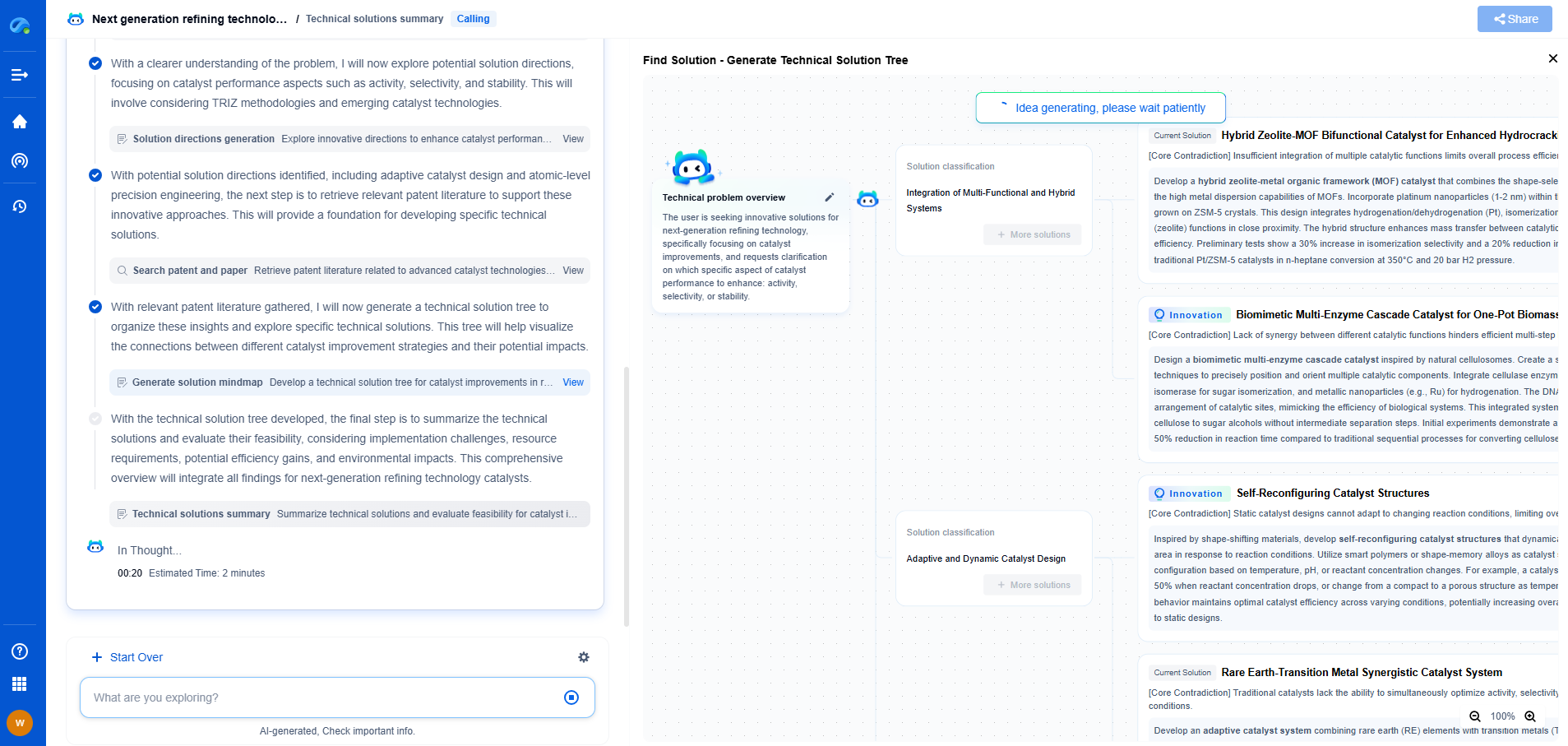
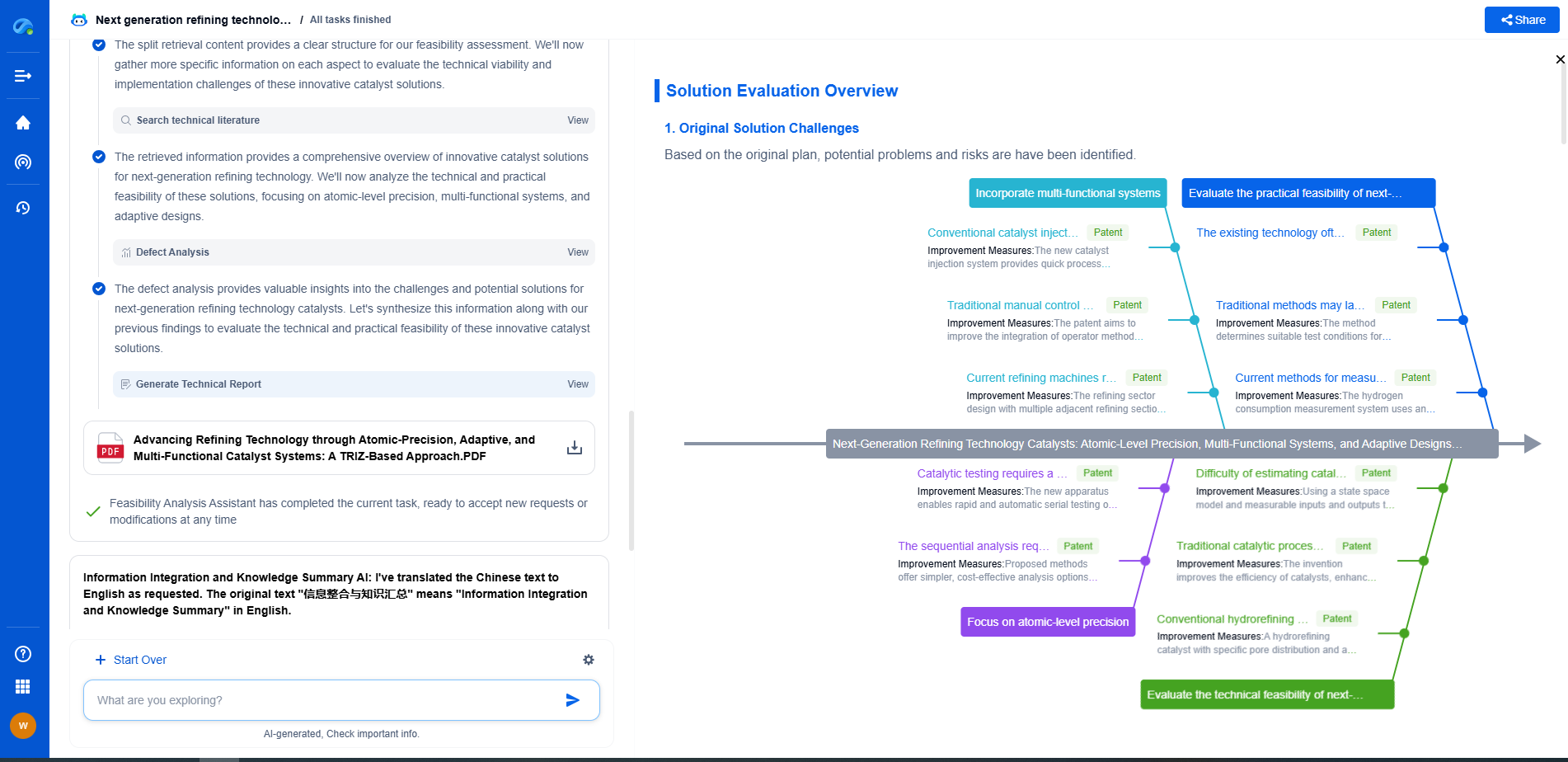
How a Single-Axis vs. Dual-Axis Solar Tracker Impacts Energy Yield
JUL 22, 2025 |
Solar energy continues to be one of the most sustainable and increasingly popular sources of renewable energy. As the demand for solar power systems grows, so does the need for maximizing their efficiency. One of the key factors in enhancing the energy yield of solar panels is the use of solar trackers. Specifically, the choice between single-axis and dual-axis solar trackers can significantly impact the energy output. This blog delves into how these two types of trackers work and their influence on energy yield.
Understanding Solar Trackers
Before diving into the specifics of single-axis and dual-axis trackers, it’s essential to understand what solar trackers are. Solar trackers are devices that automatically orient solar panels toward the sun to maximize their exposure to sunlight throughout the day. By maintaining the optimal angle, solar trackers enhance the performance and efficiency of solar power systems.
Single-Axis Solar Trackers
Single-axis solar trackers rotate on one axis, typically moving horizontally from east to west. These trackers follow the sun’s path across the sky during the day, ensuring that solar panels capture sunlight more effectively than fixed installations. Single-axis trackers are relatively simple and cost-effective compared to dual-axis systems.
Energy Yield Impact of Single-Axis Solar Trackers
The primary advantage of single-axis solar trackers is their ability to increase energy yield by up to 25-35% compared to fixed-tilt systems. By tracking the sun's movement horizontally, these trackers ensure that solar panels receive maximum sunlight exposure, especially during peak sun hours. Their straightforward design and lower maintenance requirements make them a popular choice for large-scale solar farms.
Dual-Axis Solar Trackers
Dual-axis solar trackers, on the other hand, offer an additional level of rotation. These trackers not only follow the sun’s path horizontally but also adjust the tilt angle vertically. This dual movement allows solar panels to maintain the optimal angle of incidence throughout the day and across different seasons, maximizing solar energy absorption.
Energy Yield Impact of Dual-Axis Solar Trackers
The dual-axis trackers provide a significant boost in energy yield, often increasing it by 35-45% compared to fixed systems. This increase is due to their ability to adjust both the azimuth and elevation angles, allowing solar panels to capture sunlight at the most efficient angles regardless of the time or season. While dual-axis trackers are more complex and costly, the higher energy yield can justify the investment, especially in areas with variable weather conditions or where maximizing energy output is critical.
Comparative Analysis: Single-Axis vs. Dual-Axis
When choosing between single-axis and dual-axis solar trackers, several factors come into play, including cost, complexity, and specific project needs.
Cost and Complexity: Single-axis trackers are generally less expensive and easier to install and maintain than dual-axis systems. They have fewer moving parts and require less sophisticated technology, making them a more economical choice for projects with budget constraints.
Energy Yield and Efficiency: Dual-axis trackers offer superior energy yield due to their ability to optimize the angle of incidence continuously. However, the complexity and higher cost may not always be justified, particularly in regions with consistent sunlight where the additional yield might be minimal.
Site and Weather Conditions: The choice between single-axis and dual-axis trackers can also depend on geographic location and climate. In regions with high latitudes or frequent cloud cover, dual-axis trackers may provide a more significant advantage in capturing available sunlight.
Conclusion
Both single-axis and dual-axis solar trackers offer valuable benefits in enhancing the energy yield of solar panels. The decision between the two ultimately boils down to balancing cost, complexity, and desired energy output. For projects where budget and simplicity are priorities, single-axis trackers may suffice. However, for those aiming to maximize efficiency and energy yield in diverse weather conditions, dual-axis trackers could be the better choice. By understanding the differences and their impact on energy yield, solar power developers can make informed decisions to optimize the performance of their solar installations.
As solar technology races ahead—from perovskite cells to tandem architectures, from anti-reflective coatings to transparent electrodes—staying on top of fast-moving innovation has become a strategic imperative.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚡ Ready to accelerate your solar innovation journey? Try Patsnap Eureka today and let AI help you harness the full power of the sun—and your IP strategy.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com