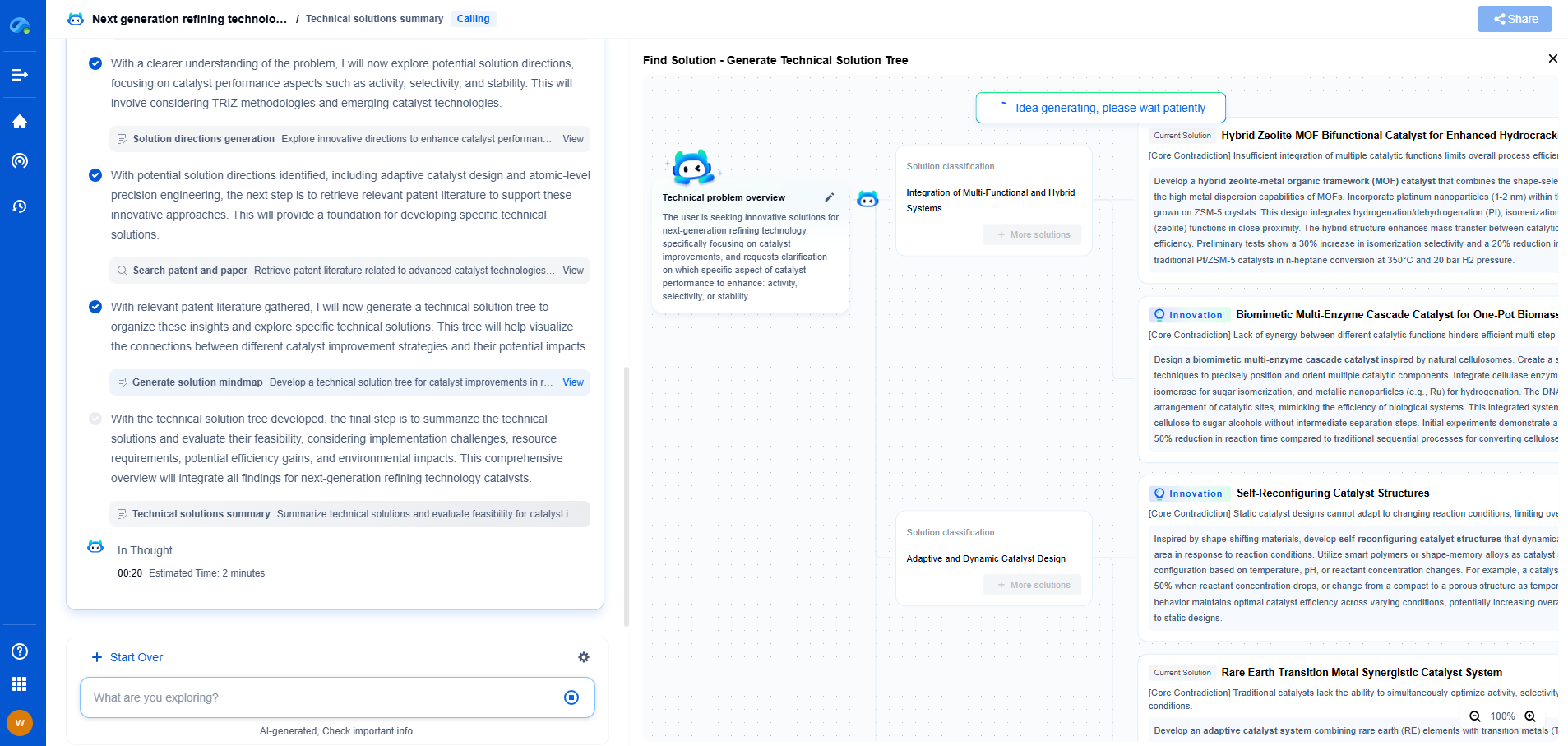
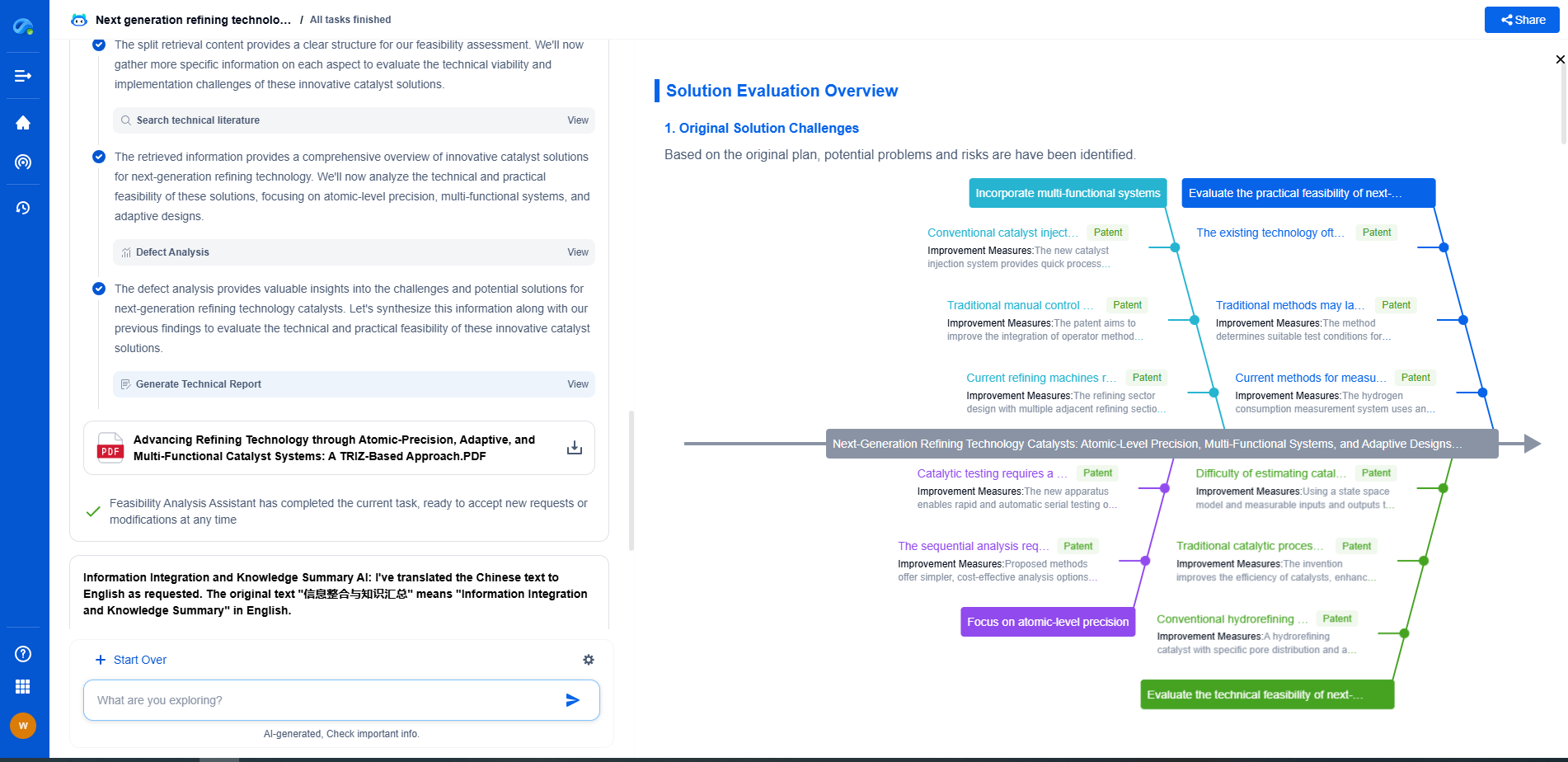
Film Capacitor Dielectric Materials: PET, PP, PTFE – Which Is Best?
JUL 9, 2025 |
Film capacitors are fundamental components used in various electronic applications, prized for their reliability, stability, and performance. The choice of dielectric material in film capacitors significantly influences their characteristics and suitable applications. Three popular dielectric materials are PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate), PP (Polypropylene), and PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene). Each of these materials has distinct properties that make them suitable for specific purposes. This blog delves into the characteristics of these dielectric materials, comparing their strengths and weaknesses to determine which might be best suited for different applications.
Properties of PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate)
PET is a thermoplastic polymer resin commonly used in film capacitors. It is known for its excellent mechanical strength and thermal stability. PET capacitors offer good tolerance to high temperatures, making them suitable for applications where heat resistance is crucial. Additionally, PET capacitors have a high dielectric constant, which allows them to achieve greater capacitance values in a smaller package.
However, PET capacitors have some limitations. They may exhibit higher dissipation factors compared to PP capacitors, which can result in energy losses in high-frequency applications. Additionally, their performance can degrade under prolonged exposure to humidity. Despite these challenges, PET capacitors remain popular due to their cost-effectiveness and reliability in many applications.
Advantages of PP (Polypropylene) Dielectrics
PP is another widely used dielectric material in film capacitors, known for its low dissipation factor and excellent electrical properties. One of the most significant advantages of PP capacitors is their outstanding performance in high-frequency applications, thanks to their low dielectric losses. This makes them highly suitable for applications in telecommunications and radio frequency circuits.
Furthermore, PP capacitors have excellent moisture resistance, contributing to their long-term reliability in humid environments. They are also known for good thermal stability, although not as high as PTFE. However, PP capacitors can be bulkier compared to PET capacitors when achieving the same capacitance, which can be a consideration in space-constrained applications. Overall, PP capacitors are an excellent choice for applications requiring high efficiency and minimal energy losses.
Exploring PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) Capacitors
PTFE, commonly known by the brand name Teflon, is a high-performance dielectric material used in film capacitors. PTFE capacitors offer exceptional thermal stability, capable of withstanding very high temperatures without significant degradation, making them ideal for high-temperature applications. They also have a low dielectric constant and low dissipation factor, which contributes to their excellent performance in high-frequency applications.
One of the unique properties of PTFE is its chemical inertness, which gives it excellent resistance to chemical reactions and environmental factors. This makes PTFE capacitors highly reliable in challenging environments. However, PTFE capacitors are generally more expensive to produce compared to PET and PP capacitors, which can be a limiting factor for budget-sensitive applications. Despite the higher cost, PTFE capacitors are unmatched when it comes to performance in extreme conditions.
Comparative Analysis
When comparing PET, PP, and PTFE film capacitors, it becomes evident that the choice of dielectric material depends heavily on the specific requirements of the application. PET capacitors are an economical choice for general-purpose applications, offering a good balance between performance and cost. PP capacitors, with their low energy losses and moisture resistance, are better suited for high-frequency and outdoor applications. Meanwhile, PTFE capacitors, though more expensive, provide superior performance in extreme thermal and chemical environments.
Conclusion
There is no one-size-fits-all answer when it comes to selecting the best dielectric material for film capacitors. Each material—PET, PP, and PTFE—has its unique set of advantages and limitations. Engineers and designers must carefully consider the specific requirements of their application, including factors like temperature stability, frequency range, environmental conditions, and budget constraints, to determine the most suitable dielectric material. By understanding the properties and benefits of each type, informed decisions can be made to achieve optimal capacitor performance in various electronic applications.
Looking to accelerate your capacitor innovation pipeline?
As capacitor technologies evolve—from miniaturized MLCCs for smartphones to grid-scale energy storage devices—so must the way your team accesses critical knowledge.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Try Patsnap Eureka now and discover a faster, smarter way to research and innovate in capacitor technology.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com