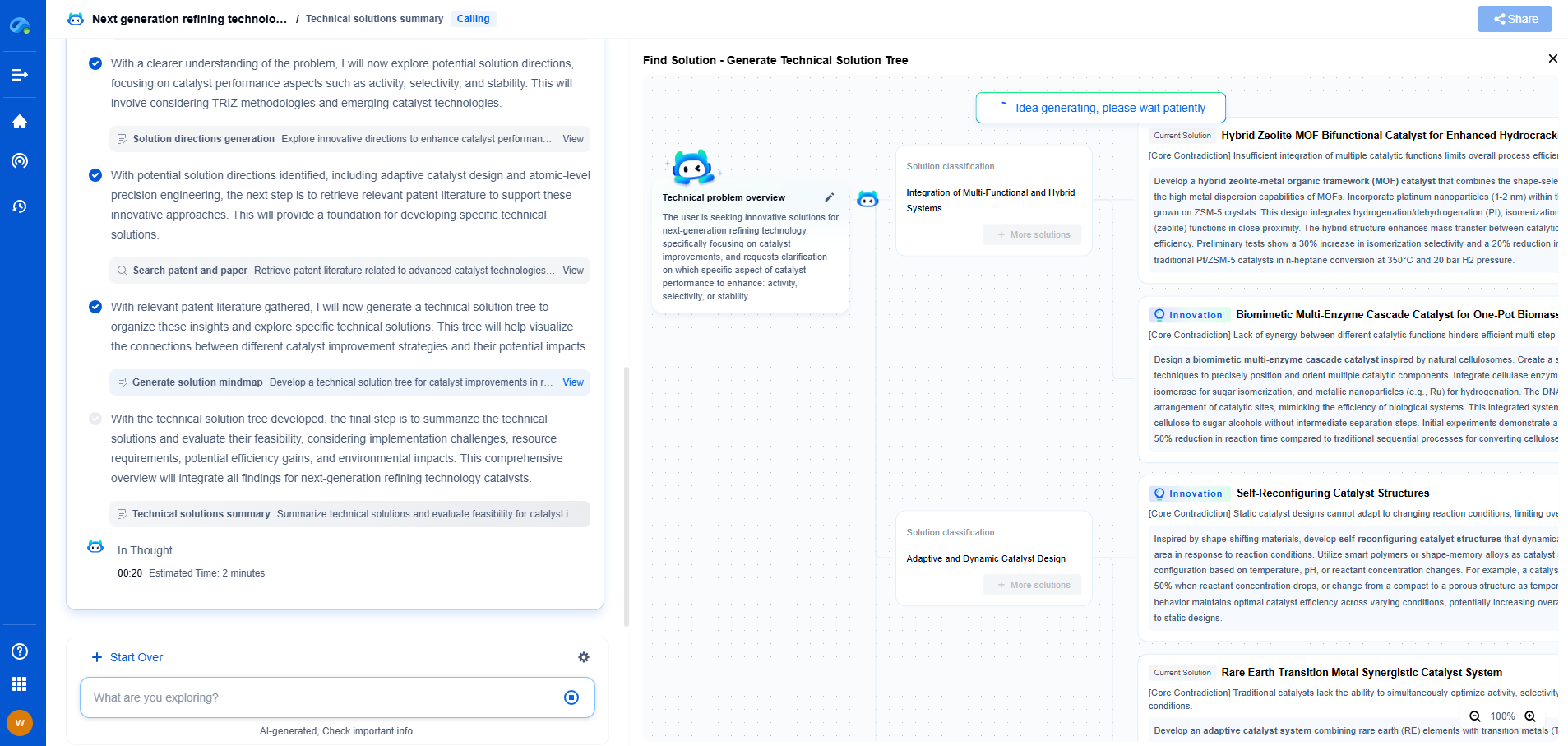
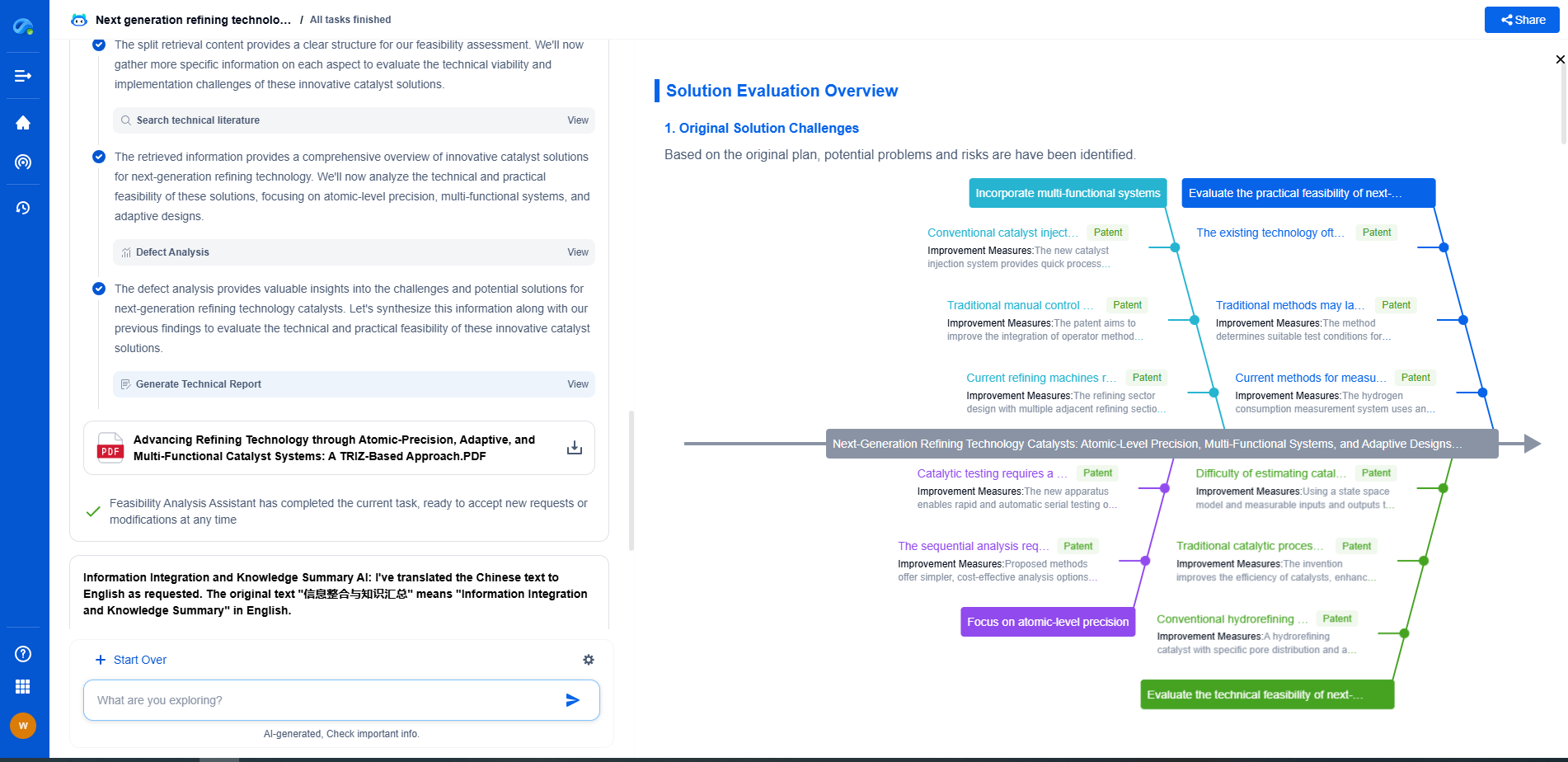
High ESR vs. Low ESR Capacitors: Use Cases and Trade-offs
JUL 9, 2025 |
Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) is an intrinsic characteristic of capacitors that significantly influences their performance in electronic circuits. ESR refers to the internal resistance that appears in series with the ideal capacitor, affecting how efficiently the capacitor can store and release energy. High ESR and low ESR capacitors each have distinctive properties that make them suitable for specific applications, and understanding these differences is essential for making informed decisions in electronic design.
Characteristics of High ESR Capacitors
High ESR capacitors exhibit greater energy loss due to their higher internal resistance. This results in reduced efficiency when it comes to rapid charge and discharge cycles. These capacitors often generate more heat and can lead to potential thermal management issues if not properly addressed. Despite these limitations, high ESR capacitors are widely used in various applications due to their unique properties.
One of the primary advantages of high ESR capacitors is their cost-effectiveness. They are generally less expensive than their low ESR counterparts, making them an attractive option for budget-conscious projects. Additionally, high ESR capacitors can tolerate higher voltages, making them suitable for power supply applications where voltage spikes and surges are common.
Applications of High ESR Capacitors
High ESR capacitors are often found in power supply circuits where high voltage resistivity is more critical than rapid charging capabilities. They are also used in applications where energy efficiency is not the top priority, such as in simple analog devices or circuits where size and cost constraints are more pressing concerns. Moreover, their ability to withstand high temperatures due to the heat generated by their internal resistance makes them suitable for environments where thermal conditions are less than ideal.
Characteristics of Low ESR Capacitors
In contrast, low ESR capacitors are designed to minimize energy loss, making them highly efficient at rapid charge and discharge cycles. Their low internal resistance ensures that they can deliver and absorb energy quickly, which is crucial in applications requiring fast response times. This efficiency is particularly valuable in high-frequency applications where slow response can lead to performance issues.
Low ESR capacitors also generate less heat during operation, reducing the need for extensive cooling solutions and enhancing the overall reliability and longevity of the device. However, these capacitors tend to be more expensive than high ESR alternatives due to the advanced materials and manufacturing techniques required to achieve low resistance.
Applications of Low ESR Capacitors
Low ESR capacitors are ideal for applications requiring high efficiency and fast energy transfer, such as in switching power supplies, DC-DC converters, and high-performance audio equipment. They are also essential in digital circuits and computing devices where rapid response and minimal energy loss are critical for optimal performance. In these applications, the benefits of low ESR outweigh the higher costs, making them the preferred choice for demanding electronic designs.
Trade-offs and Considerations
When choosing between high ESR and low ESR capacitors, several factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and cost-efficiency. The specific requirements of the application, including voltage, frequency, and thermal conditions, dictate the appropriate type of capacitor. Designers must balance the need for efficiency against budget constraints, considering both the initial cost and the long-term operational benefits.
Additionally, the physical size and form factor of the capacitor may influence the decision. Low ESR capacitors, due to their advanced materials, might have a larger footprint than high ESR types, posing potential challenges in compact designs.
Conclusion
The choice between high ESR and low ESR capacitors ultimately depends on the specific needs of the application. High ESR capacitors offer cost savings and high voltage tolerance, making them suitable for less demanding environments. In contrast, low ESR capacitors deliver high efficiency and rapid energy transfer, ideal for high-performance and high-frequency applications. By understanding the characteristics, applications, and trade-offs of each type, designers can make informed choices that align with their project's requirements.
Looking to accelerate your capacitor innovation pipeline?
As capacitor technologies evolve—from miniaturized MLCCs for smartphones to grid-scale energy storage devices—so must the way your team accesses critical knowledge.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Try Patsnap Eureka now and discover a faster, smarter way to research and innovate in capacitor technology.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com