How Gear Hobbing Differs from Gear Shaping and Milling
JUL 2, 2025 |
Gear manufacturing is a crucial process in various industries, facilitating the creation of components that transmit torque and motion. Among the plethora of techniques available, gear hobbing, shaping, and milling are prominent methods that cater to different requirements. Understanding their distinctive features is essential for manufacturers in making informed decisions about which technique to employ.
What is Gear Hobbing?
Gear hobbing is a widely used technique in gear manufacturing that involves the use of a rotating cutter called a hob. The hob progressively cuts the gear teeth while both the workpiece and the hob rotate. This method is particularly favored for its efficiency and ability to produce gears with complex profiles.
Advantages of Gear Hobbing
One of the primary advantages of gear hobbing is its speed and efficiency, especially for high-volume production. It allows for continuous tooth cutting, making it ideal for producing spur, helical, and worm gears. Additionally, gear hobbing is flexible, accommodating different gear sizes and profiles with relative ease.
Limitations of Gear Hobbing
Despite its advantages, gear hobbing has limitations. The initial setup and hob cost can be high, which might not be economically viable for small batches or unique gear designs. Moreover, hobbing may struggle with producing internal gears due to accessibility issues.
Understanding Gear Shaping
Gear shaping employs a cutting tool that reciprocates vertically while the gear blank rotates. Unlike hobbing, the cutting tool mimics the shape and size of the gear teeth, creating the desired profile through successive passes.
Advantages of Gear Shaping
Gear shaping is versatile in producing both external and internal gears, providing an edge over hobbing in certain applications. It is particularly effective for creating gears with complex profiles or in situations where accessibility is a concern.
Limitations of Gear Shaping
The main drawback of gear shaping is its slower processing speed compared to hobbing. The reciprocating motion of the cutter limits the rate at which material can be removed, making it less efficient for high-volume production.
Exploring Gear Milling
Gear milling typically involves using a milling machine equipped with a cutter designed to produce the desired gear profile. This method can either be performed in a single pass or multiple passes depending on the gear size and complexity.
Advantages of Gear Milling
Gear milling is highly versatile, capable of producing gears of varying sizes and profiles with high precision. It is particularly beneficial for prototype production and small batch manufacturing where flexibility and precision are paramount.
Limitations of Gear Milling
Despite its precision, gear milling is generally slower compared to hobbing and shaping. It is less suitable for mass production due to the time-consuming nature of the milling process. Additionally, the setup for gear milling can be complex and require skilled operators.
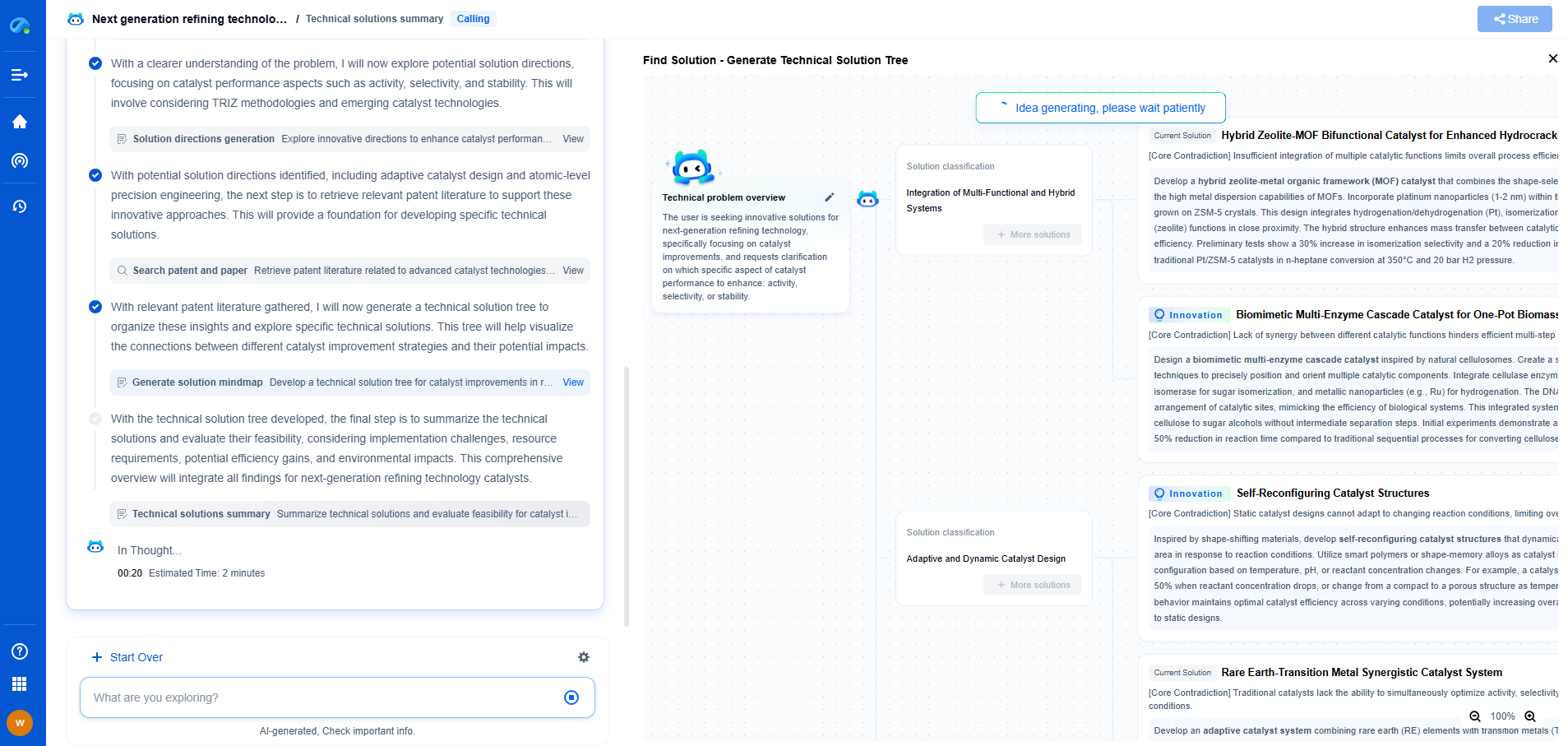
Comparative Analysis
While gear hobbing, shaping, and milling each have their strengths, choosing the right technique depends on factors such as production volume, gear complexity, and cost considerations. Hobbing is ideal for large-scale production with straightforward profiles, while shaping is better suited for internal gears and intricate designs. Milling, on the other hand, offers unparalleled precision for custom or small batch production.
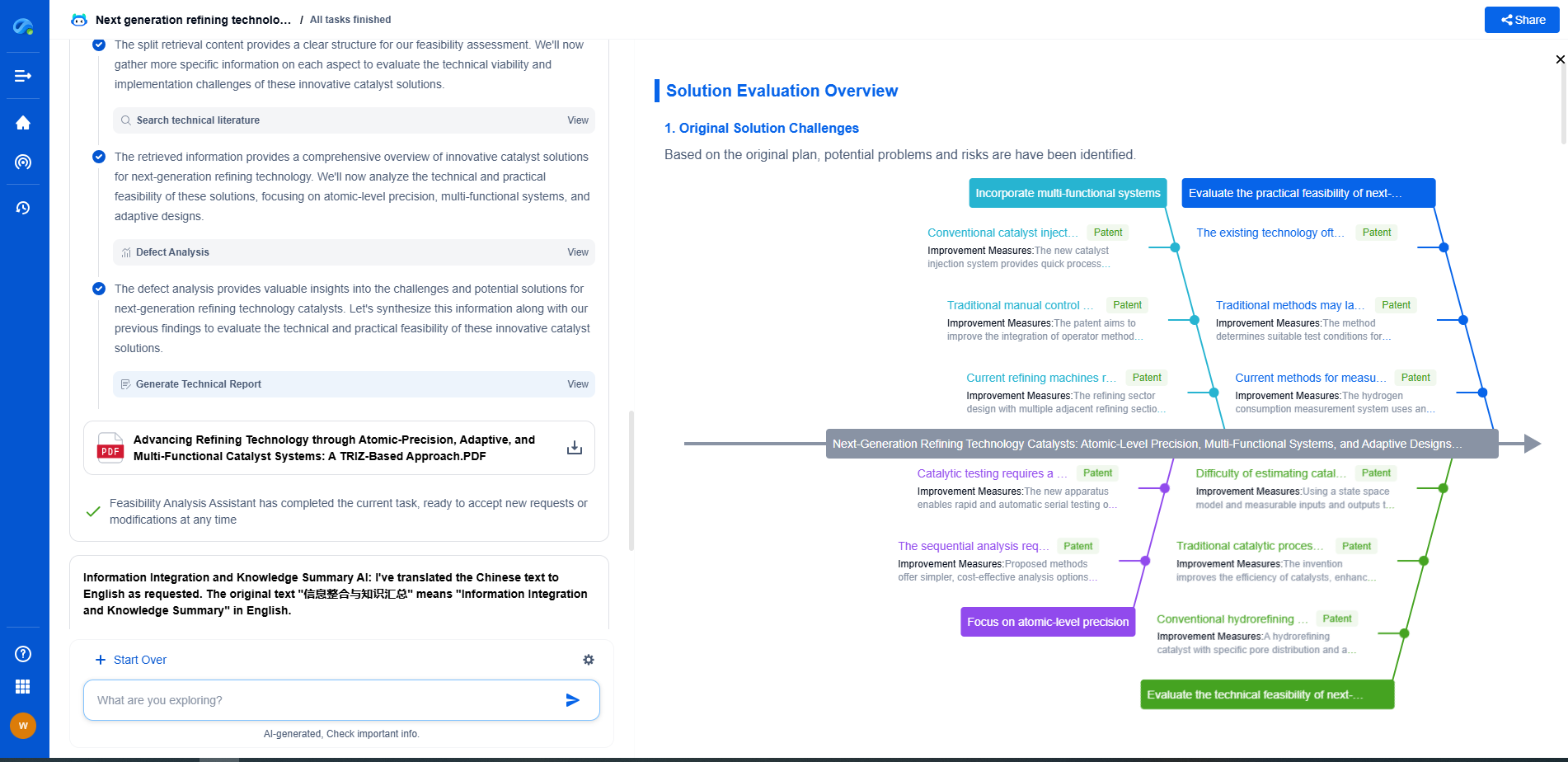
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between gear hobbing, shaping, and milling is crucial for manufacturers aiming to optimize their gear production process. By evaluating the specific needs of their projects, manufacturers can select the most appropriate technique, ensuring efficient, cost-effective, and high-quality gear manufacturing.
Boost Innovation in Gears & Transmissions with Patsnap Eureka
Whether you're designing a next-gen planetary gearbox or optimizing gear tooth profiles for noise reduction, keeping up with the fast-evolving landscape of mechanical transmissions requires more than just experience—it takes insight, speed, and smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Whether you're streamlining a manual transmission system or exploring electromechanical actuation, Patsnap Eureka helps your team move from concept to novelty faster than ever.
👉 Experience Eureka in action—request a personalized demo today and see how AI can revolutionize your gear innovation workflows.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com