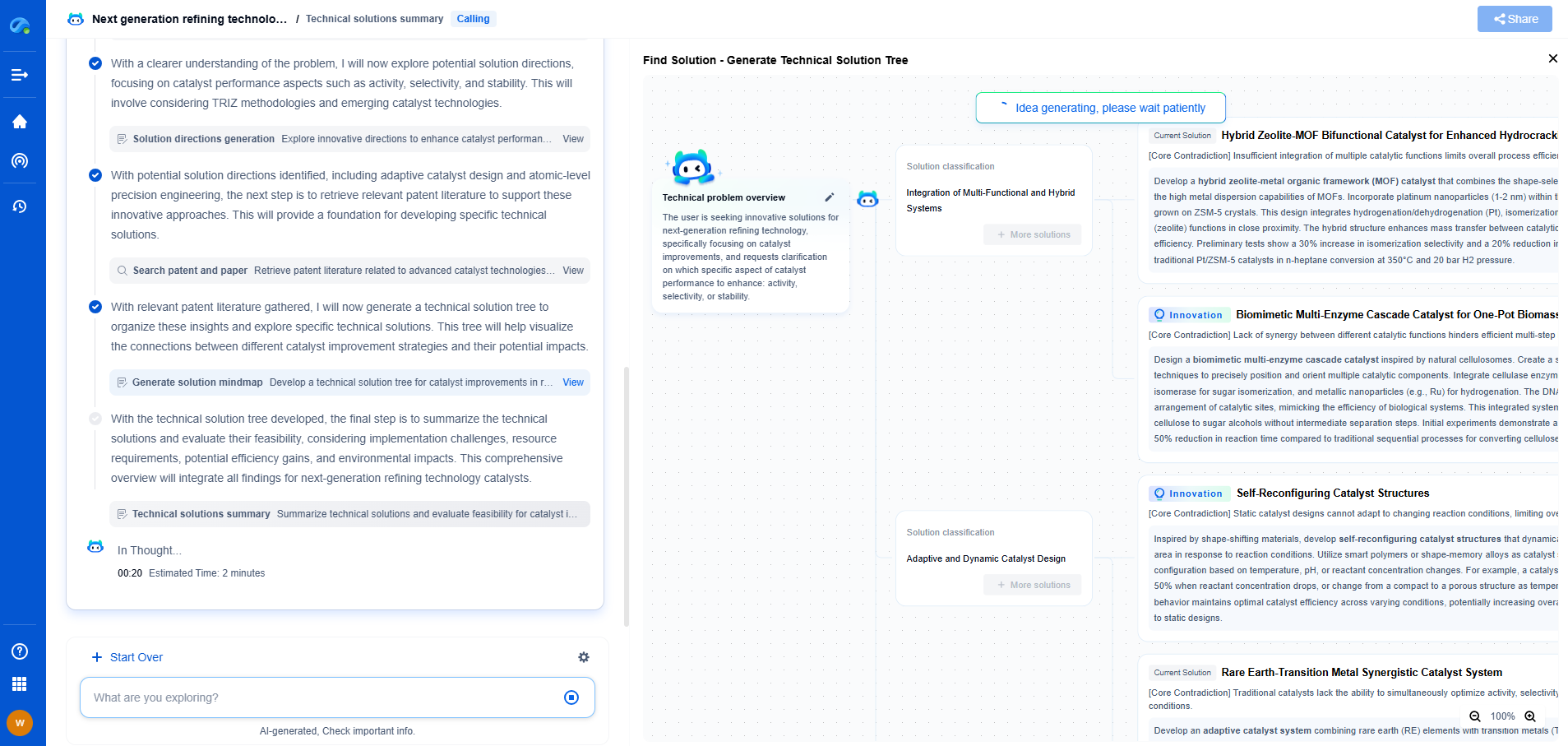
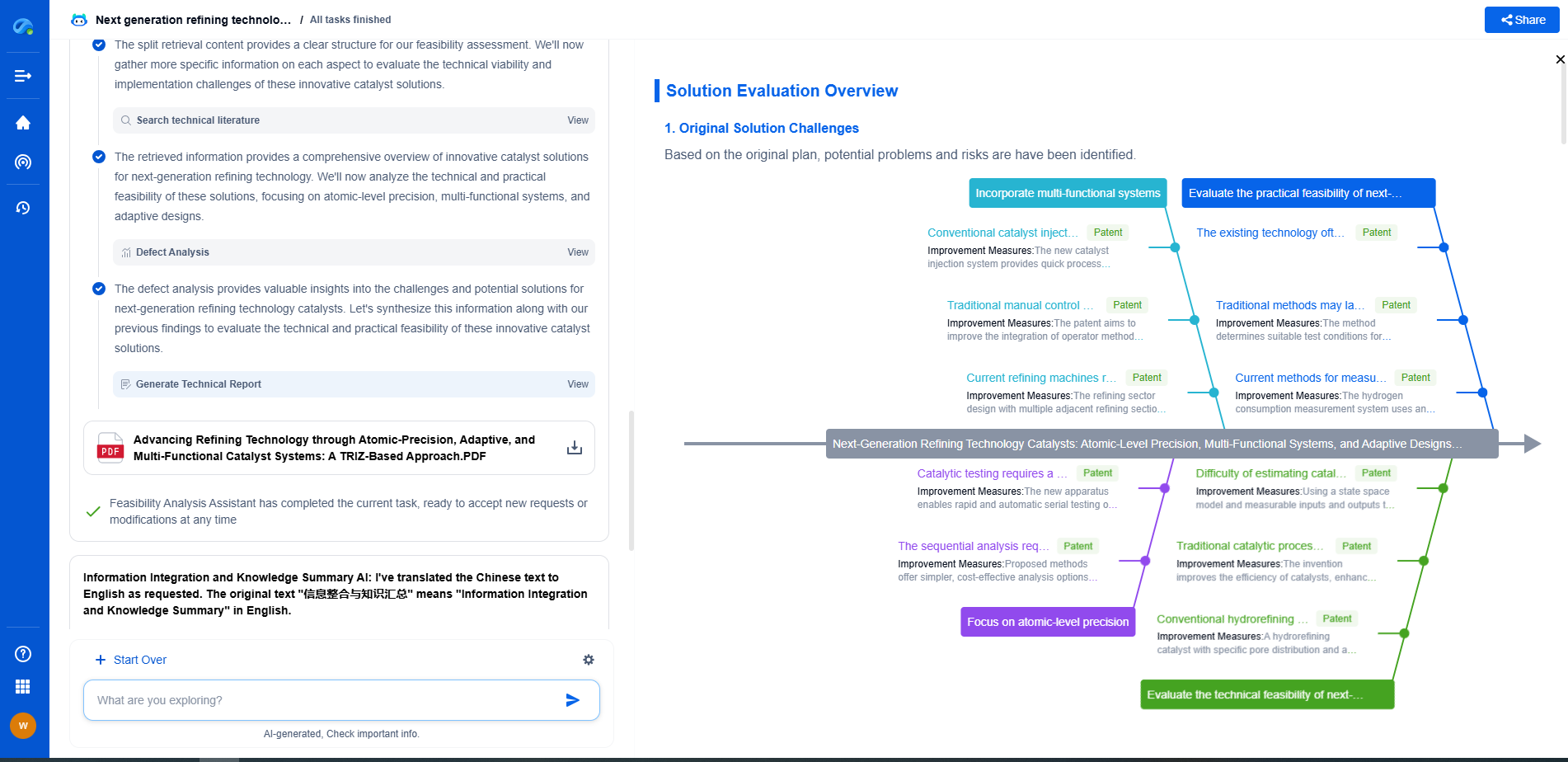
Digital Multimeter (DMM) Guide: How to Measure Voltage, Current, and Resistance Accurately
JUL 9, 2025 |
Digital Multimeters (DMMs) are essential tools in electronics and electrical work, offering the ability to measure voltage, current, and resistance with precision. They are invaluable for troubleshooting circuits, testing batteries, and diagnosing electrical issues in various devices. To use a DMM effectively, it’s crucial to understand its functions and how to apply them accurately.
Getting Started with Your DMM
Before diving into measurements, familiarize yourself with your DMM. It will typically have a digital display, a rotary switch to select different measurement modes, and several input jacks for connecting test leads. Most DMMs have three primary measurement capabilities: voltage (V), current (A), and resistance (Ω). Additionally, they may feature continuity tests, diode tests, and more, but this guide will focus on the three main measurements.
Measuring Voltage
Voltage is the electrical potential difference between two points in a circuit. To measure voltage, follow these steps:
1. **Select the Correct Mode:** Set the rotary switch to the appropriate voltage measurement type: DCV (direct current voltage) for batteries and most electronics, or ACV (alternating current voltage) for household outlets.
2. **Connect Test Leads:** Insert the black test lead into the COM (common) jack and the red test lead into the V (voltage) jack.
3. **Measure the Voltage:** Touch the test leads to the two points between which you want to measure the voltage. The red lead typically connects to the more positive point, and the black lead to the more negative point. Read the voltage on the DMM display.
4. **Safety Precautions:** Always start with a higher voltage range and adjust downward to avoid damaging the DMM. Ensure the circuit is de-energized when connecting or disconnecting the DMM.
Measuring Current
Measuring current involves a different approach as the DMM must be part of the circuit. Here's how to measure current:
1. **Select the Current Mode:** Set the rotary switch to the current measurement mode, choosing either DCA (direct current amperes) or ACA (alternating current amperes) based on the circuit type.
2. **Connect Test Leads:** Connect the black lead to the COM jack and the red lead to the correct current jack (often marked with an A). Some DMMs have separate jacks for different current ranges.
3. **Insert the DMM into the Circuit:** The DMM must be connected in series. This means you need to break the circuit at the point where you want to measure current and insert the DMM in line with the circuit components.
4. **Read the Current:** Once connected, the DMM will display the current flowing through the circuit. Be cautious of the DMM's current rating to prevent damage.
5. **Consider Safety:** Ensure the circuit is off before inserting or removing the DMM to prevent shock or damage to the meter and components.
Measuring Resistance
Resistance measurement is straightforward but requires attention to detail:
1. **Select the Resistance Mode:** Turn the rotary switch to the resistance measurement setting, denoted by the Ω symbol.
2. **Connect Test Leads:** Insert the black lead into the COM jack and the red lead into the Ω jack.
3. **Prepare the Circuit:** Ensure there is no power in the circuit or component you are testing to avoid inaccurate readings or damaging the DMM.
4. **Measure the Resistance:** Place the test leads across the resistor or component whose resistance you want to measure. The DMM will display the resistance value.
5. **Open Circuit Awareness:** Keep in mind that an open circuit will result in an infinite resistance reading, while a closed short circuit will show nearly zero resistance.
Troubleshooting Tips
1. **Check Your Connections:** Ensure test leads are firmly connected and in the correct jacks for the measurement type.
2. **Verify Settings:** Double-check that the rotary switch is set to the correct measurement mode and range.
3. **Inspect the Battery:** A weak or dead battery in your DMM can lead to inaccurate readings.
4. **Consult the Manual:** Every DMM model is slightly different, so it’s beneficial to review the manual for specific instructions and safety warnings.
Conclusion
A digital multimeter is a versatile and powerful tool for anyone dealing with electronics or electrical systems. By understanding how to measure voltage, current, and resistance accurately, you can diagnose issues, ensure safety, and enhance your projects' reliability. Always prioritize safety and refer to your DMM's manual for model-specific guidance to make the most of this essential instrument.
Navigating the evolving world of electrical measurement—from high-precision signal integrity to advanced test protocols like BERT or TDR—demands more than just expertise; it demands smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka empowers you to keep up—by turning complex patent data, technical parameters, and industry signals into actionable insight. It’s your AI partner for exploring what’s next in test, measurement, and electrical diagnostics.
💡 Try Patsnap Eureka for free and see how it transforms the way you work with electrical measurement technologies.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com