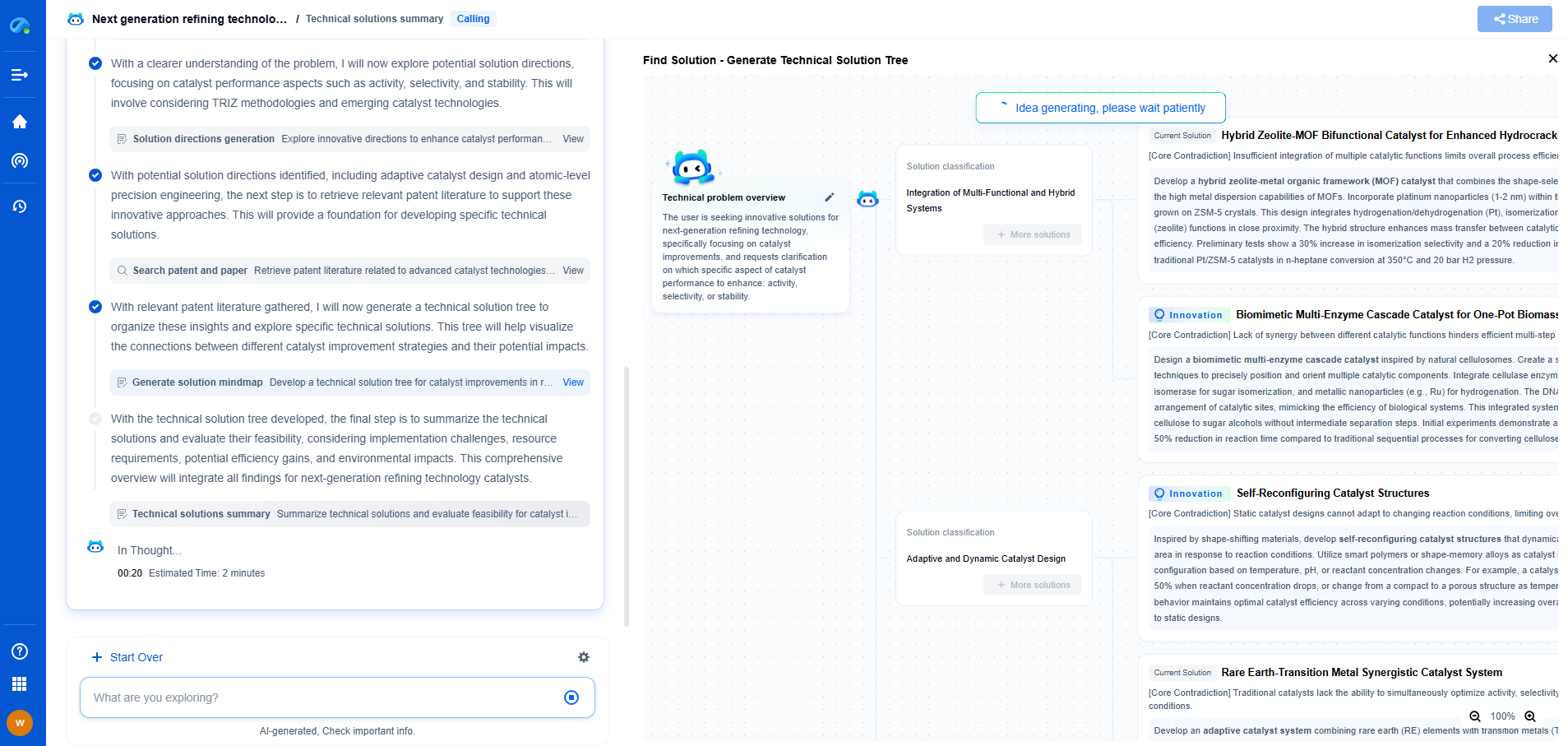
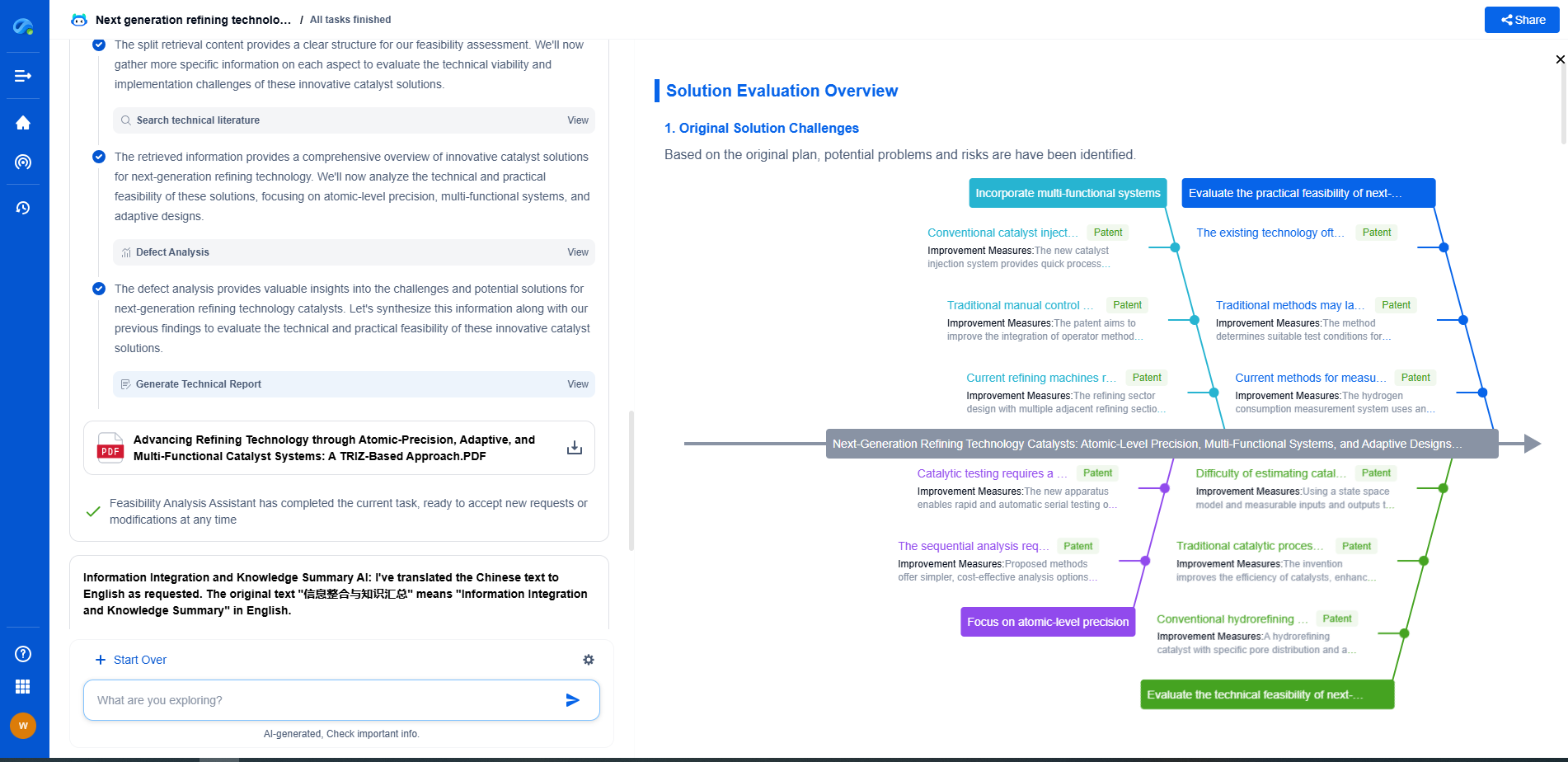
How Belt Drive and Chain Drive Systems Compare in Efficiency
JUL 2, 2025 |
When we consider mechanical power transmission, two of the most common systems are belt drives and chain drives. These systems are pivotal in a wide range of applications, from bicycles and motorcycles to industrial machinery and automobile engines. Understanding how these systems compare in terms of efficiency can be crucial for engineers, manufacturers, and even hobbyists in selecting the right system for their needs.
Mechanics of Belt Drives
Belt drives operate on the principle of friction, where a belt is looped over pulleys to transmit power. The key components of a belt drive system are the belt itself and the pulleys, which can vary in size depending on the specific application. They are generally quieter and smoother compared to chain drives due to their elastic nature, which allows for slight misalignments and absorbs shocks.
However, one of the drawbacks of belt systems is their susceptibility to slippage, especially if the tension is not properly maintained. This can lead to a loss in efficiency as energy is lost through the slipping movement.
Mechanics of Chain Drives
Chain drives, in contrast, rely on a meshing action between the chain and sprockets. This positive engagement ensures that slippage is minimized, making chain drives generally more efficient under high load conditions. Chain drives are constructed with metal links that provide high durability and can transmit large amounts of power over short distances.
Despite their efficiency, chain drives can be noisier and require more maintenance compared to belt drives. Regular lubrication is necessary to reduce wear and tear, and the alignment of sprockets must be precise to prevent excessive strain on the chain links.
Efficiency Comparison
When comparing the efficiency of belt and chain drives, several factors must be considered, including the type of load, the distance of power transmission, and environmental conditions.
1. Load and Speed: Chain drives tend to be more efficient under high load and high-speed conditions. They provide a direct drive mechanism that minimizes energy losses. On the other hand, belt drives can be more suitable for low-load applications where the flexibility and quiet operation outweigh the efficiency losses due to slippage.
2. Distance and Alignment: For long-distance power transmission, belt drives can be advantageous due to their ability to span greater distances without the need for intermediate supports. However, maintaining tension and alignment becomes crucial to prevent efficiency losses. Chain drives, confined to shorter distances, excel in maintaining a consistent output due to their robust engagement mechanism.
3. Environmental Factors: In environments with dust, dirt, or moisture, chain drives can suffer from increased wear unless properly maintained. Belt drives, while less durable in harsh environments, can be protected with covers and tensioning systems to enhance their lifespan.
Maintenance Considerations
The efficiency of both systems is heavily influenced by maintenance practices. Belt drives require periodic tension checks and adjustments to prevent slippage. Misalignment can further exacerbate energy losses in belt systems. Chain drives, while more forgiving to initial misalignment, demand regular lubrication and inspection of link integrity to maintain their efficiency.
Conclusion
Choosing between belt and chain drive systems involves a careful consideration of their inherent advantages and limitations. While chain drives offer superior efficiency in high-load applications, they come with increased noise and maintenance requirements. Belt drives provide smoother operation with less maintenance but at the cost of potential efficiency losses due to slippage.
Ultimately, the decision should be based on the specific operational conditions and priorities, whether it be efficiency, maintenance, noise, or cost. By understanding the nuances of each system, users can make informed decisions that align with their performance and budgetary needs.
Boost Innovation in Gears & Transmissions with Patsnap Eureka
Whether you're designing a next-gen planetary gearbox or optimizing gear tooth profiles for noise reduction, keeping up with the fast-evolving landscape of mechanical transmissions requires more than just experience—it takes insight, speed, and smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Whether you're streamlining a manual transmission system or exploring electromechanical actuation, Patsnap Eureka helps your team move from concept to novelty faster than ever.
👉 Experience Eureka in action—request a personalized demo today and see how AI can revolutionize your gear innovation workflows.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com