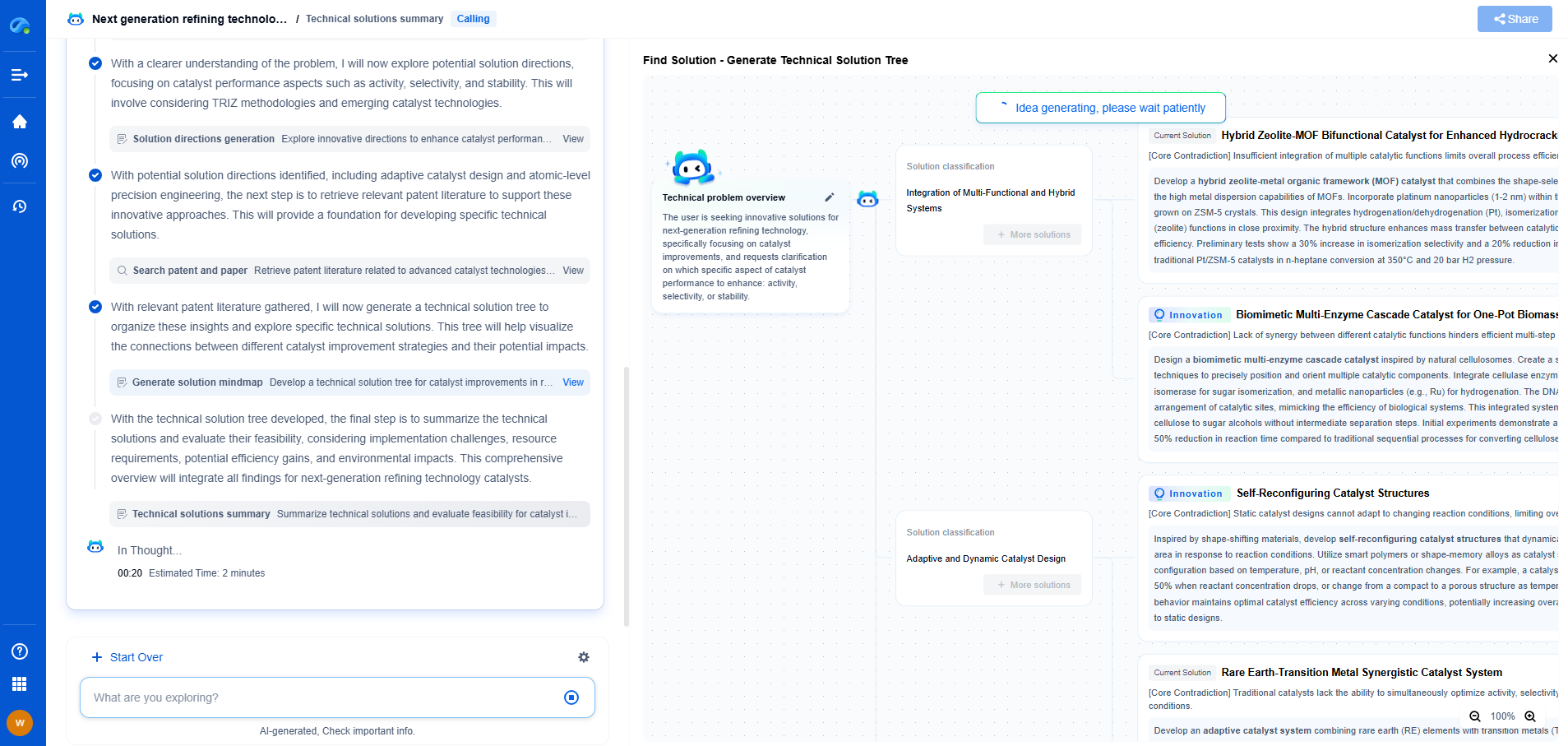
Environmental impact comparison: WBM vs OBM vs SBM
JUN 20, 2025 |
In the world of drilling fluids, the choice between Water-Based Mud (WBM), Oil-Based Mud (OBM), and Synthetic-Based Mud (SBM) is a critical decision impacting not only drilling efficiency but also environmental sustainability. Each type of drilling fluid presents unique characteristics, advantages, and potential environmental impacts. This article aims to delve into the environmental implications of these drilling fluids, comparing their ecological footprints to illuminate the best choice for environmentally conscious operations.
Water-Based Mud (WBM)
Water-Based Mud is widely considered the most environmentally friendly option among the three types. Composed primarily of water, clay, and various additives, WBMs are often praised for their reduced toxicity and biodegradability.
Environmental Benefits
WBM is less likely to pose significant harm to aquatic life due to its low toxicity, making it a preferred choice in environmentally sensitive areas. It is easier to dispose of as well because it often requires less stringent regulatory compliance for handling and disposal. Additionally, WBMs are often more cost-effective due to the relative abundance and low cost of water and other natural additives.
Environmental Concerns
Despite its benefits, WBM can still pose environmental challenges. The introduction of additives, such as biocides and corrosion inhibitors, albeit necessary for drilling efficiency, may still lead to localized environmental impacts if not managed properly. Moreover, WBMs can sometimes lead to increased disposal volumes, as they require larger quantities to achieve desired performance compared to more concentrated OBMs and SBMs.
Oil-Based Mud (OBM)
Oil-Based Mud consists of oil as the continuous phase with water and additives dispersed within it. Known for providing superior lubrication and thermal stability, OBM is often used in complex drilling operations.
Environmental Benefits
The primary environmental advantage of OBM is its efficacy in minimizing wellbore instability, leading to fewer issues and potentially less waste generation during drilling. Its recyclability is another benefit, as OBM can often be reconditioned and reused in subsequent drilling operations.
Environmental Concerns
OBM poses significant environmental challenges. Its high toxicity levels and slower biodegradability compared to WBM can lead to long-term ecological damage if spills or leaks occur. Proper handling, storage, and disposal are also more complex and costly due to these factors. Regulatory compliance for OBM is strict, given the potential for water contamination and soil degradation.
Synthetic-Based Mud (SBM)
Synthetic-Based Mud is designed to combine the benefits of both OBM and WBM, using synthetic oils that offer a more environmentally friendly alternative to traditional oil-based fluids.
Environmental Benefits
SBM is less toxic and more biodegradable than OBM, providing a middle ground between the environmental impacts of WBM and OBM. The improved lubricity and thermal stability reduce the likelihood of drilling-related issues, which can minimize environmental disruption. SBMs often have less impact on air quality as they emit fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to OBM.
Environmental Concerns
While SBMs are generally more environmentally friendly than OBM, potential challenges remain. The production of synthetic components can be energy-intensive, and the cost of SBMs is typically higher than WBMs. Moreover, while less toxic, the synthetic components can still pose risks if not managed properly.
Conclusion
Choosing the right drilling fluid involves a careful balance between operational efficiency and environmental responsibility. While Water-Based Mud offers the least environmental impact, its limitations in complex drilling environments may necessitate the use of Oil-Based or Synthetic-Based Muds. OBM provides superior performance but comes with significant environmental challenges. In contrast, SBM offers a compromise, enhancing performance while mitigating some of the environmental concerns associated with OBM.
Ultimately, the decision on which drilling fluid to use should consider the specific conditions of the drilling site, regulatory requirements, and long-term environmental impacts. As technology advances, the development of new additives and drilling fluid formulations may continue to reduce the ecological footprint of drilling operations, promoting a more sustainable future for the industry.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com