Gas Turbine Compressor vs Electric Compressor: Pros and Cons
JUN 20, 2025 |
Compressors play a pivotal role in various industrial applications, from powering machinery to compressing gas for transportation. Two prominent types of compressors often compared are gas turbine compressors and electric compressors. Each has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different scenarios. This blog will delve into the pros and cons of each type, helping you make an informed decision based on your specific needs.
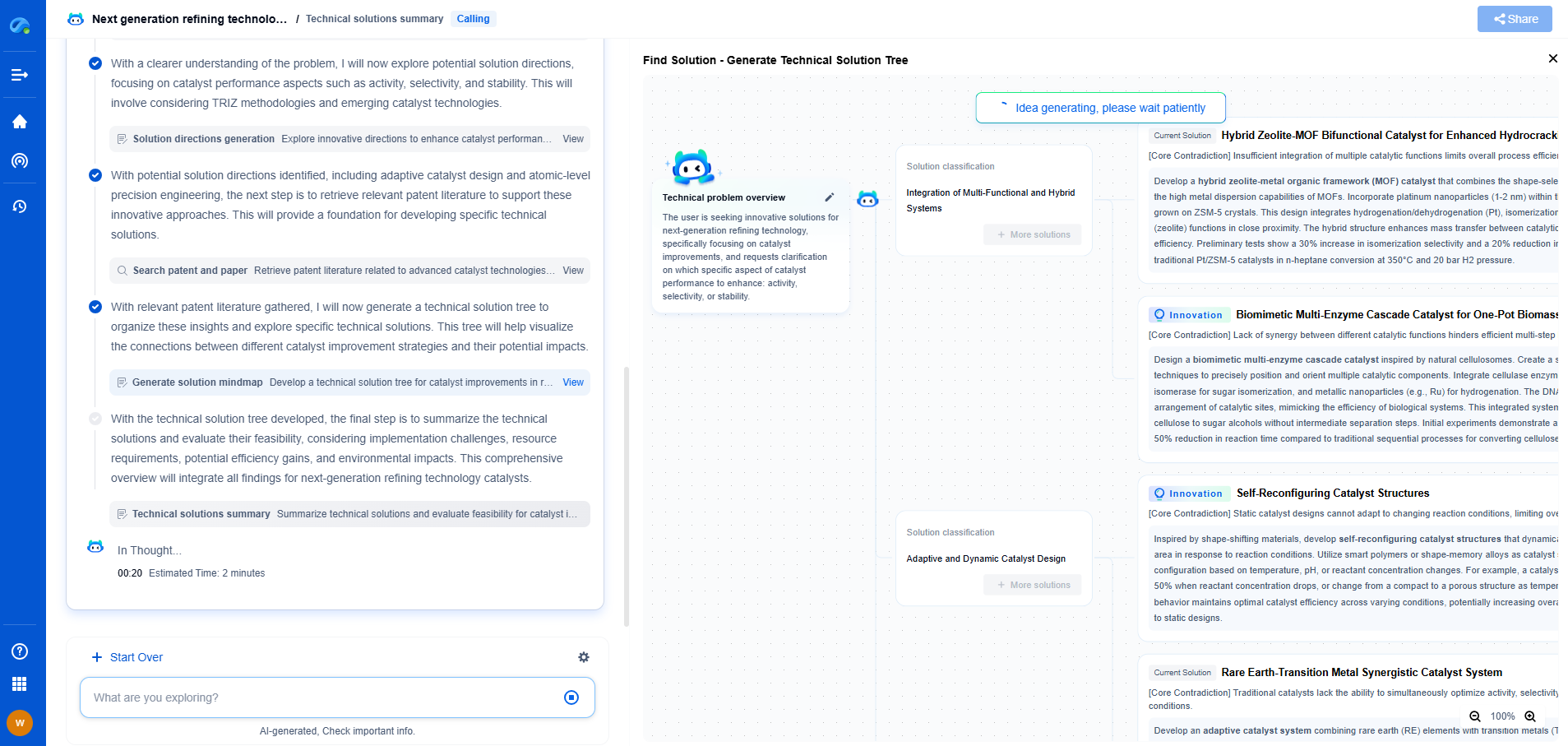
Gas Turbine Compressors: Pros and Cons
Pros of Gas Turbine Compressors
1. High Power Output: Gas turbine compressors are known for their ability to deliver high power output. They are ideal for large-scale operations where substantial energy is required.
2. Fuel Flexibility: These compressors can operate on a variety of fuels, including natural gas and diesel. This flexibility can be beneficial in regions where certain fuels are more accessible or cost-effective.
3. Quick Start-Up: Gas turbines can achieve full load rapidly, making them suitable for applications that demand immediate power.
4. Robust Performance: They are capable of operating under harsh environmental conditions, such as high temperatures and altitudes, without significant performance degradation.
Cons of Gas Turbine Compressors
1. High Initial Costs: The initial capital investment for gas turbine compressors is often higher than that of electric compressors, which can be a barrier for some businesses.
2. Maintenance Intensive: They require regular and specialized maintenance, which can lead to increased operational costs over time.
3. Lower Efficiency at Part Load: Gas turbines tend to be less efficient when operating at partial load, potentially leading to higher fuel consumption and operational costs.
4. Environmental Concerns: Gas turbines can produce significant emissions, contributing to environmental concerns unless equipped with advanced emission control technologies.
Electric Compressors: Pros and Cons
Pros of Electric Compressors
1. Energy Efficiency: Electric compressors are generally more energy-efficient, especially at part load, which can result in significant cost savings over time.
2. Lower Emissions: By relying on electricity, these compressors contribute to reduced emissions, particularly if the electricity is sourced from renewable energy.
3. Reduced Maintenance: Electric compressors typically require less maintenance compared to their gas turbine counterparts, translating to lower long-term operational costs.
4. Simpler Installation: Often easier and quicker to install, electric compressors can be a more convenient option for many facilities.
Cons of Electric Compressors
1. Dependency on Electrical Grid: Electric compressors are entirely dependent on the availability and reliability of the electrical grid, which can be a limitation in areas with unstable power supply.
2. Power Limitations: While they are suitable for a wide range of applications, electric compressors may not be able to meet the power demands of some large-scale industrial operations.
3. Initial Setup Constraints: In some cases, the existing electrical infrastructure may need significant upgrades to support high-capacity electric compressors, potentially increasing initial costs.
4. Limited Fuel Flexibility: Unlike gas turbines, electric compressors do not offer the same level of fuel flexibility, which might be a disadvantage in certain strategic contexts.
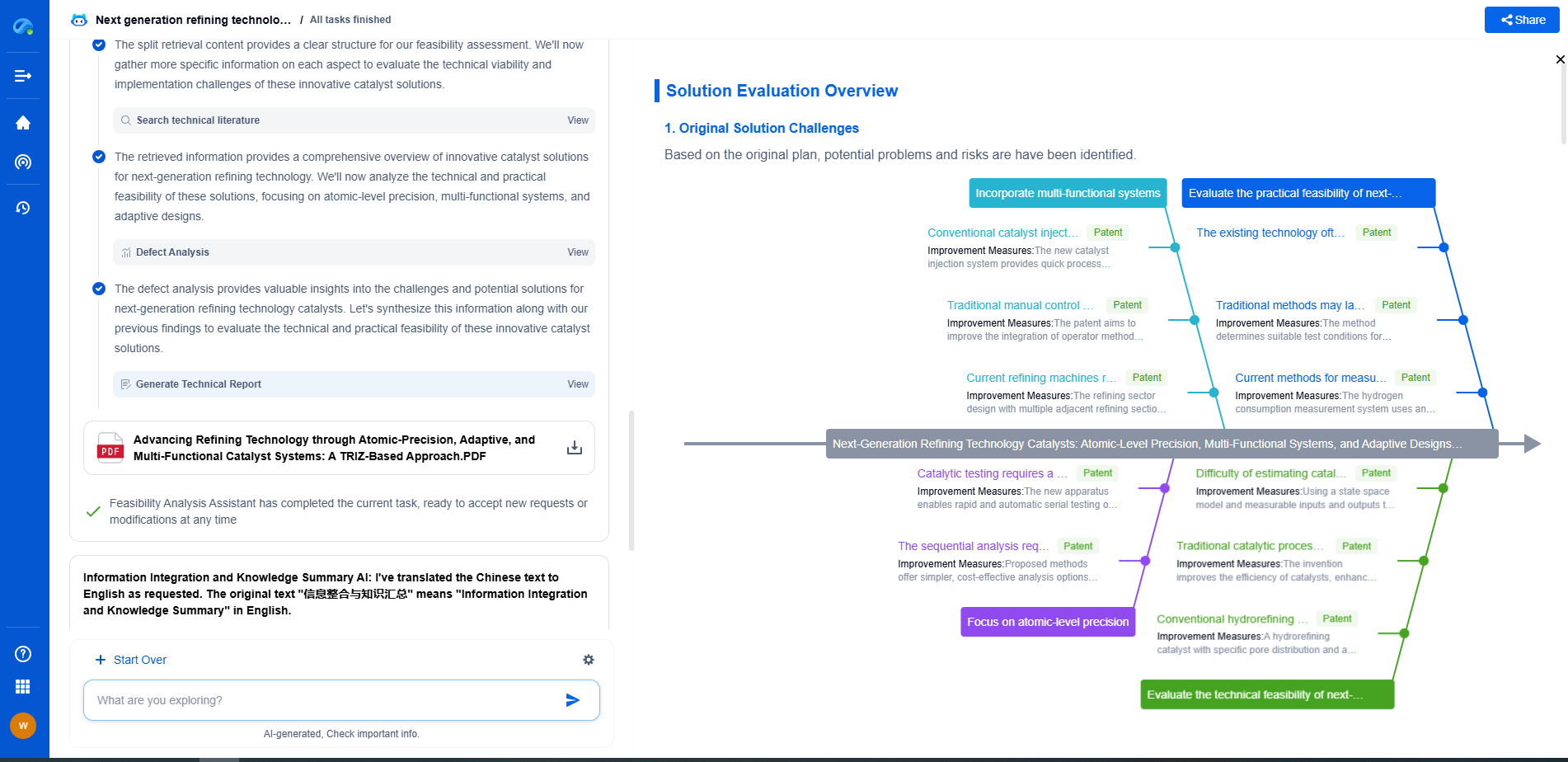
Conclusion
Choosing between a gas turbine compressor and an electric compressor depends on various factors, including operational scale, environmental considerations, and budget constraints. Gas turbine compressors are well-suited for large-scale, demanding applications where fuel flexibility and robust performance are crucial, despite their higher initial and maintenance costs. On the other hand, electric compressors offer energy efficiency, lower emissions, and reduced maintenance, making them ideal for environmentally conscious operations with stable electricity supply.
Ultimately, the decision should align with your specific operational needs, long-term goals, and environmental priorities. By understanding the pros and cons of each type, you can make a more informed choice that best suits your industrial requirements.
Transform the Way You Innovate in Pipeline Technology—with AI-Powered Intelligence
From corrosion-resistant materials to smart monitoring systems and advanced flow control mechanisms, the pipeline industry is undergoing rapid technological transformation. Yet keeping up with evolving engineering solutions, regulatory landscapes, and competitive patents can be a major bottleneck for R&D and IP teams.
Patsnap Eureka is your AI-powered research companion—built specifically for professionals in high-tech and infrastructure domains like pipeline technology. Whether you're designing high-pressure transport systems, assessing trenchless installation innovations, or safeguarding proprietary flow assurance solutions, Eureka provides real-time insights into global patent trends, emerging technologies, and R&D intelligence—all in one intuitive interface.
Empower your team to innovate faster, reduce technical blind spots, and stay ahead of industry shifts. Discover Patsnap Eureka today and bring clarity and confidence to your pipeline technology decisions.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com