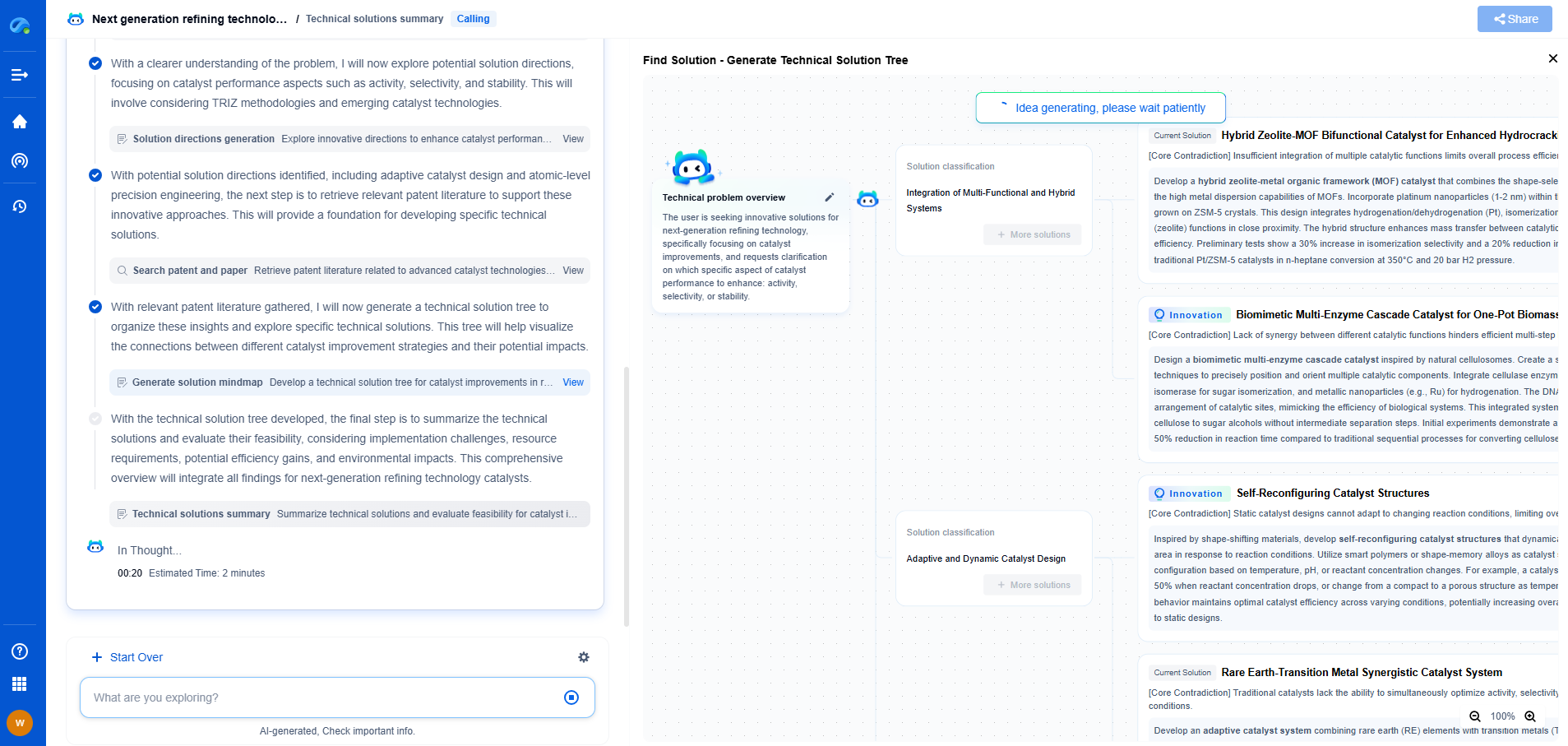
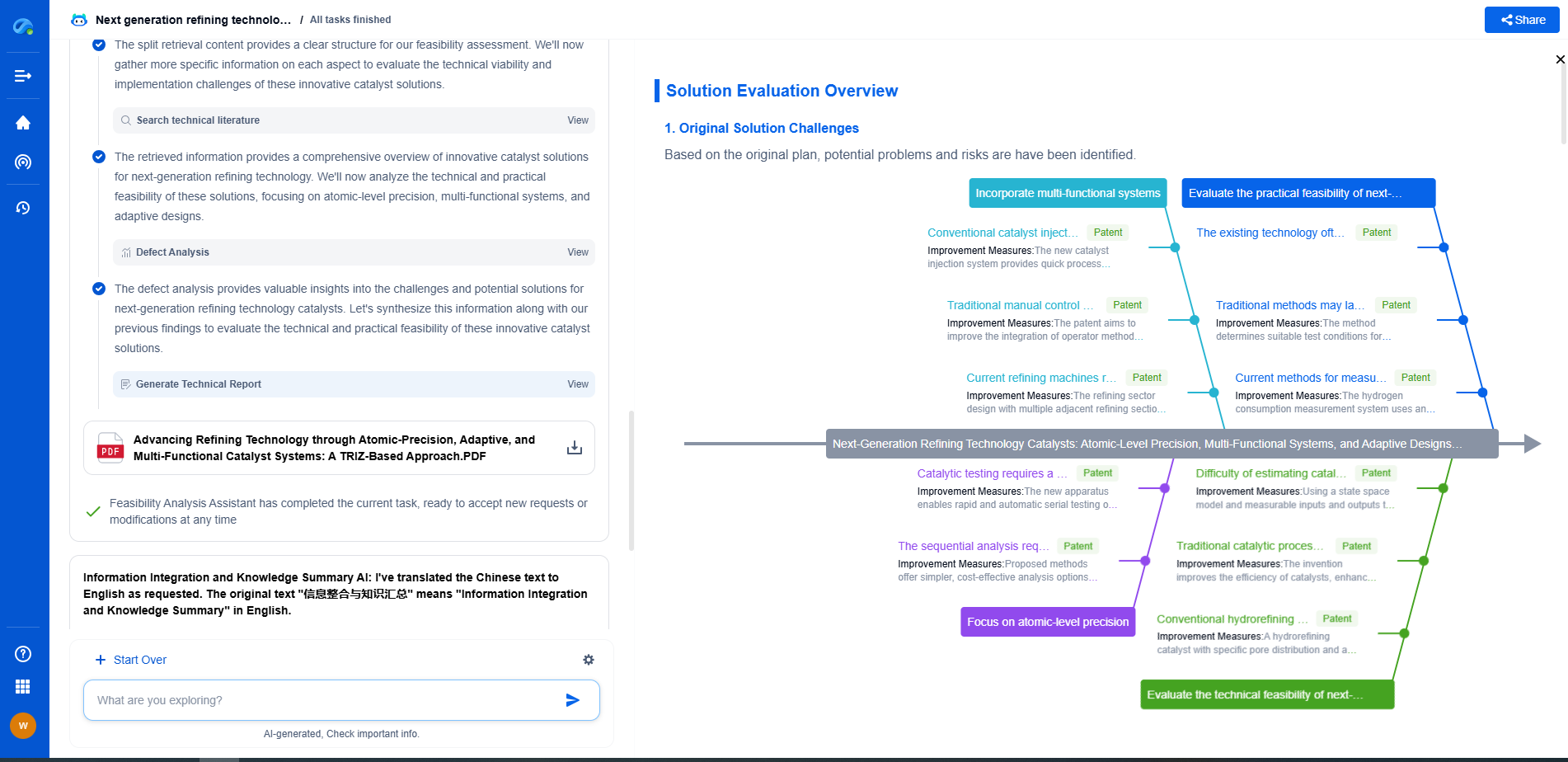
Dust-Resistant Glass Coatings: SiO2 Nanoparticle Spray vs. Permanent CVD Films
JUL 22, 2025 |
In recent years, the demand for dust-resistant glass coatings has surged, driven by the need to maintain transparency and cleanliness in various applications, from consumer electronics to architectural structures. Two popular technologies have emerged as frontrunners in this field: SiO2 nanoparticle sprays and permanent chemical vapor deposition (CVD) films. Both methods offer unique advantages and pose specific challenges. This blog delves into the details of each approach, comparing their effectiveness, application processes, and long-term performance.
SiO2 Nanoparticle Spray
SiO2 nanoparticle sprays have gained popularity due to their ease of application and cost-effectiveness. These sprays consist of silicon dioxide nanoparticles suspended in a liquid medium. When applied to a glass surface, they create a thin, transparent coating that reduces dust adherence.
Advantages
One of the primary benefits of SiO2 nanoparticle sprays is their simplicity. They can be applied using standard spraying equipment, making them accessible for small-scale projects and DIY enthusiasts. Additionally, the spray can be reapplied easily without requiring extensive surface preparation. This feature is particularly advantageous for applications where frequent maintenance is feasible.
Furthermore, SiO2 nanoparticle coatings are known for their hydrophobic properties, which help repel water and prevent the accumulation of dust particles. This characteristic is valuable in climates with high humidity or frequent rain.
Challenges
Despite their benefits, SiO2 nanoparticle sprays have limitations. The durability of these coatings is generally lower compared to permanent solutions. Over time, environmental factors such as UV exposure and abrasion can degrade the coating, necessitating reapplication. This maintenance requirement might not be ideal for structures where constant upkeep is impractical.
Moreover, achieving uniform coverage and consistent thickness can be challenging, especially on large surfaces. Uneven application can lead to areas with reduced dust resistance, impacting the overall effectiveness of the coating.
Permanent CVD Films
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a more sophisticated method for creating dust-resistant glass coatings. In this process, gaseous reactants are introduced into a reaction chamber, where they decompose and deposit a solid film on the substrate.
Advantages
CVD films are renowned for their durability and longevity. Once applied, these coatings form a permanent bond with the glass surface, offering excellent resistance against environmental wear and tear. This durability makes them suitable for applications where long-term performance is critical, such as in high-rise buildings or solar panels.
The precision of the CVD process ensures uniform thickness and consistent properties across large areas, eliminating concerns about patchy coverage. Additionally, CVD films can be engineered to exhibit specific properties, such as enhanced UV resistance, which further prolongs their lifespan.
Challenges
The primary drawback of CVD films is their complexity and cost. The equipment required for CVD processes is expensive, and the application must be performed in controlled environments, limiting accessibility for smaller projects or on-site applications.
Additionally, once applied, CVD films cannot be easily removed or modified. This inflexibility may be a disadvantage if future changes to the glass surface are anticipated.
Comparison and Consideration
When choosing between SiO2 nanoparticle sprays and CVD films, several factors must be considered, including the intended application, budget, and maintenance capabilities. SiO2 sprays are ideal for projects requiring a balance between cost and performance, especially when frequent reapplication is feasible. In contrast, CVD films are better suited for applications demanding long-term durability and minimal maintenance.
Conclusion
Both SiO2 nanoparticle sprays and permanent CVD films offer effective solutions for dust-resistant glass coatings, each with distinct advantages and limitations. By understanding these differences, stakeholders can make informed decisions to match the right technology with their specific needs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity for their glass surfaces.
As solar technology races ahead—from perovskite cells to tandem architectures, from anti-reflective coatings to transparent electrodes—staying on top of fast-moving innovation has become a strategic imperative.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚡ Ready to accelerate your solar innovation journey? Try Patsnap Eureka today and let AI help you harness the full power of the sun—and your IP strategy.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com