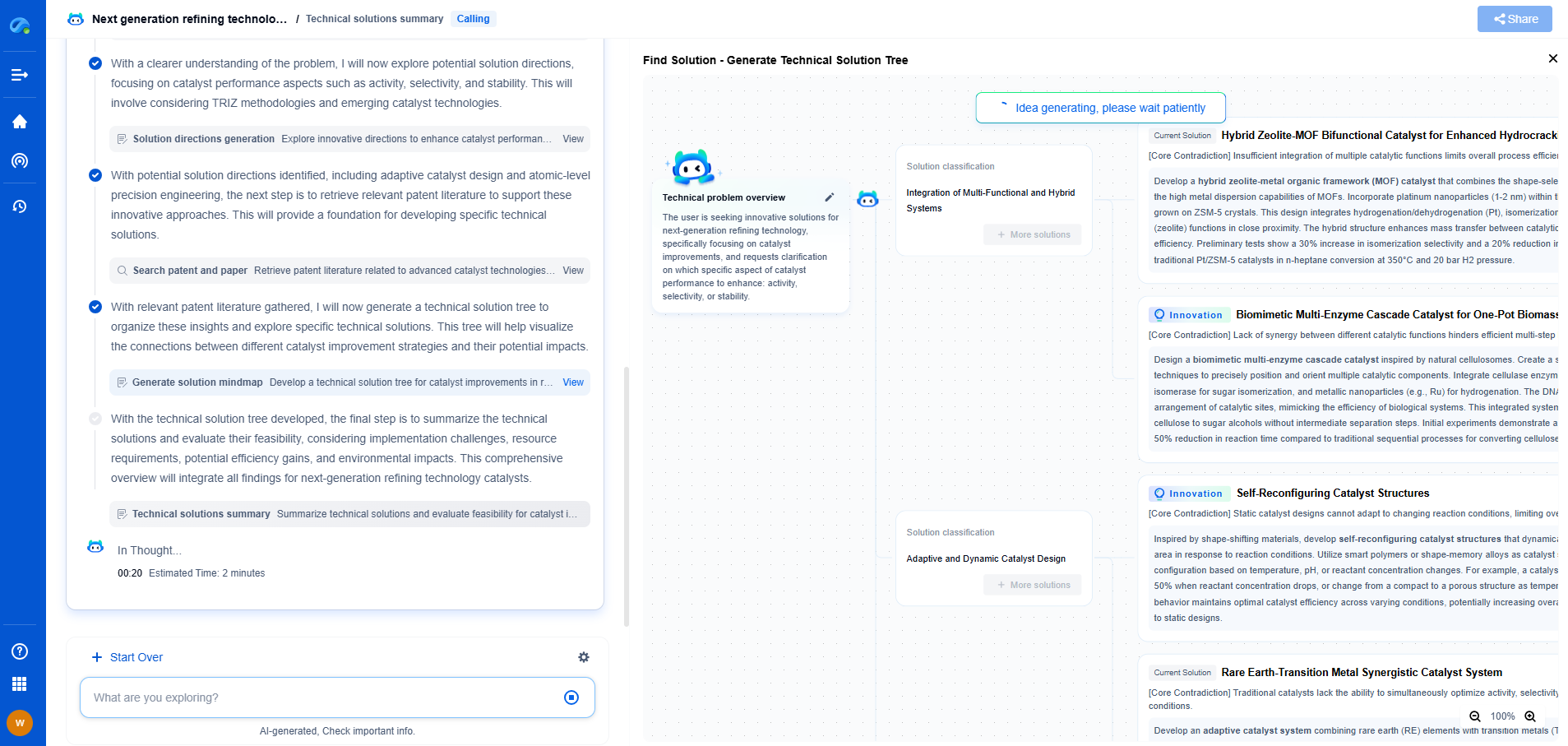
Flexible PV vs. Rigid Solar Panels: Which Works Better for Wearables?
JUL 22, 2025 |
The world of wearable technology is rapidly evolving, and solar power is playing an increasingly significant role in this advancement. Wearable devices, from fitness trackers to smartwatches, are often limited by battery life. Incorporating solar technology can offer a sustainable solution, extending the functionality and lifespan of these devices. In the quest to harness solar energy, two primary types of photovoltaic (PV) solutions are considered: flexible PV and rigid solar panels. Each comes with its own set of advantages and drawbacks, particularly when applied to wearables.
Understanding Flexible PV Panels
Flexible PV panels are made using thin-film technology. These panels are composed of layers of photovoltaic material that are deposited onto a flexible substrate. The result is a lightweight, bendable panel that can be easily adapted to various shapes and surfaces. This flexibility makes them incredibly attractive for wearable applications where comfort and adaptability are paramount.
Pros of Flexible PV for Wearables:
1. Lightweight and Bendable: Flexible panels can conform to the contours of the human body, making them ideal for clothing, wristbands, or other wearable items. Their lightweight nature ensures that they do not add unnecessary bulk or discomfort.
2. Strong Aesthetic Appeal: With their ability to blend seamlessly into fabrics and other materials, flexible PV panels maintain the aesthetic integrity of wearables.
3. Robust Durability: Often constructed with materials that resist cracking and breaking, flexible panels can withstand the physical stresses of daily wear and tear.
Cons of Flexible PV for Wearables:
1. Lower Efficiency: Typically, flexible PV panels are less efficient than their rigid counterparts in converting sunlight into electricity. This inefficiency can be a critical drawback, especially in low-light conditions.
2. Cost: The advanced manufacturing processes required to produce flexible PV panels often result in higher costs. This can be a limiting factor for large-scale adoption in cost-sensitive markets.
Exploring Rigid Solar Panels
Rigid solar panels are the traditional choice in solar energy applications. They are typically made from crystalline silicon and are known for their higher efficiency in converting sunlight into electricity. However, their rigidity means they are best suited for static applications, such as rooftops or solar farms.
Pros of Rigid Solar Panels for Wearables:
1. High Efficiency: Rigid panels generally have higher conversion efficiencies, meaning they can generate more power from the same amount of sunlight as flexible panels.
2. Proven Technology: As the most common type of solar panel, they have a long track record of reliability and performance.
Cons of Rigid Solar Panels for Wearables:
1. Lack of Flexibility: The rigidity of these panels makes them unsuitable for most wearable applications where adaptability and comfort are essential.
2. Increased Bulk: Rigid panels tend to be heavier, which can impede user comfort and practicality when applied to wearables.
Practical Considerations for Wearables
When evaluating which type of solar panel works better for wearables, several factors need to be considered:
1. Use Case: The specific application of the wearable device will significantly influence the choice between flexible and rigid panels. For instance, applications that demand high power output, even at the expense of comfort, might still consider rigid solutions.
2. Design Aesthetics: Wearables are often as much about fashion as function. Flexible panels offer an advantage in integrating seamlessly into sleek designs without compromising the look.
3. Environmental Conditions: Considerations such as exposure to sunlight, temperature extremes, and physical stress must be factored into the decision. Flexible panels might be preferred in harsher conditions due to their robustness and adaptability.
Future Prospects and Innovations
The future of solar technology in wearables looks promising. Advances in material science and manufacturing techniques are expected to bridge the efficiency gap between flexible and rigid solar panels. Researchers are exploring hybrid solutions that combine the strengths of both types of panels, potentially offering high efficiency with the adaptability required for wearables.
Conclusion
Both flexible PV and rigid solar panels have their places in the realm of wearable technology. The choice between the two largely depends on the specific application, desired efficiency, cost considerations, and user comfort. As technology progresses, the lines between these options may blur, offering even more innovative solutions for energy-harvesting wearables. For now, flexible PV panels seem to hold the most promise for integrating solar power into wearable devices, thanks to their adaptability, design versatility, and growing potential in efficiency improvements.
As solar technology races ahead—from perovskite cells to tandem architectures, from anti-reflective coatings to transparent electrodes—staying on top of fast-moving innovation has become a strategic imperative.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚡ Ready to accelerate your solar innovation journey? Try Patsnap Eureka today and let AI help you harness the full power of the sun—and your IP strategy.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com