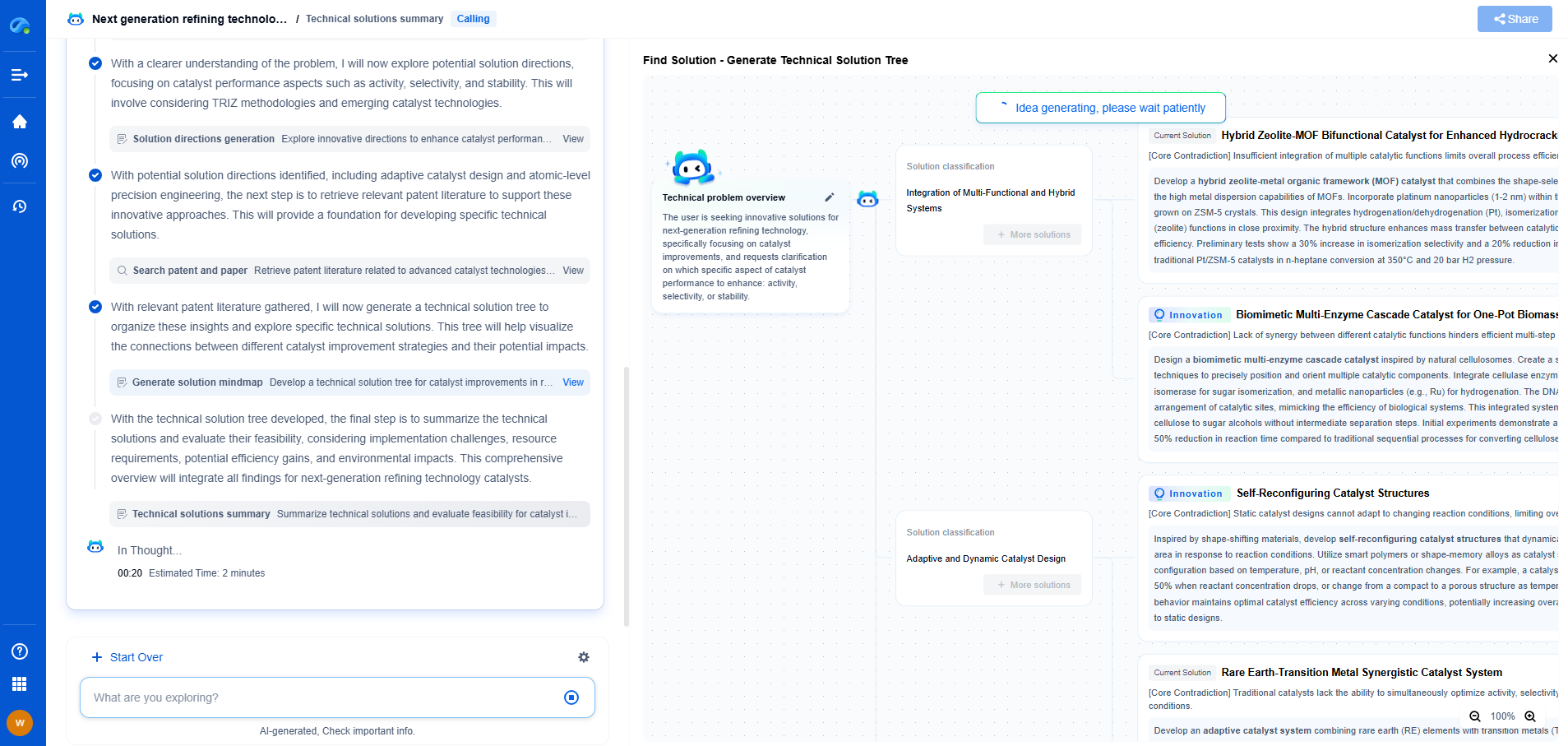
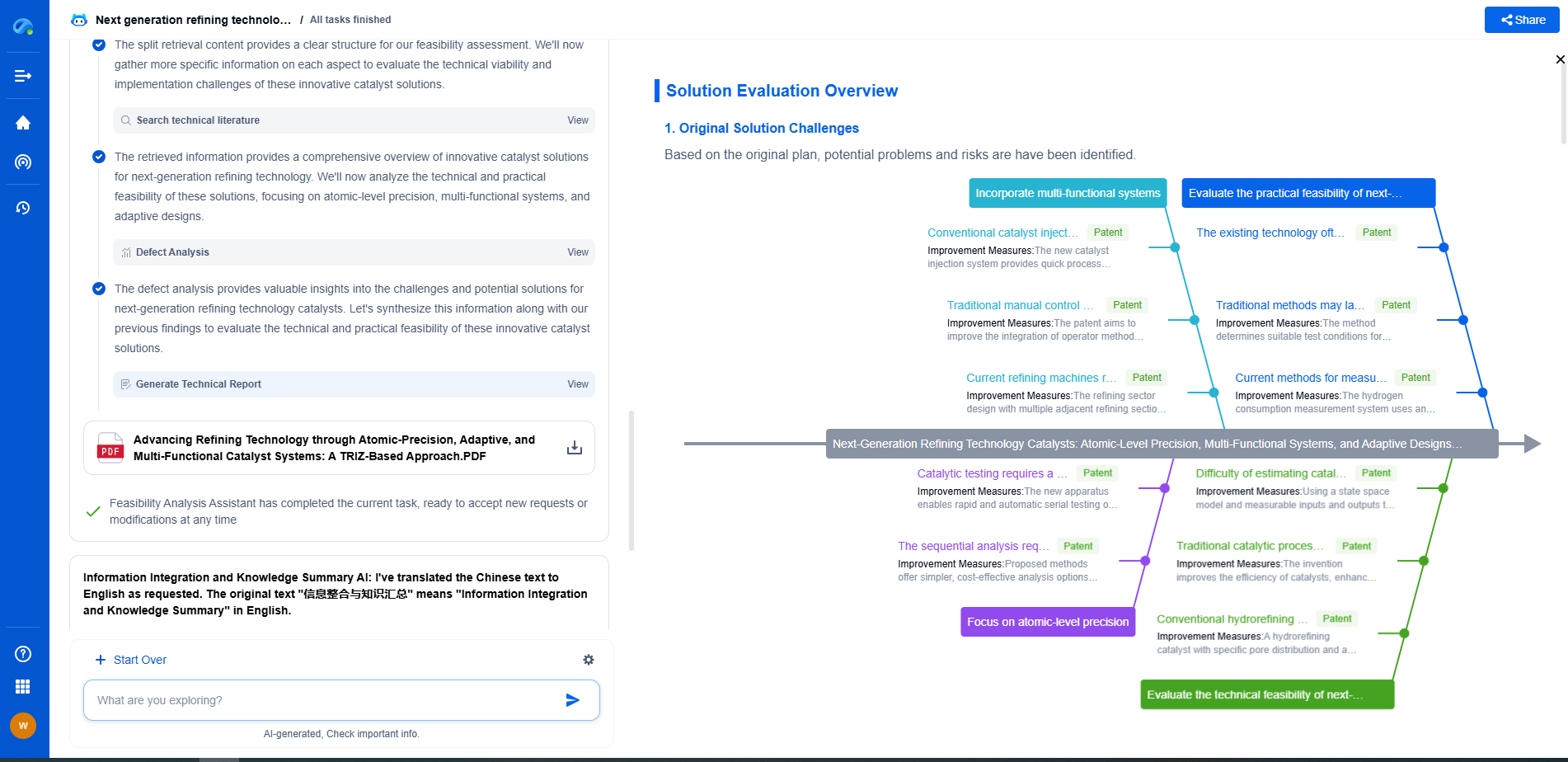
Geothermal vs oil & gas drilling: how different are the technologies?
JUN 20, 2025 |
Geothermal energy and oil & gas drilling are both earth-based energy extraction processes, yet they serve distinct purposes and utilize different technologies. Geothermal energy harnesses heat from the Earth's core to generate electricity and heating, while oil & gas drilling accesses fossil fuels to provide energy for various applications. This article explores the technological differences between these two processes, highlighting their unique characteristics and similarities.
The Core Processes
Geothermal Drilling
Geothermal drilling involves accessing the Earth's heat stored beneath its surface. The process begins with identifying geothermal reservoirs, which are areas with considerable heat potential. This is done through geological surveys and heat flow measurements. Once a suitable location is found, drilling commences to reach the hot water or steam reservoirs. Wells are typically drilled to depths ranging from a few hundred meters to several kilometers, depending on the geothermal gradient.
The drilled wells allow the hot water or steam to be extracted and directed to the surface. Here, the thermal energy is converted into electrical power through various types of turbines. Some systems, known as binary cycle plants, use heat exchangers to transfer the heat to a secondary fluid with a lower boiling point, enhancing efficiency.
Oil & Gas Drilling
Oil & gas drilling aims to extract hydrocarbons trapped in sedimentary rock formations. The process begins with exploration, involving seismic surveys to map underground structures and pinpoint potential reserves. Once a reservoir is identified, a drilling rig is set up to penetrate the Earth's crust.
Drilling methods vary based on the type of reservoir, but typically include rotary drilling, where a rotating drill bit is used to cut through the rock layers. After reaching the targeted depth, casing is installed to maintain well integrity and prevent contamination. Hydraulic fracturing or “fracking” may be used to increase permeability and facilitate extraction in unconventional reservoirs.
Once the hydrocarbons are accessed, they are brought to the surface, processed, and transported for further refinement and use in various industries.
Technological Differences
Equipment and Tools
While both geothermal and oil & gas drilling involve penetrating the Earth's crust, the equipment used can differ significantly. Geothermal drilling often requires specialized equipment capable of handling higher temperatures and high-pressure steam. Tools like mud motors and air drilling systems are common in geothermal projects to manage extreme heat conditions.
In contrast, oil & gas drilling employs heavy-duty rigs capable of enduring the harsher conditions associated with hydrocarbon reservoirs. These may include high-pressure equipment for hydraulic fracturing and advanced drilling technologies like horizontal drilling to access unconventional oil and gas reserves.
Environmental Impact
Geothermal energy is widely regarded as having a lower environmental impact compared to oil & gas. Geothermal plants produce minimal greenhouse gas emissions, as they rely on a renewable heat source. Additionally, they typically require less land area and have a smaller footprint.
On the other hand, oil & gas drilling can have significant environmental implications, including air and water pollution. The extraction process can lead to habitat disruption, and the potential for spills poses a risk to ecosystems.
Cost and Efficiency
The cost of geothermal drilling and oil & gas extraction varies based on location, technology, and market conditions. Geothermal projects often have higher initial costs due to the need for specialized equipment and exploratory surveys. However, the longevity and sustainability of geothermal energy can result in lower operational costs over time.
Oil & gas drilling can be more economically viable in terms of initial investment, particularly when tapping into conventional reservoirs. Yet, fluctuating market prices for oil and gas can impact long-term financial stability, alongside the environmental costs associated with fossil fuel extraction.
Conclusion
Despite the shared goal of extracting energy from the Earth, geothermal and oil & gas drilling differ significantly in their technologies, equipment, and environmental impact. Geothermal drilling focuses on sustainable energy production with minimal ecological footprint, whereas oil & gas drilling targets fossil fuel extraction with varying environmental consequences. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions regarding energy development and sustainability. As technological advancements continue to evolve, both industries must adapt to meet growing energy demands while prioritizing environmental stewardship.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com