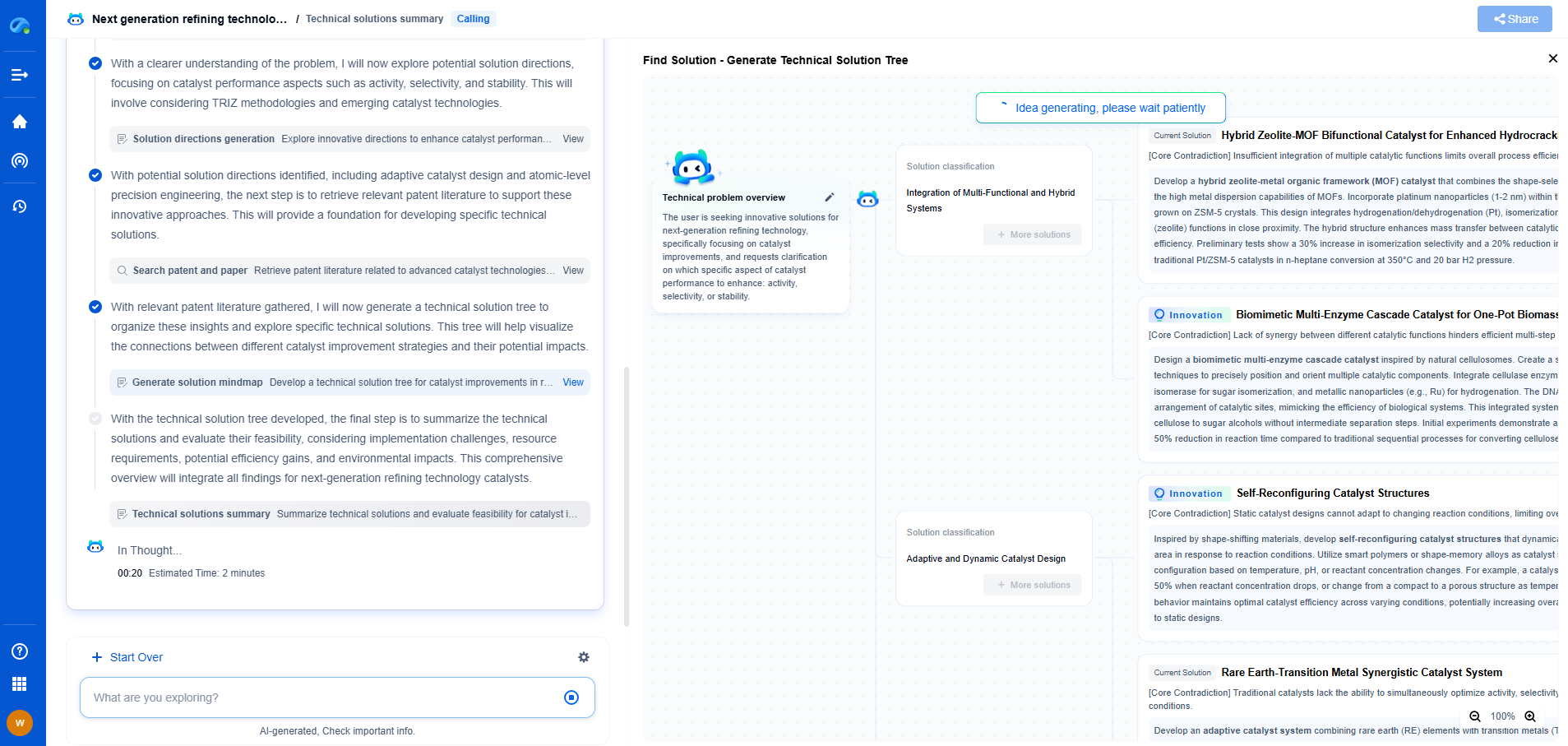
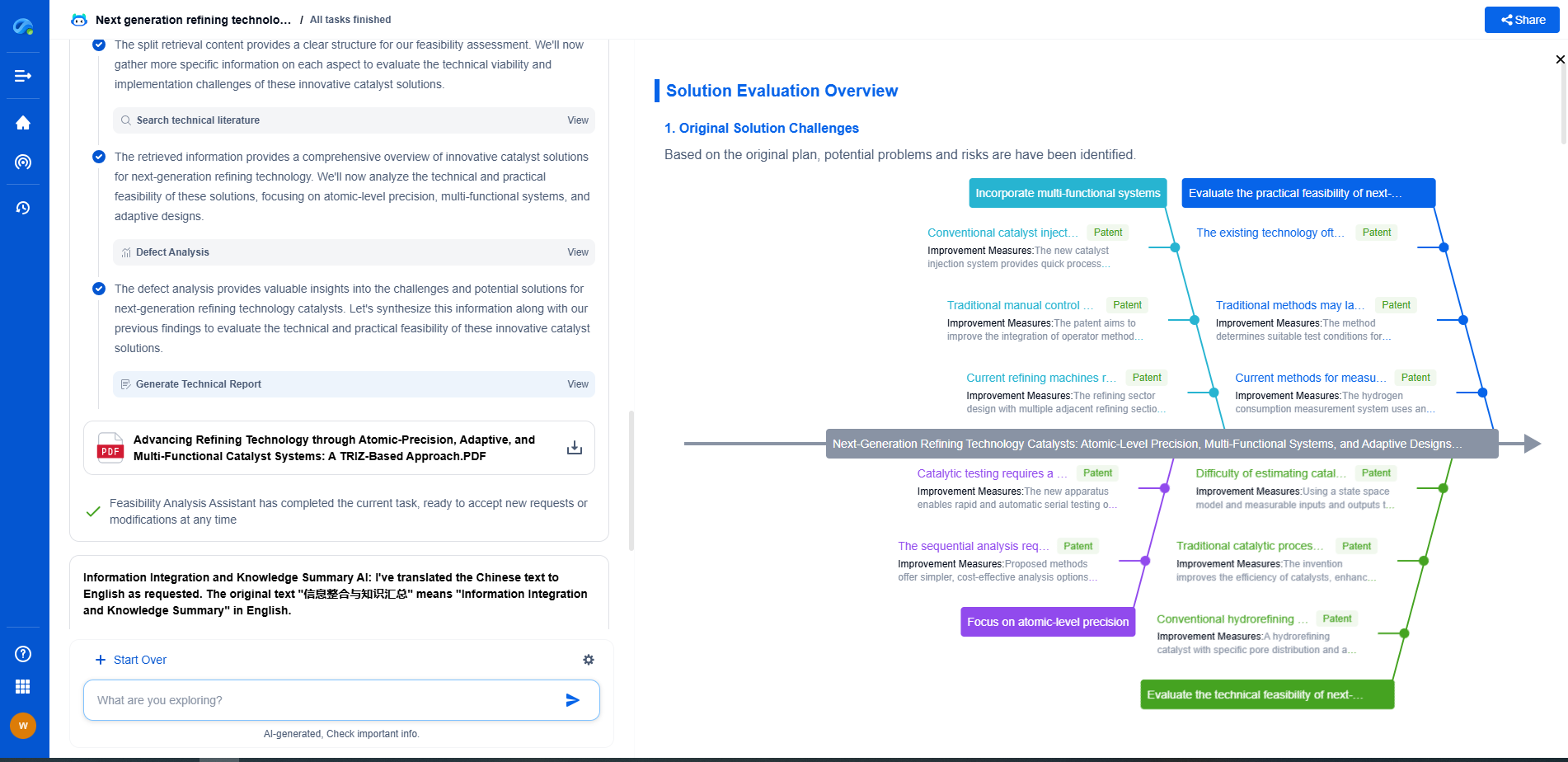
HART Protocol Explained: How Analog and Digital Coexist on 4–20 mA
JUL 14, 2025 |
The HART (Highway Addressable Remote Transducer) protocol is a popular communication protocol in the field of industrial automation and process control. It is particularly known for its ability to allow both analog and digital communication over the same wire, specifically utilizing the 4–20 mA current loop. This unique advantage makes HART a versatile and efficient choice for many applications, providing both real-time data and diagnostic capabilities.
The 4–20 mA Current Loop: A Brief Overview
Before delving into the coexistence of analog and digital signals, it's important to understand the 4–20 mA current loop, which has been a staple in industrial processes for decades. The loop is highly reliable for transmitting analog signals, particularly because it is less susceptible to electrical noise and can be transmitted over long distances. In the 4–20 mA loop, the current level represents a measurement variable such as temperature, pressure, or flow rate. The range of 4 to 20 mA is chosen because it allows for easy detection of open-circuit conditions (anything below 4 mA is considered an error).
Introducing Digital Communication to the Analog World
The need for more data in complex industrial systems led to the introduction of digital communication. However, completely replacing the established analog system was neither practical nor cost-effective. This is where HART protocol comes into play. By superimposing digital signals on the existing 4–20 mA loop, HART provides a seamless way to add digital communication without disrupting the existing infrastructure.
How HART Protocol Works
HART protocol employs Frequency Shift Keying (FSK) to encode digital communication over the existing analog current loop. Specifically, it uses two frequencies: 1,200 Hz to represent binary 1 and 2,200 Hz to represent binary 0. These frequencies are chosen such that they do not interfere with the analog signal, ensuring that the integrity of the analog data is maintained.
The digital communication layer offers significant advantages. It allows for bidirectional communication, meaning that the control system can not only receive data from field instruments but also send commands and configuration settings back to these devices. This bidirectional capability supports advanced functionalities such as device diagnostics, configuration, and even firmware updates—all while maintaining the continuous real-time data flow provided by the analog signal.
Advantages of HART Protocol
The hybrid nature of HART brings several benefits to industrial systems:
1. **Cost-Effective Integration**: Because it leverages existing wiring infrastructure, implementing HART is more cost-effective than installing a separate digital communication system.
2. **Enhanced Data Availability**: The digital layer provides additional information that is not possible with analog signals alone, such as device health, diagnostics, and identification.
3. **Improved Reliability**: HART's ability to communicate even in noisy environments ensures that both analog and digital data are transmitted reliably.
4. **Flexibility and Scalability**: HART devices are compatible with both legacy systems and modern digital control systems, offering a scalable solution for evolving industrial needs.
5. **Global Standard**: Recognized as an international standard, HART is supported by numerous manufacturers, ensuring broad compatibility and support.
Applications of HART Protocol
Given its robust features, HART protocol is used in a wide range of applications. These include:
- **Process Control**: Used extensively in industries such as oil and gas, chemicals, and manufacturing, where precise process control and monitoring are critical.
- **Asset Management**: HART-based systems can provide valuable diagnostics that help in asset management and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and improving efficiency.
- **Remote Monitoring**: Ideal for remote monitoring applications where long-distance data transmission is required without sacrificing data integrity.
Future of HART Protocol
As industrial environments become increasingly digitized, the value of HART protocol continues to grow. With the advent of Industry 4.0 and the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), HART is poised to play a key role in integrating analog devices into digital ecosystems. Its ability to provide real-time data alongside complex diagnostics makes it a vital tool in the transformation towards smarter, more connected industrial systems.
In conclusion, the HART protocol exemplifies how analog and digital technologies can coexist and complement each other, providing a powerful solution for modern industrial communication needs. Its hybrid approach ensures that the reliability of analog systems is maintained while unlocking the potential of digital data for enhanced process control and operational efficiency.
From 5G NR to SDN and quantum-safe encryption, the digital communication landscape is evolving faster than ever. For R&D teams and IP professionals, tracking protocol shifts, understanding standards like 3GPP and IEEE 802, and monitoring the global patent race are now mission-critical.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
📡 Experience Patsnap Eureka today and unlock next-gen insights into digital communication infrastructure, before your competitors do.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com