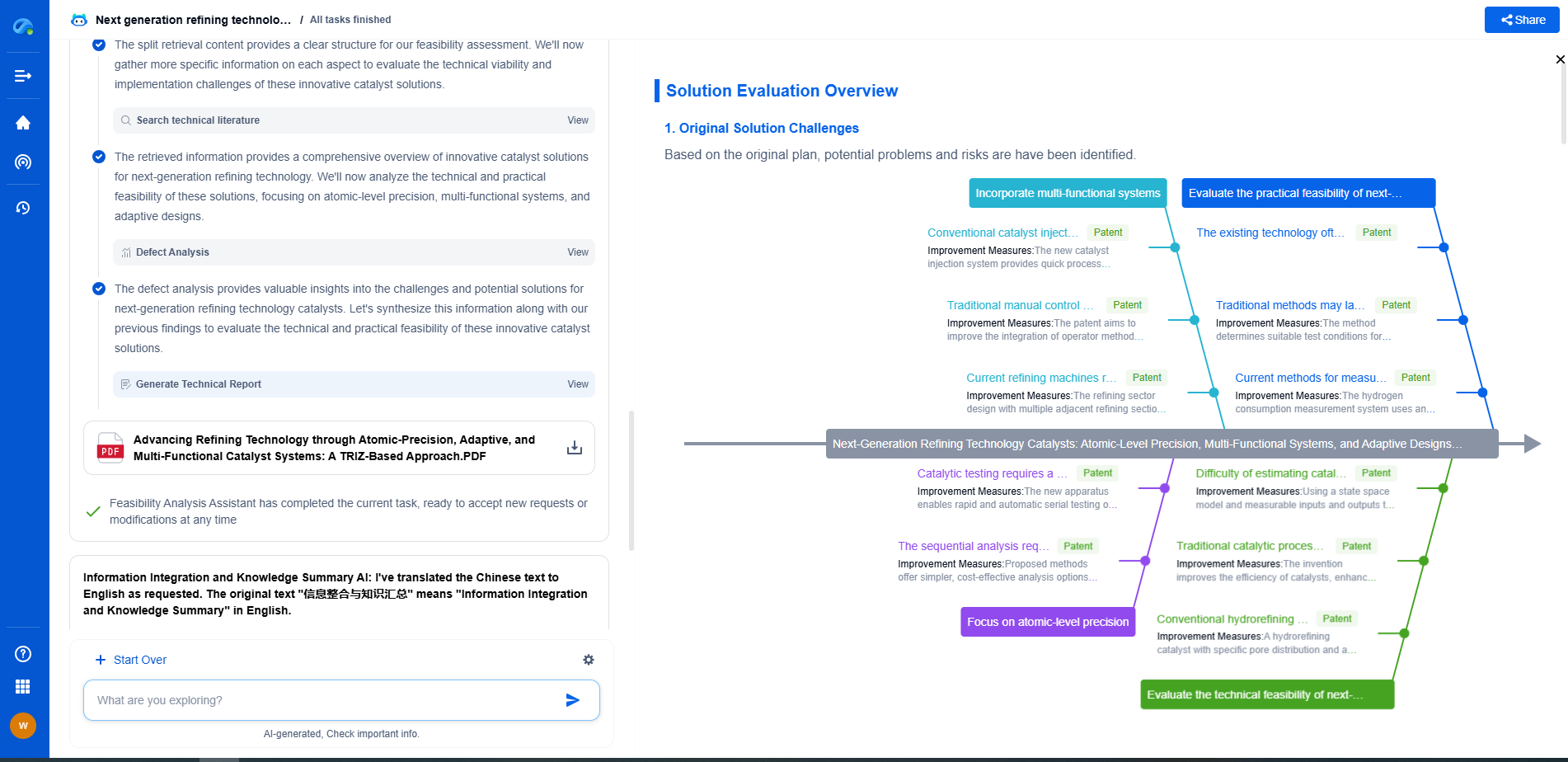
Depth Sensing Technologies: Time-of-Flight vs. Structured Light vs. Stereo
JUL 10, 2025 |
In the rapidly evolving world of technology, depth sensing has emerged as a crucial aspect of numerous applications, ranging from augmented reality and gaming to autonomous vehicles and robotics. The ability to accurately sense and interpret depth information allows devices to interact with their environment in a more intelligent and sophisticated manner. Three prominent technologies driving these advancements are Time-of-Flight (ToF), Structured Light, and Stereo Vision. Each of these methods comes with its own set of advantages and limitations, making them suitable for different applications.
Time-of-Flight (ToF)
Time-of-Flight technology operates on a relatively simple but powerful principle. It measures the time it takes for a light signal to travel from the sensor to the object and back. By calculating the time delay, the distance to the object can be determined with high precision.
Advantages:
1. High Precision: ToF sensors are known for their accuracy in measuring distances over a wide range, which makes them ideal for applications requiring exact depth information.
2. Speed: Since ToF measures time delays directly, it offers rapid data acquisition suitable for real-time applications.
3. Versatility: ToF sensors can function effectively in a variety of lighting conditions, including complete darkness, making them suitable for diverse environments.
Limitations:
1. Cost: The technology is relatively expensive, which can be a limiting factor for mass-market products.
2. Range Limitations: While ToF sensors work well over short to medium distances, their accuracy diminishes significantly over very long distances due to signal attenuation.
3. Interference: Multiple ToF sensors operating in close proximity can interfere with each other, potentially affecting accuracy.
Structured Light
Structured Light technology involves projecting a known pattern of light onto a scene. The deformation of this pattern, when viewed from a different angle, allows the system to compute depth information.
Advantages:
1. Accuracy: Structured Light can deliver high-resolution depth maps, making it suitable for applications like 3D scanning and facial recognition.
2. Detail: This method is adept at capturing fine details and intricate textures on surfaces.
3. Stability: It provides stable results in controlled environments, particularly where the lighting conditions are managed.
Limitations:
1. Environmental Limitations: Structured Light systems can struggle in bright sunlight or reflective environments, which can distort the projected patterns.
2. Complexity: The need for precise calibration and alignment of the projector and camera adds to the complexity and cost.
3. Limited Range: This technology is best suited for close-range applications, typically under a few meters.
Stereo Vision
Stereo Vision is inspired by human binocular vision, using two or more cameras to capture images from slightly different angles. By analyzing the disparity between these images, depth information can be inferred.
Advantages:
1. Cost-Effective: Stereo systems can be relatively inexpensive, utilizing off-the-shelf camera technology.
2. Passive Sensing: Unlike ToF and Structured Light, Stereo Vision does not require active illumination, making it energy-efficient and discreet.
3. Scalability: It can be scaled up with multiple cameras to cover larger areas or more complex environments.
Limitations:
1. Complexity in Processing: Extracting depth information from stereo images requires substantial computational power and sophisticated algorithms.
2. Texture Requirement: Stereo Vision relies on variations in the scene's texture to compute depth, which can be problematic in textureless or homogeneous areas.
3. Sensitivity to Lighting: Although Stereo Vision doesn’t require specific lighting conditions, significant variations in lighting can affect performance.
Comparative Analysis
When comparing these technologies, the choice often boils down to the specific requirements of the application. For high precision and speed in varying lighting conditions, ToF is often preferred. Structured Light excels in controlled environments where detailed surface mapping is necessary. On the other hand, Stereo Vision is a great option for applications where cost is a significant consideration, and the scene has sufficient texture.
Applications and Use Cases
Time-of-Flight is commonly used in gesture recognition, automotive LiDAR systems, and industrial automation. Structured Light finds its niche in 3D modeling and biometric applications, such as facial recognition. Stereo Vision is widely applied in areas like robotics, where depth perception is crucial for navigation and obstacle avoidance.
Conclusion
As the demand for intelligent and interactive systems grows, understanding the strengths and limitations of various depth sensing technologies becomes imperative. While Time-of-Flight, Structured Light, and Stereo Vision each have their specific advantages, the choice ultimately depends on the application's unique needs regarding precision, range, cost, and environmental conditions. As innovations continue to emerge, these technologies will undoubtedly evolve, further enhancing their capabilities and broadening their applications.
Image processing technologies—from semantic segmentation to photorealistic rendering—are driving the next generation of intelligent systems. For IP analysts and innovation scouts, identifying novel ideas before they go mainstream is essential.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
🎯 Try Patsnap Eureka now to explore the next wave of breakthroughs in image processing, before anyone else does.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com