ERW vs SAW Pipes: Structural and Cost Differences
JUN 20, 2025 |
When it comes to selecting pipes for various industrial applications, understanding the differences between Electric Resistance Welded (ERW) and Submerged Arc Welded (SAW) pipes is crucial. These two types of pipes are among the most commonly used in the oil and gas industry, construction, and other sectors. In this blog, we will explore the structural and cost differences between ERW and SAW pipes, helping you make informed decisions for your projects.
Structural Differences
Manufacturing Process
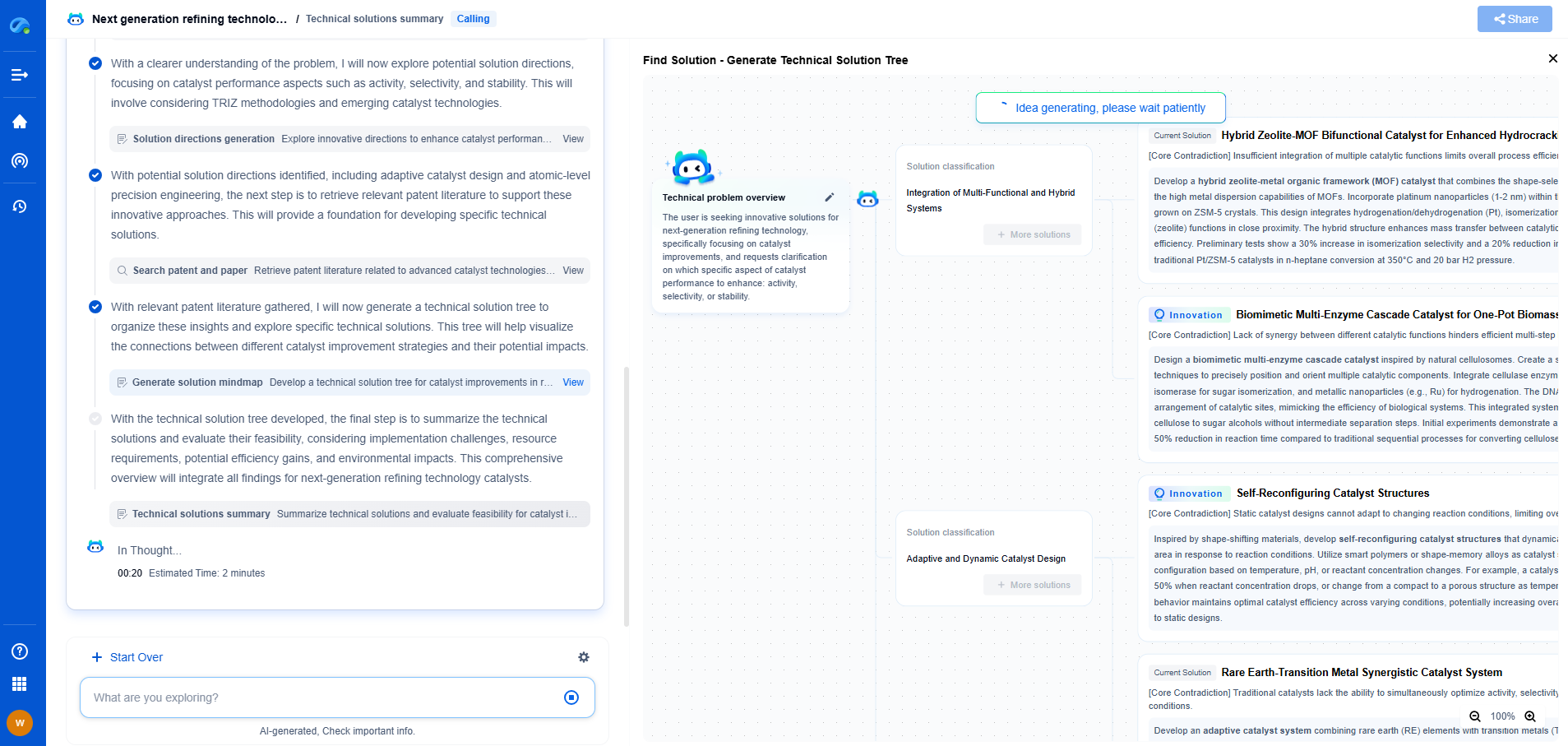
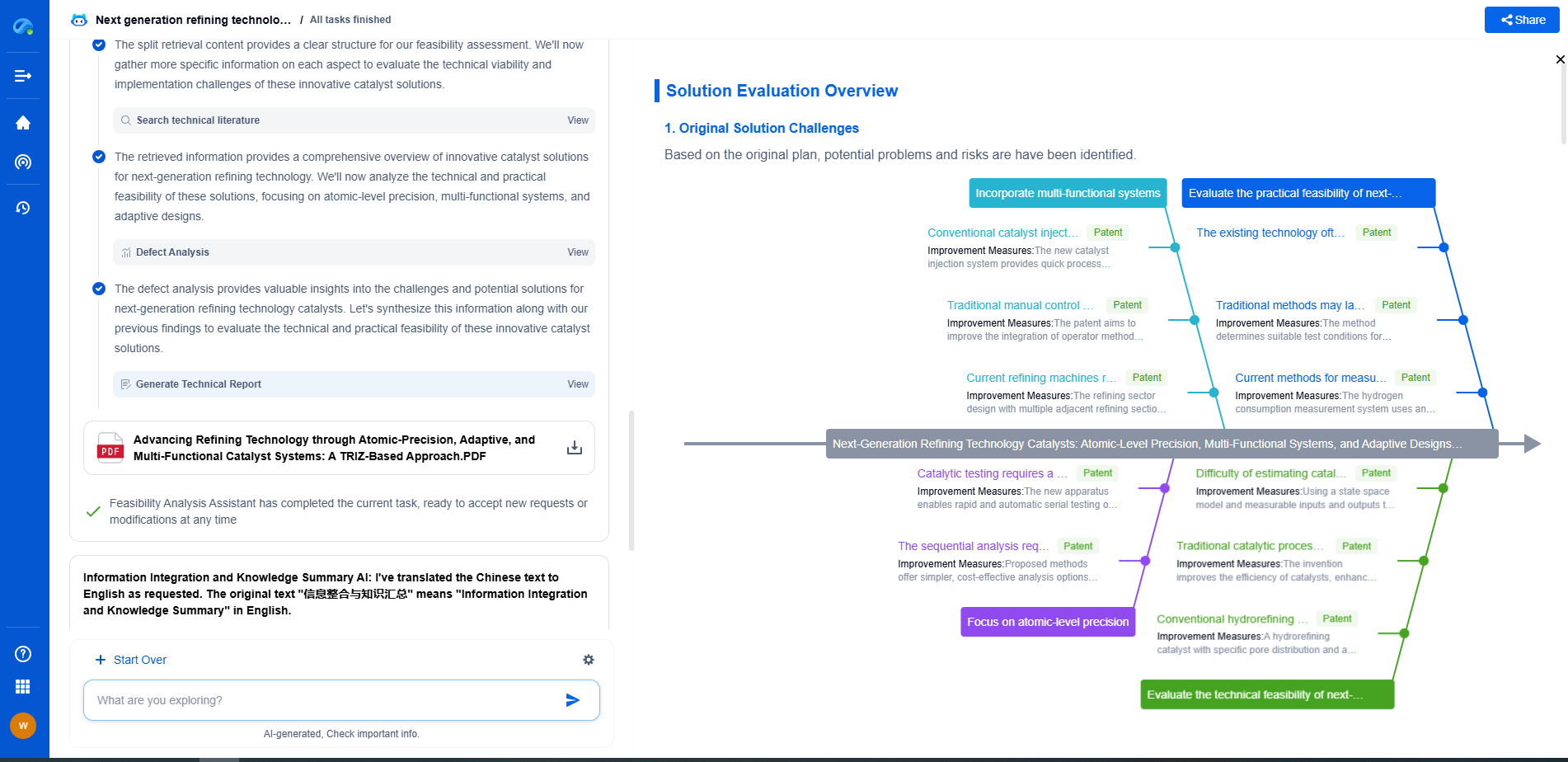
The primary difference between ERW and SAW pipes lies in their manufacturing processes. ERW pipes are made by rolling metal and then welding it longitudinally along its length using electric resistance welding. This creates a smooth and uniform seam, which is an advantage for many applications requiring precision and a clean finish. On the other hand, SAW pipes are produced by welding the edges of the rolled metal plate using an arc that is submerged under a flux layer. This process often results in a double-sided weld, which can provide added strength and durability.
Strength and Durability
Both ERW and SAW pipes have their strengths depending on the application. ERW pipes are known for their high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finish, making them ideal for applications requiring precise measurements and aesthetic considerations. However, SAW pipes typically offer superior strength due to their double-sided welding process, making them suitable for high-pressure environments. The additional weld reinforcement in SAW pipes can enhance their resistance to stress and strain, making them particularly useful in demanding applications such as underwater or buried pipelines.
Size and Thickness Variations
Another structural difference is in the size and thickness options available. ERW pipes are generally available in thinner walls and smaller diameters compared to SAW pipes, which can be manufactured in larger diameters and thicker wall sizes. This difference is significant when considering the requirements of specific projects. For projects that require larger pipes, SAW might be the preferable option, whereas ERW pipes are more suitable for smaller-scale applications.
Cost Differences
Manufacturing Costs
Cost is often a decisive factor when choosing between ERW and SAW pipes. The manufacturing process of ERW pipes tends to be more economical due to its continuous welding operation, which results in lower production costs. On the other hand, the SAW process, involving a more complex and labor-intensive welding technique, can lead to higher production costs. Therefore, ERW pipes are generally more cost-effective for projects where budget constraints are significant.
Installation Expenses
In terms of installation costs, ERW pipes can be less expensive due to their lighter weight and simpler joint requirements. This can lead to savings in transportation and installation labor costs. SAW pipes, due to their larger size and greater weight, may require more specialized handling and installation equipment, thereby increasing the overall installation expenses.
Maintenance and Longevity
While upfront costs are a consideration, long-term maintenance and the lifespan of the pipes should also be factored in. SAW pipes, with their robust welds, may offer greater longevity and lower maintenance costs over time, especially in harsh environments. ERW pipes, being less resistant to extreme pressure and corrosion, might necessitate more frequent inspections and maintenance, adding to long-term expenses.
Conclusion
Understanding the structural and cost differences between ERW and SAW pipes is essential for making the right choice for your project. ERW pipes offer precision, lower manufacturing and installation costs, making them ideal for applications with tighter budget constraints and less demanding environments. Conversely, SAW pipes provide enhanced strength and durability, making them suitable for larger-scale projects and environments where higher pressure resistance is needed.
Both ERW and SAW pipes have their unique advantages, and the decision ultimately depends on the specific requirements of your project, including budget, environmental conditions, and desired pipe characteristics. By weighing these factors carefully, you can select the most appropriate pipe type to ensure the success and longevity of your infrastructure.
Transform the Way You Innovate in Pipeline Technology—with AI-Powered Intelligence
From corrosion-resistant materials to smart monitoring systems and advanced flow control mechanisms, the pipeline industry is undergoing rapid technological transformation. Yet keeping up with evolving engineering solutions, regulatory landscapes, and competitive patents can be a major bottleneck for R&D and IP teams.
Patsnap Eureka is your AI-powered research companion—built specifically for professionals in high-tech and infrastructure domains like pipeline technology. Whether you're designing high-pressure transport systems, assessing trenchless installation innovations, or safeguarding proprietary flow assurance solutions, Eureka provides real-time insights into global patent trends, emerging technologies, and R&D intelligence—all in one intuitive interface.
Empower your team to innovate faster, reduce technical blind spots, and stay ahead of industry shifts. Discover Patsnap Eureka today and bring clarity and confidence to your pipeline technology decisions.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com