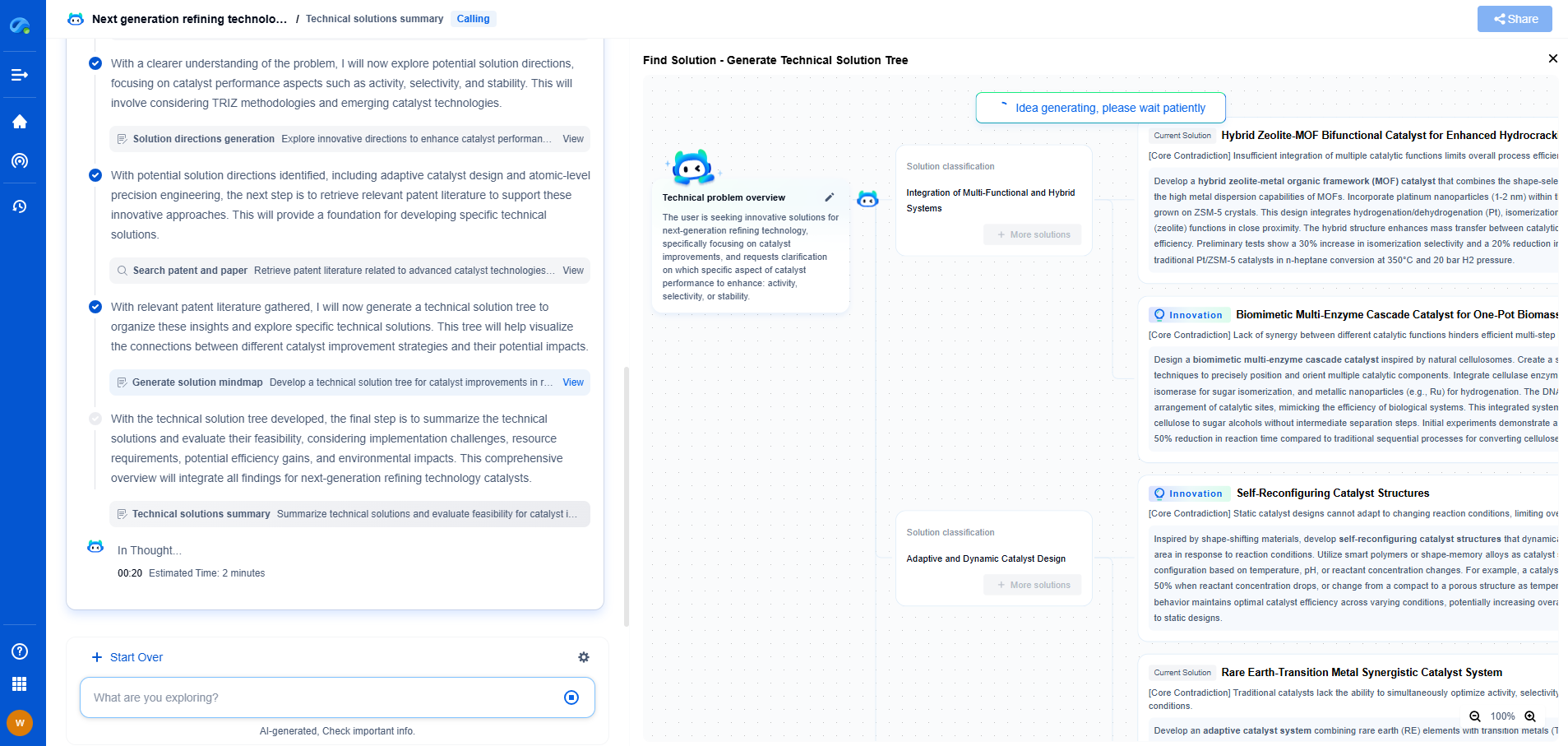
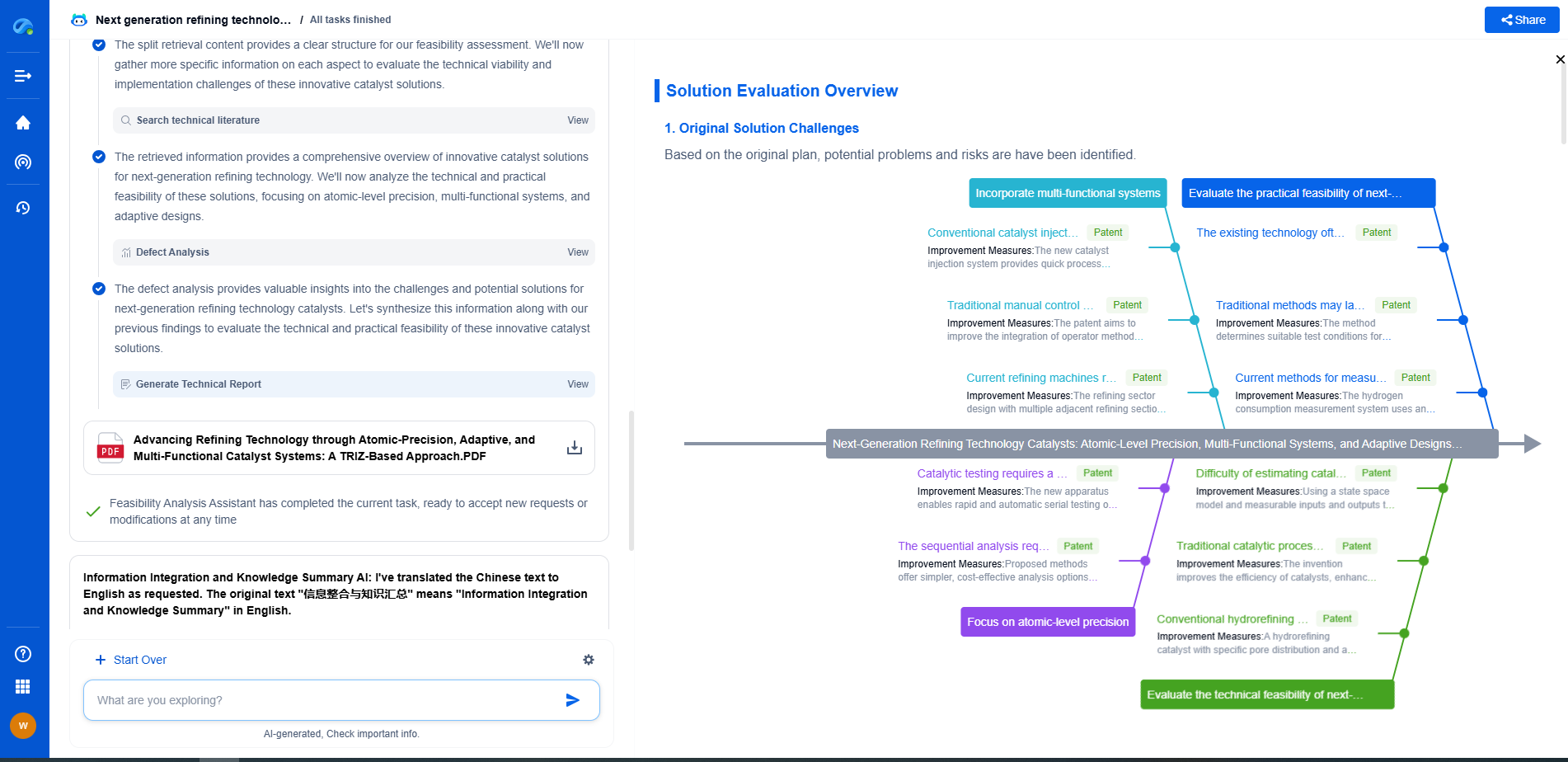
FDA 21 CFR Part 11 vs ISO 17025: Digital Compliance for Optical Instruments
JUL 15, 2025 |
In today's rapidly advancing technological landscape, digital compliance is becoming increasingly crucial for various industries, especially those dealing with sophisticated instruments like optical devices. Two prominent standards often discussed in this context are the FDA's 21 CFR Part 11 and ISO 17025. Both lay down stringent guidelines but serve different purposes. Understanding these standards' distinctions and overlaps is essential for businesses aiming to ensure compliance and maintain the integrity of their operations.
Overview of FDA 21 CFR Part 11
The FDA's 21 CFR Part 11 is a regulation that provides criteria for the acceptance of electronic records, electronic signatures, and handwritten signatures executed to electronic records. Primarily, it applies to companies regulated by the FDA, such as those in the pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device sectors. This regulation ensures that electronic records and signatures are as trustworthy, reliable, and equivalent to paper records and handwritten signatures.
Key components of 21 CFR Part 11 include:
- Validation: Ensuring that systems are accurately processing data.
- Audit Trails: Maintaining a secure, computer-generated, time-stamped audit trail to independently record the date and time of operator entries and actions that create, modify, or delete electronic records.
- System Access: Limiting system access to authorized individuals.
- Electronic Signatures: Ensuring that electronic signatures are unique to one individual and cannot be reused or reassigned.
ISO 17025: A Glimpse
On the other hand, ISO 17025 is an international standard that specifies the general requirements for the competence to carry out tests and/or calibrations, including sampling. It covers testing and calibration performed using standard methods, non-standard methods, and laboratory-developed methods. This standard is applicable to all organizations that perform tests and/or calibrations, regardless of the number of personnel or the extent of the scope of testing and/or calibration activities.
ISO 17025 is crucial for laboratories wanting to demonstrate that they operate competently and generate valid results, thereby promoting confidence in their work both nationally and internationally. The standard focuses on two main areas:
- Management Requirements: This includes the operation and effectiveness of the quality management system within the laboratory.
- Technical Requirements: These are related to the competence of staff, methodology, test/calibration equipment, and the quality and reporting of test and calibration results.
Comparing 21 CFR Part 11 and ISO 17025
While both standards aim to ensure reliability and integrity, they apply to different aspects of digital compliance and target different sectors. The primary distinction lies in their focus: 21 CFR Part 11 is centered on electronic records and signatures within FDA-regulated environments, while ISO 17025 is concerned with the competence of testing and calibration laboratories across various industries.
One of the significant overlaps between the two is the emphasis on maintaining robust data integrity and ensuring that processes are both standardized and traceable. However, 21 CFR Part 11 places more emphasis on electronic signatures and validation processes, whereas ISO 17025 focuses on laboratory competence, including the capability of performing accurate tests and calibrations.
Implications for Optical Instrumentation
For companies dealing with optical instruments, understanding the nuances of these standards is critical. Optical instruments are pivotal in medical diagnostics, telecommunications, and various scientific research fields, where precision and reliability are non-negotiable. Adhering to both 21 CFR Part 11 and ISO 17025 can greatly enhance an organization’s credibility and operational efficiency.
Organizations must evaluate their specific needs, considering both the regulatory environment they operate in and the specific requirements of their industry. For example, a laboratory that develops optical instruments for medical use must comply with 21 CFR Part 11 due to FDA regulations while also adhering to ISO 17025 to showcase competence and reliability in testing and calibration.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of digital compliance in the optical instrumentation sector requires a deep understanding of both FDA 21 CFR Part 11 and ISO 17025. While they serve different purposes, adherence to these standards ensures robust quality assurance, data integrity, and operational competence. As technological advancements continue to shape the landscape, staying informed and compliant with these standards will be crucial for companies to maintain competitive advantage and trust in their products and services.
From interferometers and spectroradiometers to laser displacement sensors and fiber optic probes, the field of optical measurement is evolving at light speed—driven by innovations in photonics, MEMS integration, and AI-enhanced signal processing.
With Patsnap Eureka, biomedical innovators can navigate cross-domain insights in optics, electronics, and biocompatible materials, while discovering IP trends across academic, clinical, and commercial datasets.
💡 Fuel your next breakthrough in optical health tech—start using Patsnap Eureka to unlock deep insights today.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com