Friction Loss in Planetary vs Spur Gear Arrangements
JUL 2, 2025 |
Gears are fundamental components in many mechanical systems, providing the necessary torque and speed adjustments to meet diverse operational requirements. Among the various types of gears, planetary and spur gear arrangements are popular due to their unique characteristics and applications. While both types serve essential functions, they exhibit different friction loss behaviors, which can significantly impact efficiency and performance.
Basics of Spur Gears
Spur gears are the simplest type of gear, featuring straight teeth arranged parallel to the gear's axis. They are known for their efficiency and ease of manufacture, making them a popular choice in mechanical applications. Spur gears are used when noise control is less of a concern because their design tends to produce more noise compared to other gear types. However, their straightforward design also contributes to lower friction losses, since the linear contact between gear teeth minimizes resistance during operation.
Introduction to Planetary Gears
Planetary gear systems, also known as epicyclic gears, are more complex and consist of three main components: a central sun gear, planet gears that rotate around the sun gear, and an outer ring gear. This arrangement allows for multiple gear ratios and the ability to handle higher torque in a compact design, offering advantages in applications where space and weight are critical. However, the complexity of planetary gears can result in higher friction losses due to more points of contact and relative motion between the components.
Friction Loss in Spur Gears
In spur gear arrangements, friction loss is primarily influenced by the meshing of teeth and the quality of lubrication. Since spur gears have teeth that mesh in a linear fashion, the contact area is consistent, allowing for predictable friction behavior. The friction losses in spur gears are generally lower compared to planetary gears, provided that there is adequate lubrication. The simplicity of the design allows for straightforward maintenance, further reducing potential friction-related issues over time.
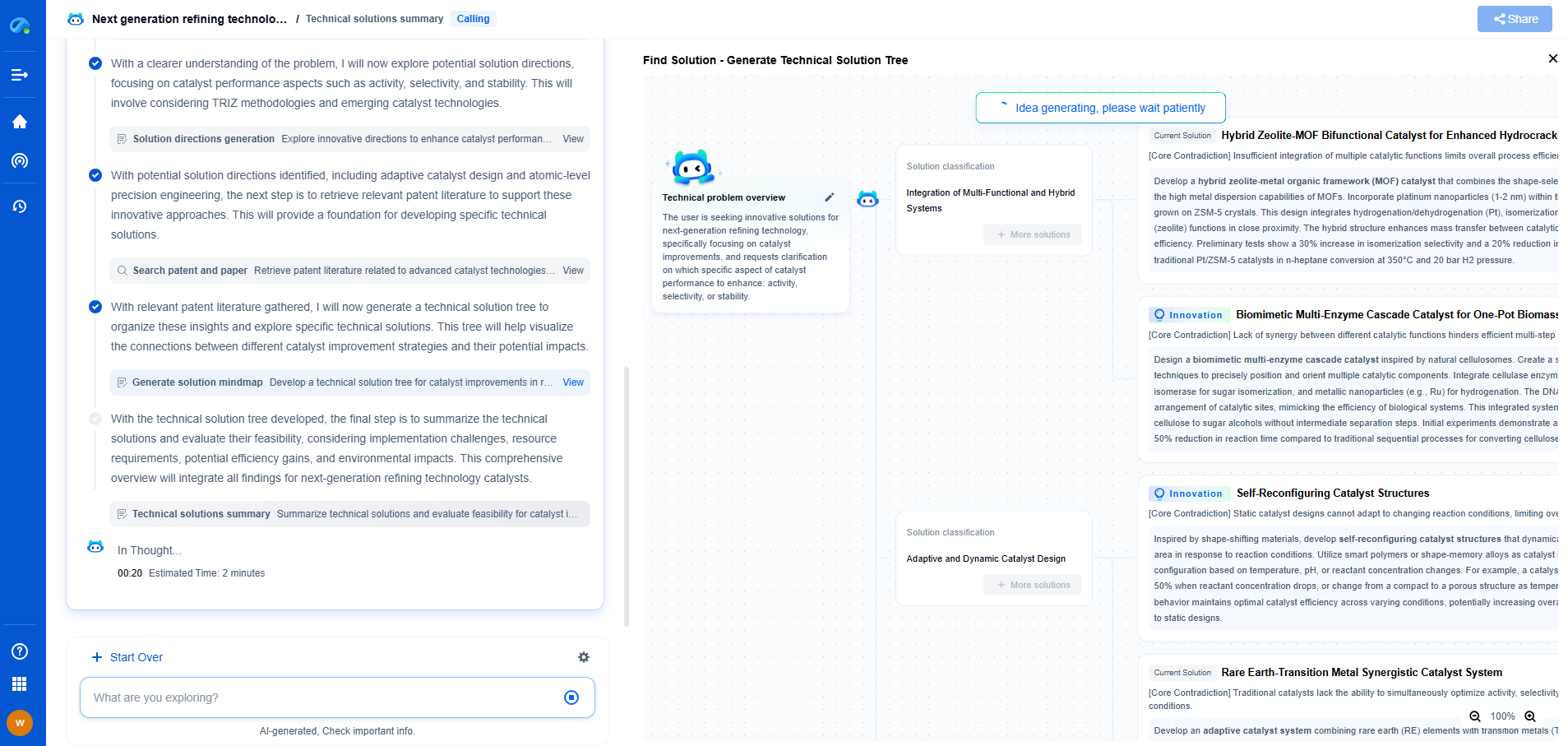
Friction Loss in Planetary Gears
Planetary gear systems, with their multiple points of contact and relative movements between the sun, planet, and ring gears, present a more complex scenario for friction loss. The increased number of moving parts leads to higher friction levels, which can affect efficiency. The interactions between gears in a planetary system mean that careful attention must be paid to lubrication and material selection to mitigate friction losses. Despite these potential issues, the advantages of high torque capacity and compactness often outweigh the drawbacks of increased friction loss in planetary gear systems.
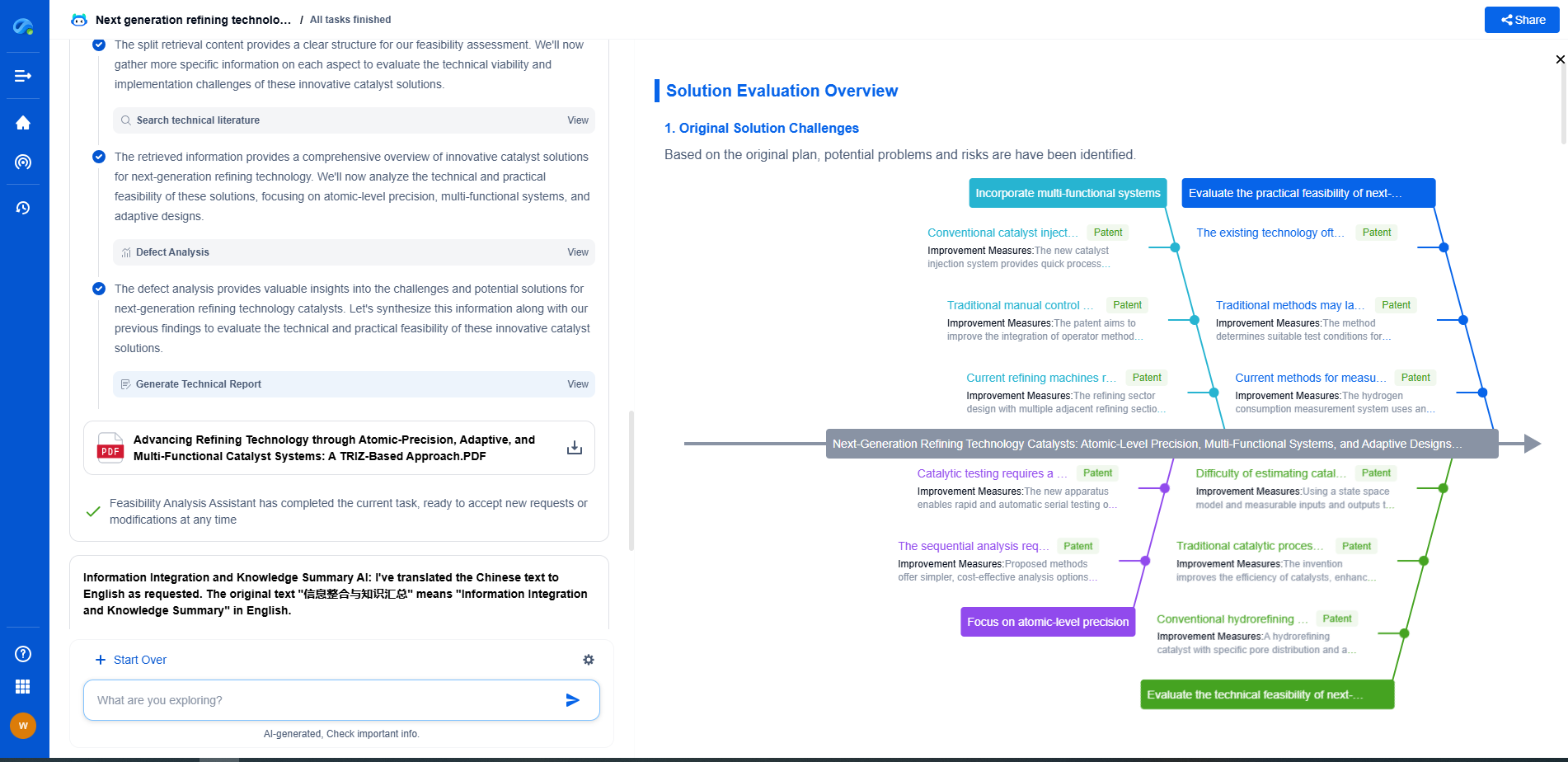
Comparative Analysis
When comparing friction loss in planetary versus spur gear arrangements, it is clear that spur gears generally exhibit lower friction due to their simpler design and fewer points of contact. However, planetary gears offer benefits in terms of torque handling and size efficiency that spur gears cannot match. The choice between these two gear types often depends on the specific application requirements, such as the need for compactness, torque capacity, and operational efficiency.
Practical Considerations
In practical applications, the decision to use planetary or spur gears should take into account the trade-offs between friction loss and the mechanical advantages each type offers. For high-efficiency systems where minimizing friction loss is paramount, spur gears may be the preferred choice. On the other hand, applications requiring high torque in a limited space might benefit from the compact design of planetary gears, despite the higher friction losses. Careful design, material selection, and maintenance practices can help optimize the performance of both gear types.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both planetary and spur gear arrangements have their unique advantages and challenges, particularly concerning friction loss. Understanding the differences in friction behavior between these gear types can guide the selection process for engineers and designers, ensuring that the chosen gear system aligns with the performance and efficiency goals of the application. By balancing the benefits and potential drawbacks of each gear type, optimal mechanical solutions can be achieved for a wide range of engineering challenges.
Boost Innovation in Gears & Transmissions with Patsnap Eureka
Whether you're designing a next-gen planetary gearbox or optimizing gear tooth profiles for noise reduction, keeping up with the fast-evolving landscape of mechanical transmissions requires more than just experience—it takes insight, speed, and smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Whether you're streamlining a manual transmission system or exploring electromechanical actuation, Patsnap Eureka helps your team move from concept to novelty faster than ever.
👉 Experience Eureka in action—request a personalized demo today and see how AI can revolutionize your gear innovation workflows.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com