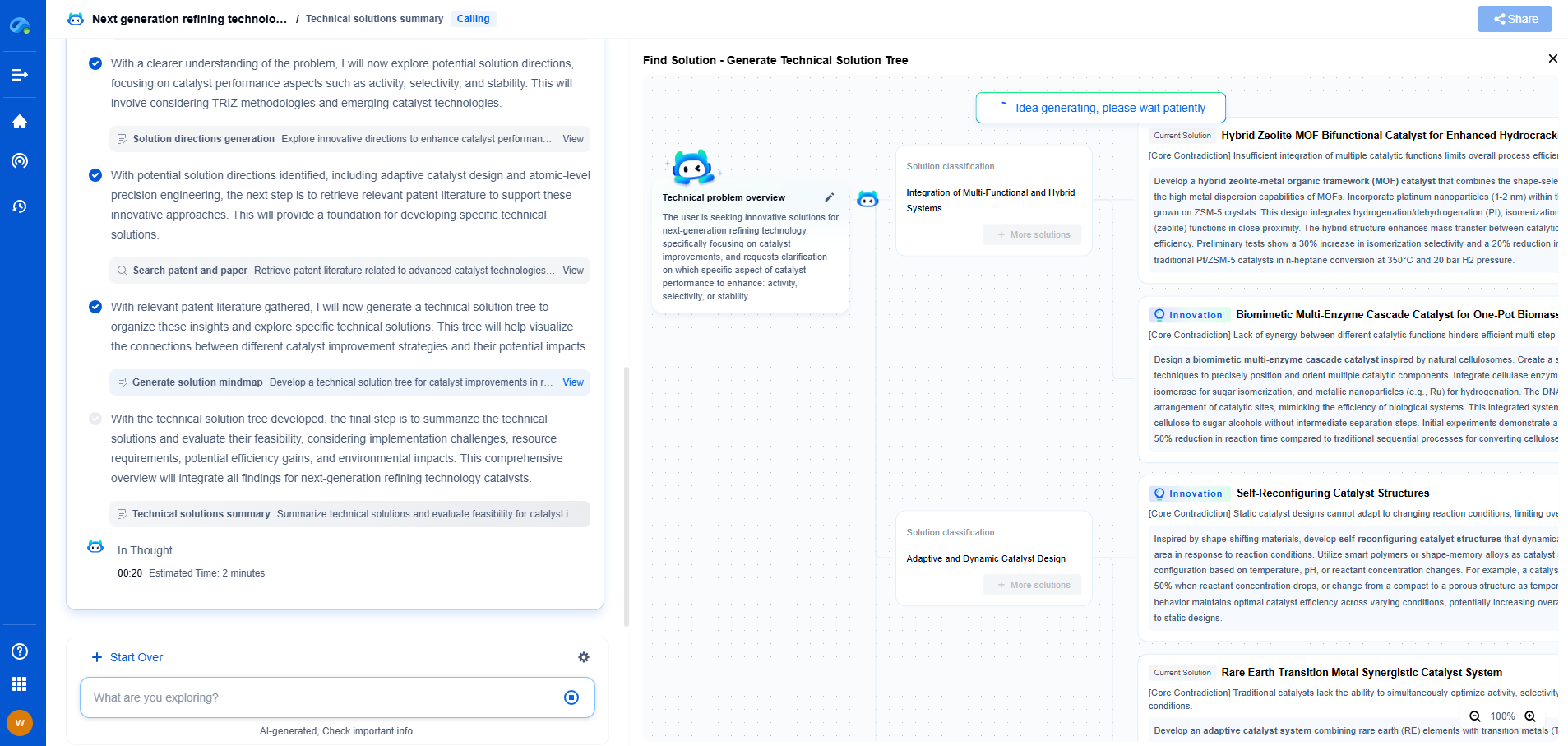
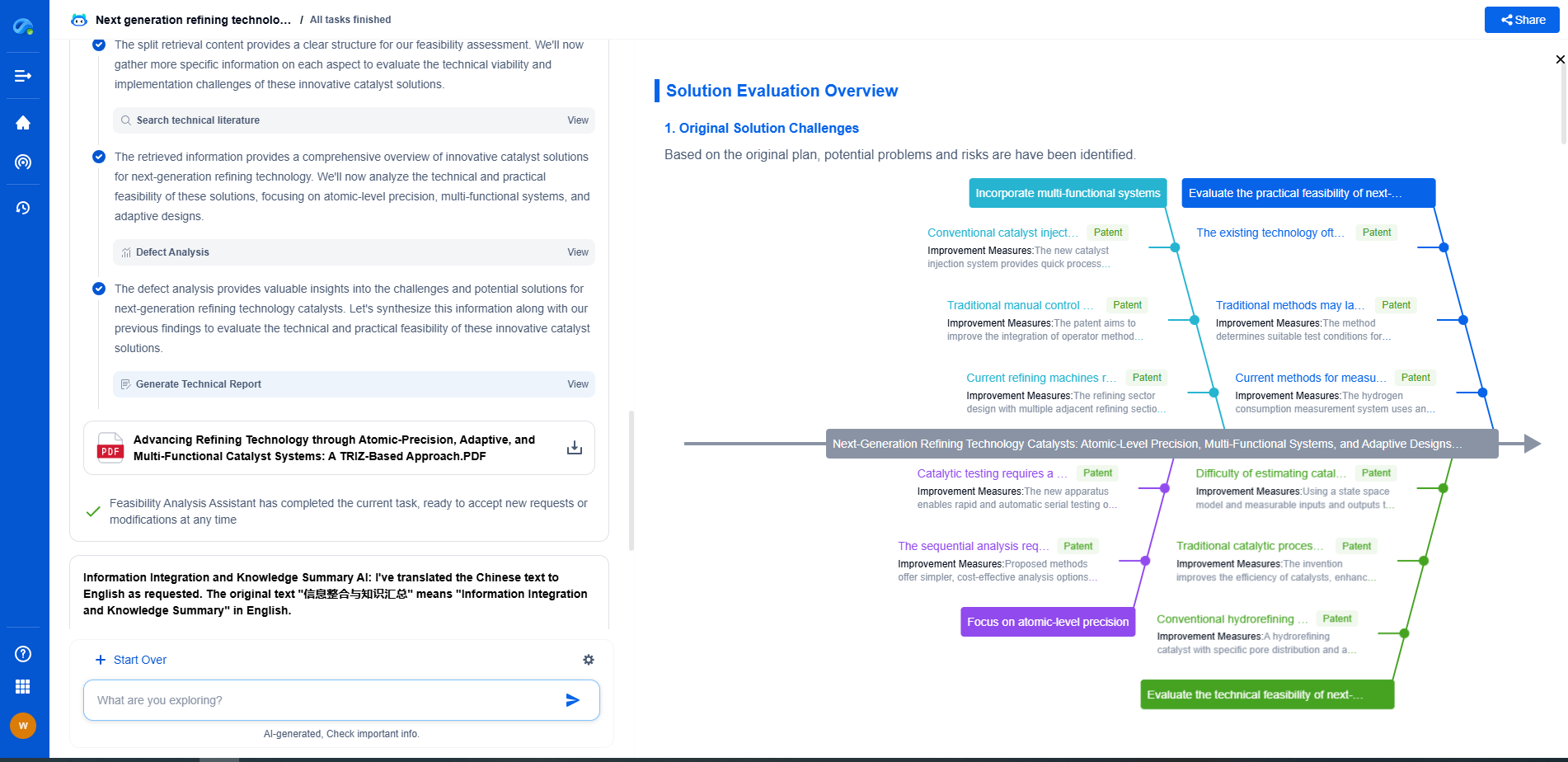
Film Capacitors vs. Ceramic Capacitors: Pros, Cons, and Best Uses
JUL 9, 2025 |
Capacitors are fundamental components in electronic circuits, serving as energy storage devices that can release energy when needed. Two of the most common types of capacitors are film capacitors and ceramic capacitors. Each type has its characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and ideal applications. Understanding the differences between these two capacitor types can help you make informed decisions for your electronic projects.
Film Capacitors Explained
Film capacitors, also known as plastic film capacitors, utilize a thin plastic film as the dielectric. This film is usually made from materials like polyester, polypropylene, or polycarbonate. These capacitors come in two main forms: metalized film capacitors, where a thin metal layer is deposited onto the film, and film/foil capacitors, where separate metal foil layers are used.
Pros of Film Capacitors
1. **Stability and Reliability**: Film capacitors offer excellent stability and durability, maintaining their performance over a wide range of temperatures and conditions. They have a low dielectric absorption and are less prone to aging.
2. **Low Dielectric Loss**: They exhibit low dielectric losses, making them efficient for high-frequency applications.
3. **High Voltage Tolerance**: Film capacitors can handle high voltages, often making them suitable for power supply and audio applications.
4. **Variety and Flexibility**: Available in a broad range of values and configurations, film capacitors provide versatility to meet specific needs.
Cons of Film Capacitors
1. **Size**: Compared to ceramic capacitors, film capacitors are bulkier, which might be a limitation in compact electronic designs.
2. **Cost**: They tend to be more expensive, especially for higher capacitance and voltage ratings.
3. **Limited Capacitance Size**: Film capacitors generally have a lower capacitance range, which may not be suitable for applications requiring high capacitance.
Best Uses for Film Capacitors
Film capacitors are ideal for applications requiring high reliability and stability, such as in audio equipment, power supplies, and signal processing. Their ability to handle higher voltages makes them perfect for precision analog circuits and AC applications.
Ceramic Capacitors Unveiled
Ceramic capacitors use ceramic material as the dielectric and are known for their small size and cost-effectiveness. They are available in two major types: multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs) and ceramic disc capacitors, with MLCCs being the most widely used due to their compact size and high capacitance per volume.
Pros of Ceramic Capacitors
1. **Compact Size**: Ceramic capacitors are small, making them suitable for densely packed printed circuit boards (PCBs).
2. **Cost-Effectiveness**: They are generally cheaper than film capacitors, providing an economical choice for high-volume applications.
3. **Wide Capacitance Range**: Ceramic capacitors offer a broad range of capacitance values, making them versatile for various applications.
4. **High Frequency Performance**: They perform well at high frequencies, which is beneficial for RF and microwave applications.
Cons of Ceramic Capacitors
1. **Temperature Sensitivity**: Their capacitance can vary with temperature and voltage, which might affect precision applications.
2. **Limited Voltage Handling**: Ceramic capacitors typically have lower voltage ratings compared to film capacitors.
3. **Microphonics**: In some instances, ceramic capacitors can exhibit microphonics, causing unwanted noise in audio applications.
Best Uses for Ceramic Capacitors
Ceramic capacitors are ideal for applications requiring small size and high-frequency performance, such as RF circuits, decoupling, and filtering. Their cost-effectiveness makes them an attractive choice for consumer electronics and general-purpose use.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Capacitor
Choosing between film and ceramic capacitors depends on the specific requirements of your application. Film capacitors are best for high-voltage and high-reliability applications, while ceramic capacitors are ideal for high-frequency, compact designs. Understanding the unique advantages and limitations of each type will guide you in selecting the most suitable capacitor for your electronic projects.
Looking to accelerate your capacitor innovation pipeline?
As capacitor technologies evolve—from miniaturized MLCCs for smartphones to grid-scale energy storage devices—so must the way your team accesses critical knowledge.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Try Patsnap Eureka now and discover a faster, smarter way to research and innovate in capacitor technology.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com