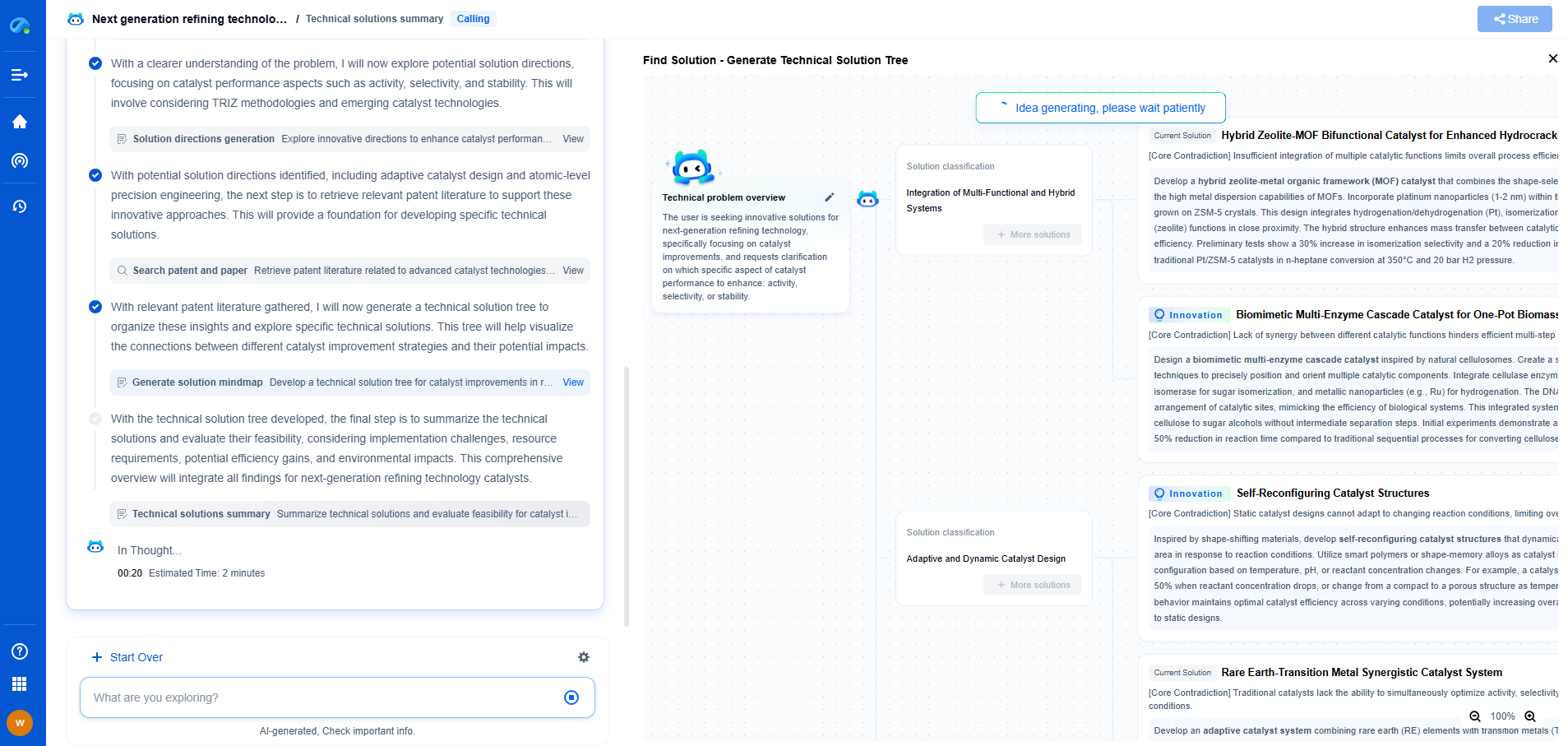
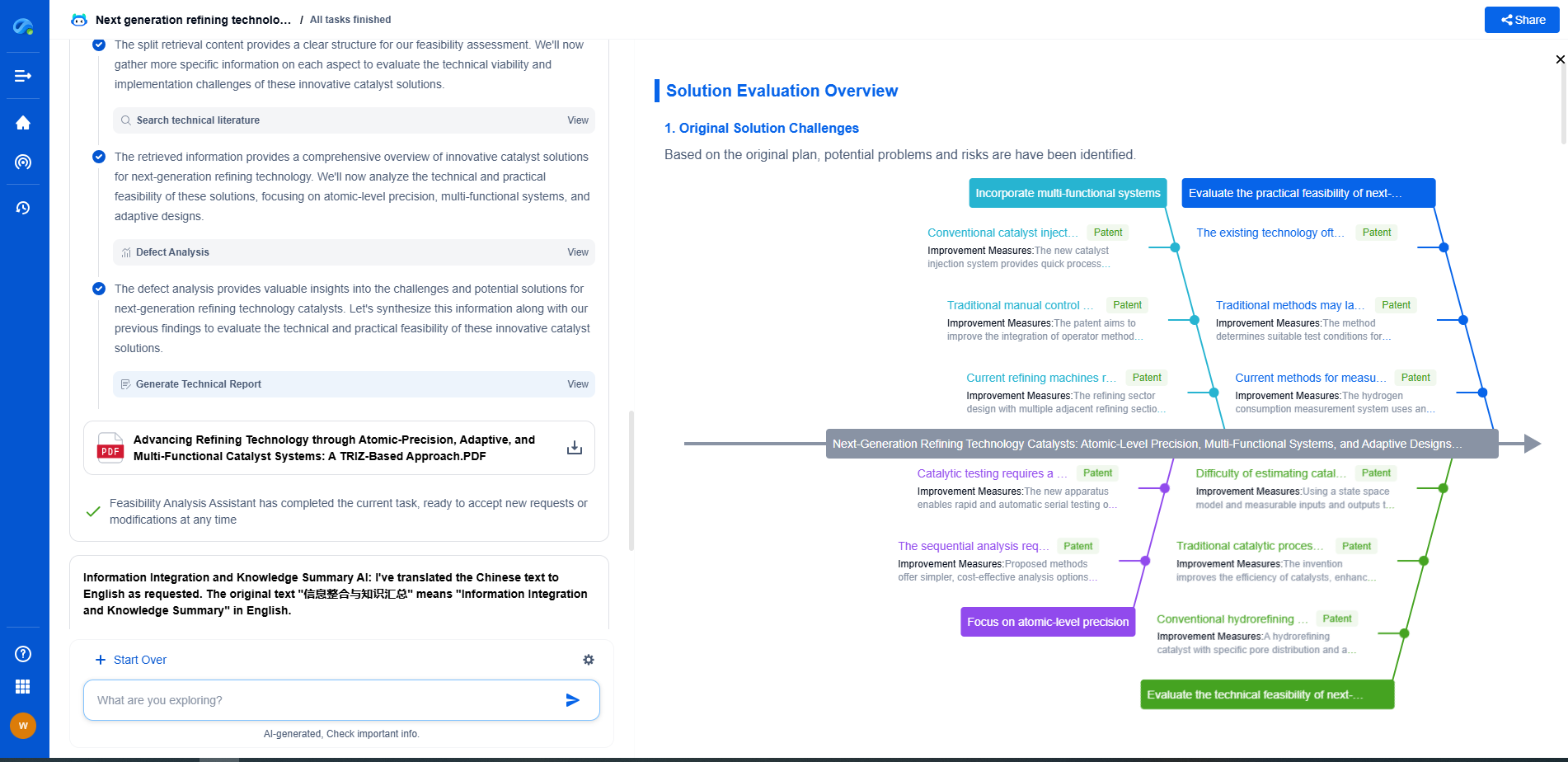
DIN 3990 vs. ISO 6336: Comparing European Gear Calculation Methods
JUL 2, 2025 |
When it comes to gear design and analysis, precision and reliability are paramount. In Europe, two prominent standards are often referenced: DIN 3990 and ISO 6336. Both serve as critical guides for engineers and designers when performing gear calculations, yet they have distinct differences rooted in their origins and methodologies.
Historical Background
DIN 3990, established by the Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN) in Germany, has long been a foundational standard for gear calculations within Europe. It was initially introduced to address the specific needs of German industries, emphasizing robustness and reliability in gear design.
ISO 6336, on the other hand, is a product of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which sought to create a more universally applicable standard. As global trade and collaboration expanded, ISO 6336 emerged to offer a comprehensive approach suitable for various international markets. This broadened its scope beyond the German-centric focus of DIN 3990.
Key Differences in Methodology
One of the primary differences between DIN 3990 and ISO 6336 lies in their methodological approaches to gear strength calculations. DIN 3990 often employs safety factors that are well-aligned with German industrial practices. These safety factors ensure that the calculated load capacity of gears remains conservative, accounting for unforeseen variables in material and manufacturing.
ISO 6336, however, aims for a more balanced approach, providing flexibility in application across various industries worldwide. It offers detailed guidelines for calculating the load capacity of gears, taking into account a wider array of international manufacturing practices and material availability.
Material and Manufacturing Considerations
Material selection and manufacturing processes are integral to gear calculation. DIN 3990 traditionally favored materials and processes that were prevalent in Germany, which sometimes limited its applicability in regions where those materials were not as commonly used.
ISO 6336, with its international focus, provides broader guidance on material selection, allowing for a more diverse range of materials and manufacturing techniques. This makes ISO 6336 more adaptable for companies operating in multiple countries with different resource availabilities.
Application and Industry Preference
The choice between DIN 3990 and ISO 6336 often depends on the specific industry and the geographical location of the operation. Industries entrenched within German engineering traditions might prefer DIN 3990 due to its alignment with local manufacturing capabilities and historical usage in German industrial projects.
Conversely, multinational companies or those looking to standardize their processes across various locations may opt for ISO 6336. Its international orientation makes it suitable for companies aiming for consistency in their gear designs across multiple global markets.
Harmonization Efforts
In recent years, there has been a concerted effort to harmonize these standards, recognizing the need for a more unified approach in gear calculations. This movement aims to integrate the strengths of both standards, providing a more cohesive guideline that benefits from the detailed specificity of DIN 3990 and the broad applicability of ISO 6336.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite these harmonization efforts, challenges remain. Engineers and designers must still navigate the intricacies of both standards, understanding the specific needs of their projects and the markets they serve. This requires a thorough knowledge of the technical aspects of both DIN 3990 and ISO 6336, as well as an understanding of how these standards interact with local regulations and practices.
Conclusion
While DIN 3990 and ISO 6336 each offer valuable insights and methodologies for gear calculations, their differences reflect broader considerations in global engineering standards. As industries continue to expand internationally, understanding these standards' unique aspects will ensure that gear designs are both efficient and compliant across various markets.
The ongoing developments in harmonizing these standards show a commitment to improving gear calculation methods, ultimately leading to more reliable and universally applicable guidelines. For engineers and designers, staying informed about these standards is crucial for successful gear design and application in an increasingly interconnected world.
Boost Innovation in Gears & Transmissions with Patsnap Eureka
Whether you're designing a next-gen planetary gearbox or optimizing gear tooth profiles for noise reduction, keeping up with the fast-evolving landscape of mechanical transmissions requires more than just experience—it takes insight, speed, and smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Whether you're streamlining a manual transmission system or exploring electromechanical actuation, Patsnap Eureka helps your team move from concept to novelty faster than ever.
👉 Experience Eureka in action—request a personalized demo today and see how AI can revolutionize your gear innovation workflows.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com