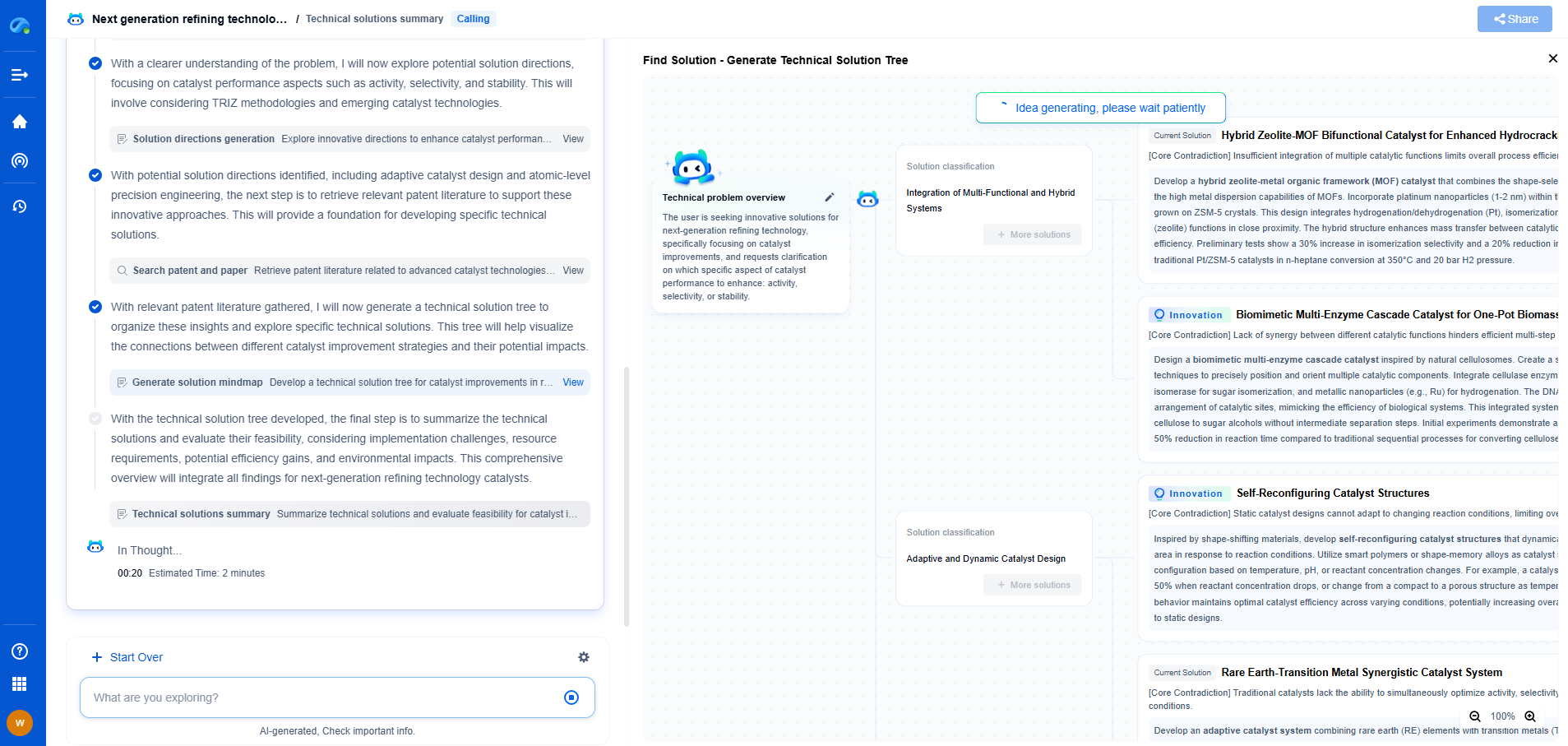
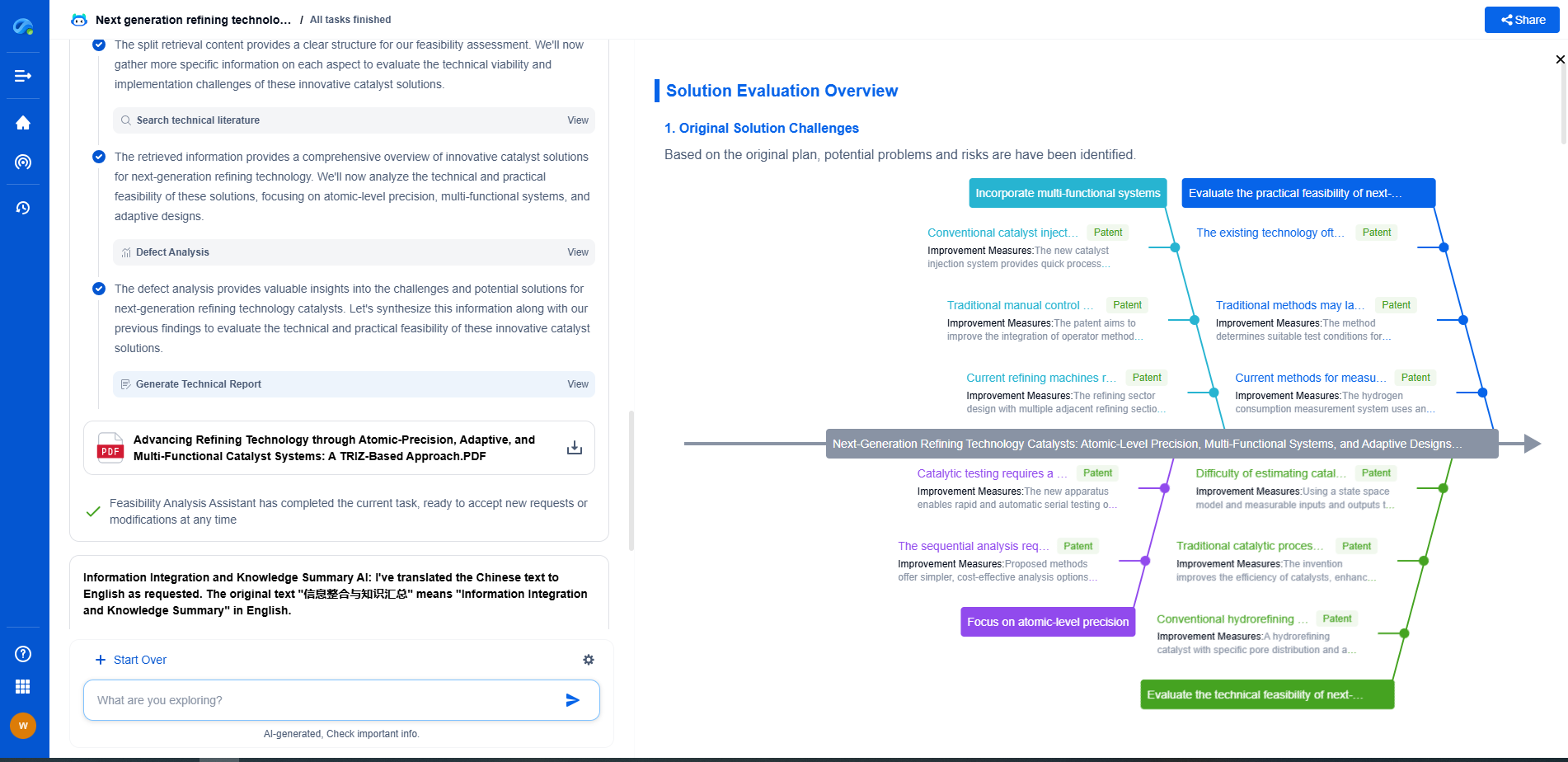
Gauge Pressure vs. Absolute Pressure Sensors: Which One Should You Use?
JUL 14, 2025 |
In the world of pressure measurement, choosing the right sensor can be crucial for the success of your application. Two common types of pressure sensors are gauge pressure sensors and absolute pressure sensors. Each has distinct characteristics and is suited for different applications. Understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision about which one to use in your specific scenario.
What is Gauge Pressure?
Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to atmospheric pressure. Gauge pressure sensors measure the difference between the pressure in a system and the ambient atmospheric pressure. These sensors essentially subtract the atmospheric pressure from the measured pressure, providing a "zero" point that is the same as the surrounding atmosphere.
Gauge pressure sensors are typically used in applications where precise atmospheric pressure compensation is necessary. For example, they are commonly used in tire pressure gauges and water treatment facilities, where the pressure readings need to account for atmospheric conditions to ensure accuracy.
The Role of Absolute Pressure
On the other hand, absolute pressure is the total pressure measured against a perfect vacuum. Absolute pressure sensors take atmospheric pressure into account as part of the total pressure reading. This means that the pressure measured is inclusive of the atmospheric pressure, providing a true representation of the actual pressure inside a system.
Absolute pressure sensors are essential in applications where pressure readings need to be consistent regardless of changes in atmospheric pressure. These sensors are often used in weather stations, altimeters, and in processes that occur in sealed environments, such as certain chemical reactions or vacuum systems.
Key Differences Between Gauge and Absolute Pressure Sensors
1. Reference Point: The primary difference between these two types of pressure sensors is their reference point. Gauge pressure sensors measure relative to atmospheric pressure, whereas absolute pressure sensors measure relative to a vacuum.
2. Application Environment: Gauge pressure sensors are suitable for applications where atmospheric pressure changes need to be compensated for, while absolute pressure sensors are ideal for environments where the pressure measurement must remain constant regardless of atmospheric changes.
3. Accuracy: Absolute pressure sensors tend to be more suitable for applications requiring high precision and consistency, as they are unaffected by fluctuations in atmospheric pressure.
Which One Should You Use?
Choosing between gauge and absolute pressure sensors largely depends on the specific requirements of your application. Here are some considerations to help you decide:
- Consider Gauge Pressure Sensors if:
- You need measurements that are relative to atmospheric pressure.
- The application involves open systems or environments where atmospheric pressure changes are relevant.
- Cost is a significant factor, and the additional calibration for absolute pressure is unnecessary.
- Consider Absolute Pressure Sensors if:
- You require consistent readings regardless of atmospheric pressure changes.
- The application involves sealed systems or environments with constant pressures.
- High accuracy and precision are critical for the application.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the differences between gauge and absolute pressure sensors is essential for selecting the appropriate sensor for your needs. Gauge pressure sensors are ideal for applications that need to account for atmospheric pressure variations, while absolute pressure sensors provide consistent readings in environments where atmospheric changes are a concern. By evaluating the specific requirements of your application, you can make an informed decision that ensures optimal performance and accuracy in your pressure measurement endeavors.
From 5G NR to SDN and quantum-safe encryption, the digital communication landscape is evolving faster than ever. For R&D teams and IP professionals, tracking protocol shifts, understanding standards like 3GPP and IEEE 802, and monitoring the global patent race are now mission-critical.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
📡 Experience Patsnap Eureka today and unlock next-gen insights into digital communication infrastructure, before your competitors do.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com