How Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs) Are Manufactured
JUL 9, 2025 |
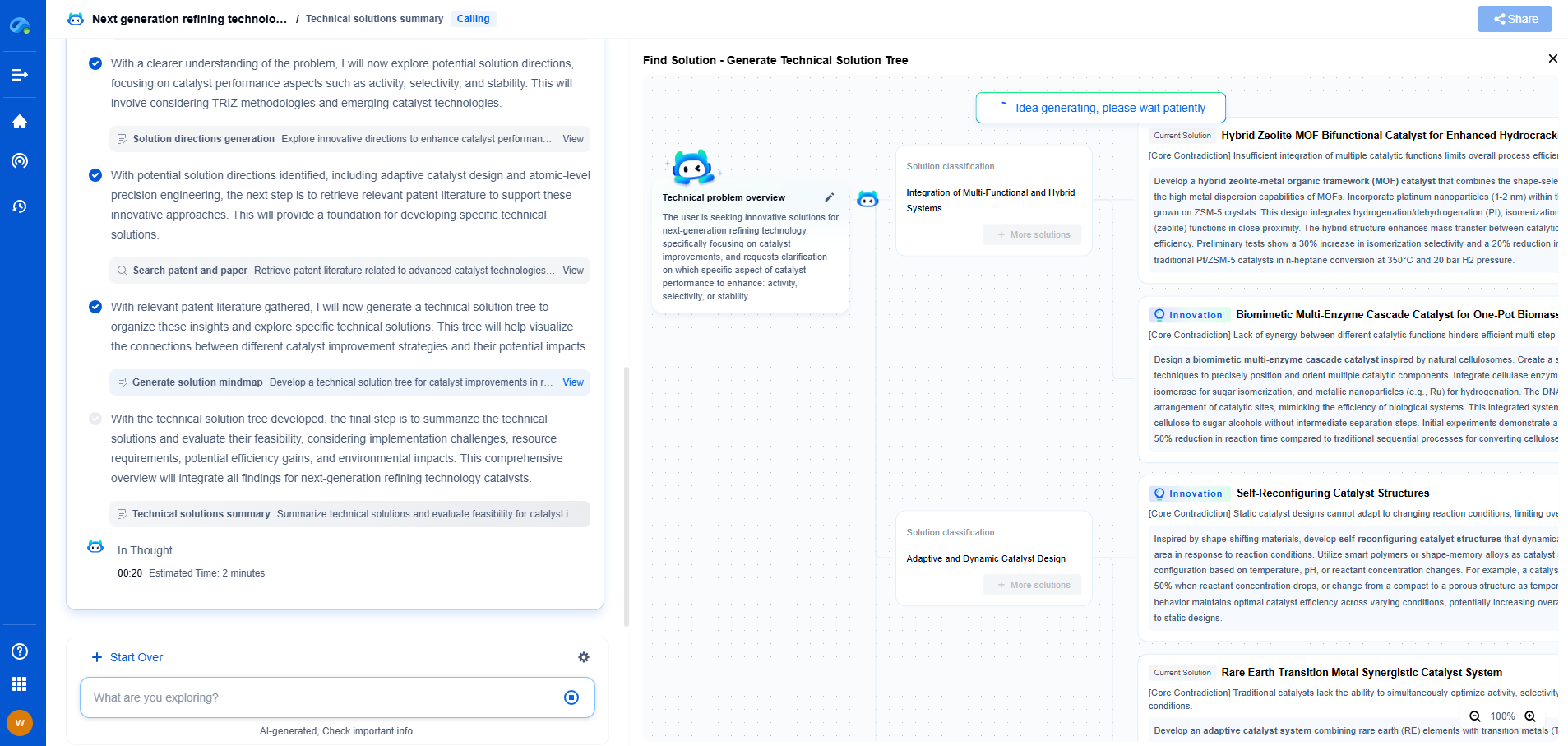
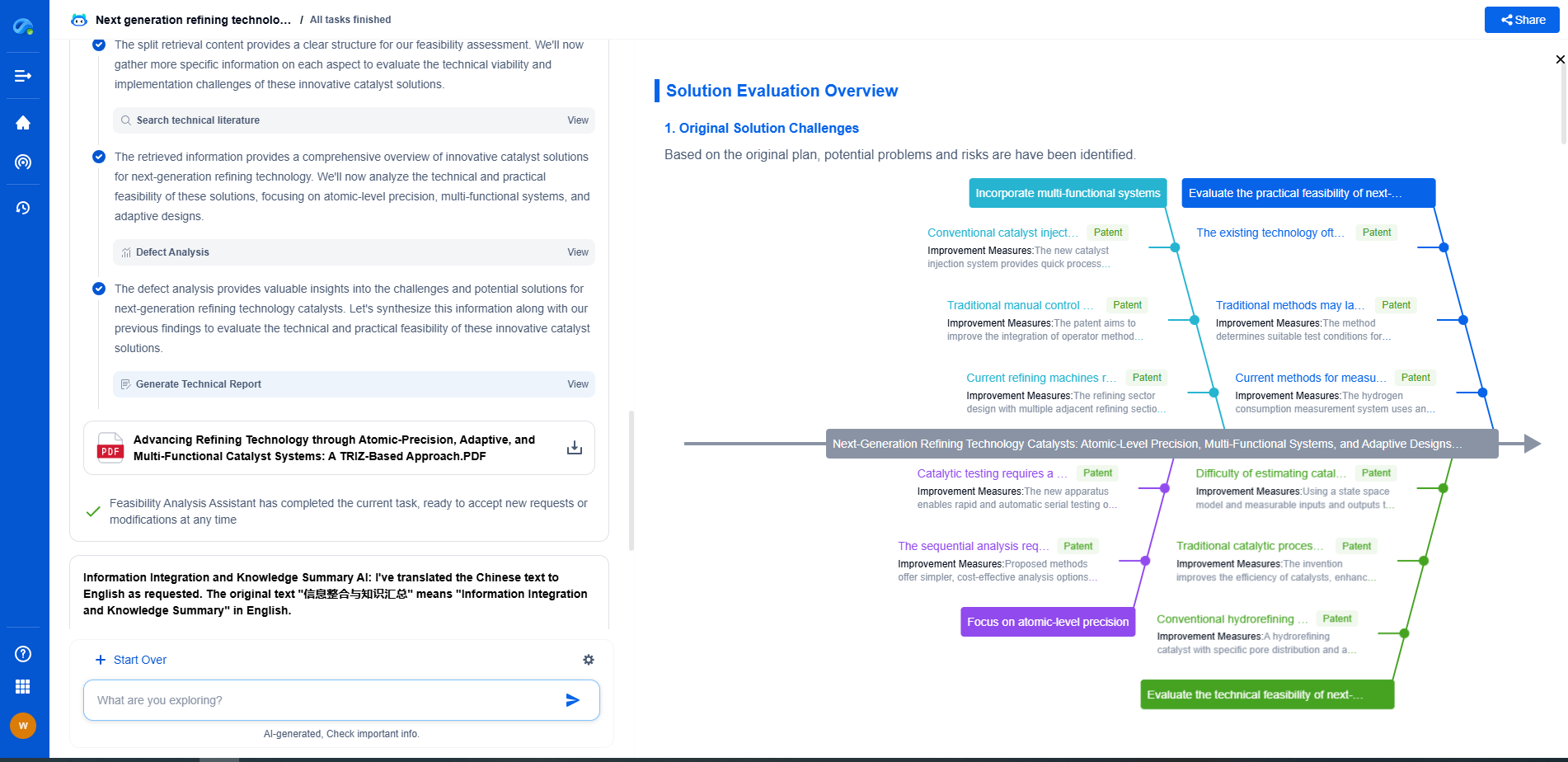
Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs) are essential components in modern electronic devices, known for their efficiency in storing and releasing electrical energy. They are widely used in a range of applications from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. Before delving into the manufacturing process, it is crucial to understand what MLCCs are made of and why they are so vital.
MLCCs consist of alternating layers of ceramic and metal, which form a capacitor. The ceramic material acts as a dielectric, while the metal layers serve as electrodes. This structure allows MLCCs to have high capacitance values in a compact size, making them ideal for use in miniaturized electronic circuits.
**The Raw Materials**
The manufacturing process begins with the selection of raw materials. The primary materials used in MLCCs are ceramic powders and metal pastes. The ceramic powder, often made of barium titanate, is essential for its dielectric properties. The metal paste, usually containing nickel or palladium, is used for the electrodes. The quality of these raw materials is crucial as it directly impacts the performance and reliability of the final product.
**The Formulation Process**
Once the raw materials are acquired, they undergo a formulation process. This involves mixing the ceramic powders with various additives to create a slurry. These additives can include binders, dispersants, and solvents, which help achieve the desired consistency and properties. The slurry is then cast into thin sheets, known as ceramic green sheets, which will later form the layers of the capacitor.
**Layering and Lamination**
The heart of MLCC manufacturing lies in the layering and lamination process. The ceramic green sheets are cut into specific sizes and are coated with metal paste to form electrodes. These metalized layers are then stacked alternately with uncoated ceramic layers. The number of layers can vary depending on the desired capacitance and size of the capacitor.
Once the layering is complete, the stack undergoes a lamination process. This involves applying heat and pressure to bond the layers together, forming a solid block. Lamination ensures the structural integrity of the capacitor and prepares it for the next stages of production.
**Sintering**
After lamination, the capacitor blocks are subjected to a sintering process. Sintering involves heating the blocks to a high temperature, which causes the ceramic particles to fuse together, enhancing the mechanical strength and dielectric properties of the capacitors. This step is critical as it solidifies the structure and prepares the capacitors for finishing processes.
**Termination and Testing**
Following sintering, the capacitors undergo termination, where external electrodes are attached. This is typically done by applying a layer of metal paste on the edges of the capacitor and firing it to create a conductive surface. These terminations allow the capacitors to be connected within electronic circuits.
Finally, each capacitor undergoes rigorous testing to ensure it meets the required specifications. This includes checking for capacitance, insulation resistance, and dielectric strength. Only capacitors that pass these tests are deemed suitable for use in electronic products.
**Final Assembly and Quality Control**
The MLCCs are then assembled onto reels or trays, ready for shipment to manufacturers. Throughout the entire production process, stringent quality control measures are in place to ensure consistency and reliability. This includes regular inspections and audits of the manufacturing facilities, as well as continuous monitoring of the production parameters.
**Conclusion**
The manufacturing of Multilayer Ceramic Capacitors is a complex process that requires precision and attention to detail. From the careful selection of raw materials to the final quality control checks, each step is crucial to producing capacitors that are reliable and efficient. As technology continues to advance, the demand for high-performance MLCCs is expected to grow, driving further innovations in manufacturing techniques and materials.
Looking to accelerate your capacitor innovation pipeline?
As capacitor technologies evolve—from miniaturized MLCCs for smartphones to grid-scale energy storage devices—so must the way your team accesses critical knowledge.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Try Patsnap Eureka now and discover a faster, smarter way to research and innovate in capacitor technology.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com