EGS vs traditional hydrothermal systems: pros and cons
JUN 20, 2025 |
Geothermal energy, originating from the Earth's internal heat, is a sustainable and renewable energy source. It's harnessed through two primary methods: traditional hydrothermal systems and Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS). Both are invaluable to the clean energy landscape, yet they differ significantly in their mechanisms, advantages, and drawbacks. This blog explores the pros and cons of EGS and traditional hydrothermal systems, highlighting their roles in the energy sector.
Understanding Traditional Hydrothermal Systems
Traditional hydrothermal systems have been the cornerstone of geothermal energy for decades. These systems rely on naturally occurring reservoirs of hot water or steam found beneath the Earth's surface. The heat from these reservoirs is brought to the surface to drive turbines, generating electricity.
Pros of Traditional Hydrothermal Systems
1. **Efficiency and Cost-effectiveness**: Traditional hydrothermal systems are highly efficient due to the natural occurrence of hot water and steam. The technology is mature, and the operational costs are relatively low compared to other energy sources.
2. **Reliability**: Given their long-standing presence and established technology, hydrothermal systems are reliable and have a proven track record in electricity production.
3. **Low Environmental Impact**: While not entirely devoid of environmental concerns, traditional hydrothermal systems generally have lower emissions compared to fossil fuels.
Cons of Traditional Hydrothermal Systems
1. **Geographical Limitations**: These systems require specific geological formations, typically near tectonic plate boundaries, limiting their deployment to certain regions.
2. **Finite Resource**: Though renewable, the availability of steam and hot water can diminish over time, potentially reducing efficiency and output.
3. **Water Usage**: Traditional hydrothermal systems can use significant amounts of water, raising concerns particularly in drier regions.
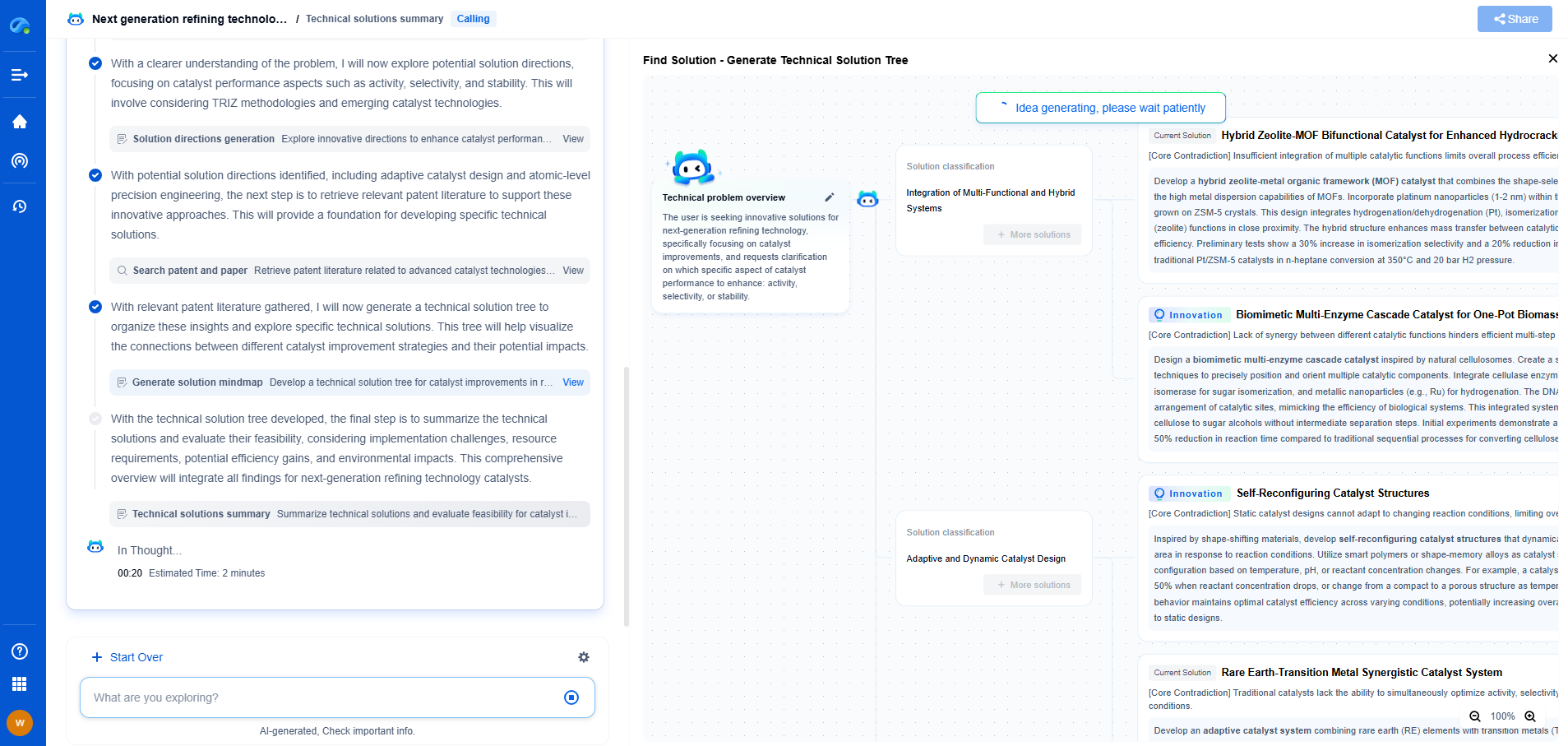
Exploring Enhanced Geothermal Systems (EGS)
Enhanced Geothermal Systems represent a more versatile approach to geothermal energy. Unlike traditional systems, EGS do not rely on naturally occurring reservoirs. Instead, they create their own geothermal reservoirs, by injecting water into hot dry rock formations deep underground.
Pros of Enhanced Geothermal Systems
1. **Expanded Geographic Potential**: EGS can be developed in areas that lack natural geothermal resources, dramatically expanding the potential footprint of geothermal energy.
2. **Sustainability**: By creating artificial reservoirs, EGS can offer a more consistent output, reducing the depletion risks associated with traditional systems.
3. **Innovative Technology**: EGS technology is advancing rapidly, with ongoing research promising further improvements in efficiency and output.
Cons of Enhanced Geothermal Systems
1. **High Initial Costs**: The development of EGS involves significant upfront investment due to the complexity of drilling and reservoir creation.
2. **Technical Challenges**: EGS technology is still evolving, and there are challenges related to managing induced seismicity and maintaining reservoir integrity.
3. **Risk of Induced Seismicity**: The process of injecting water into rock formations can potentially trigger minor earthquakes, raising concerns in some regions.
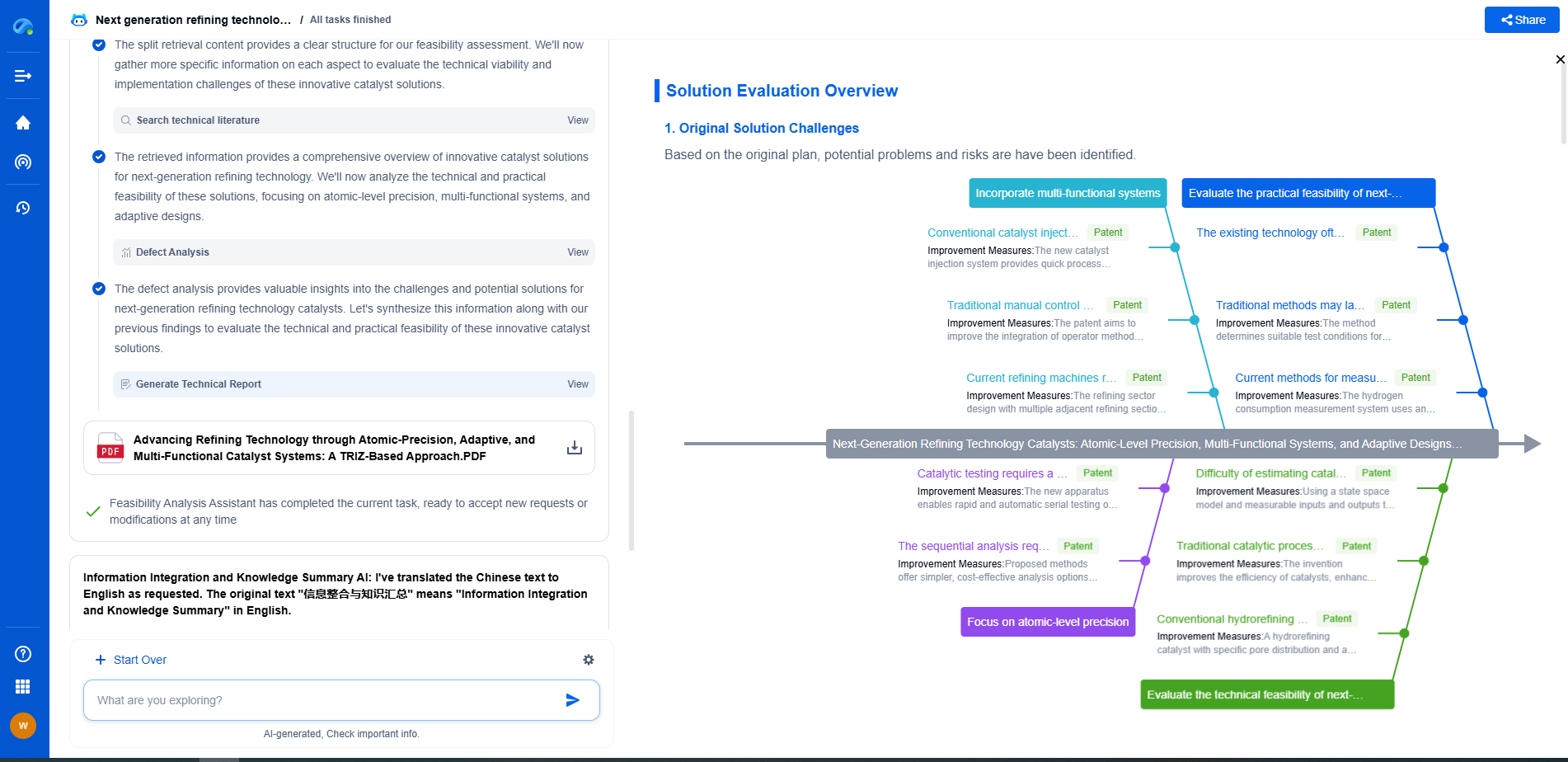
Comparison and Conclusion
Both traditional hydrothermal systems and EGS have their unique advantages and disadvantages. Traditional systems offer mature technology and reliability but are geographically limited. EGS, on the other hand, present an opportunity to expand geothermal's reach but come with higher initial costs and technical challenges.
The decision between these two systems depends heavily on regional geological conditions, economic considerations, and environmental impact assessments. As technology progresses, EGS may become more competitive, offering a viable alternative to fossil fuels on a broader scale. Ultimately, both systems are crucial to a diversified and sustainable energy future, playing complementary roles in the quest for clean, renewable power.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com