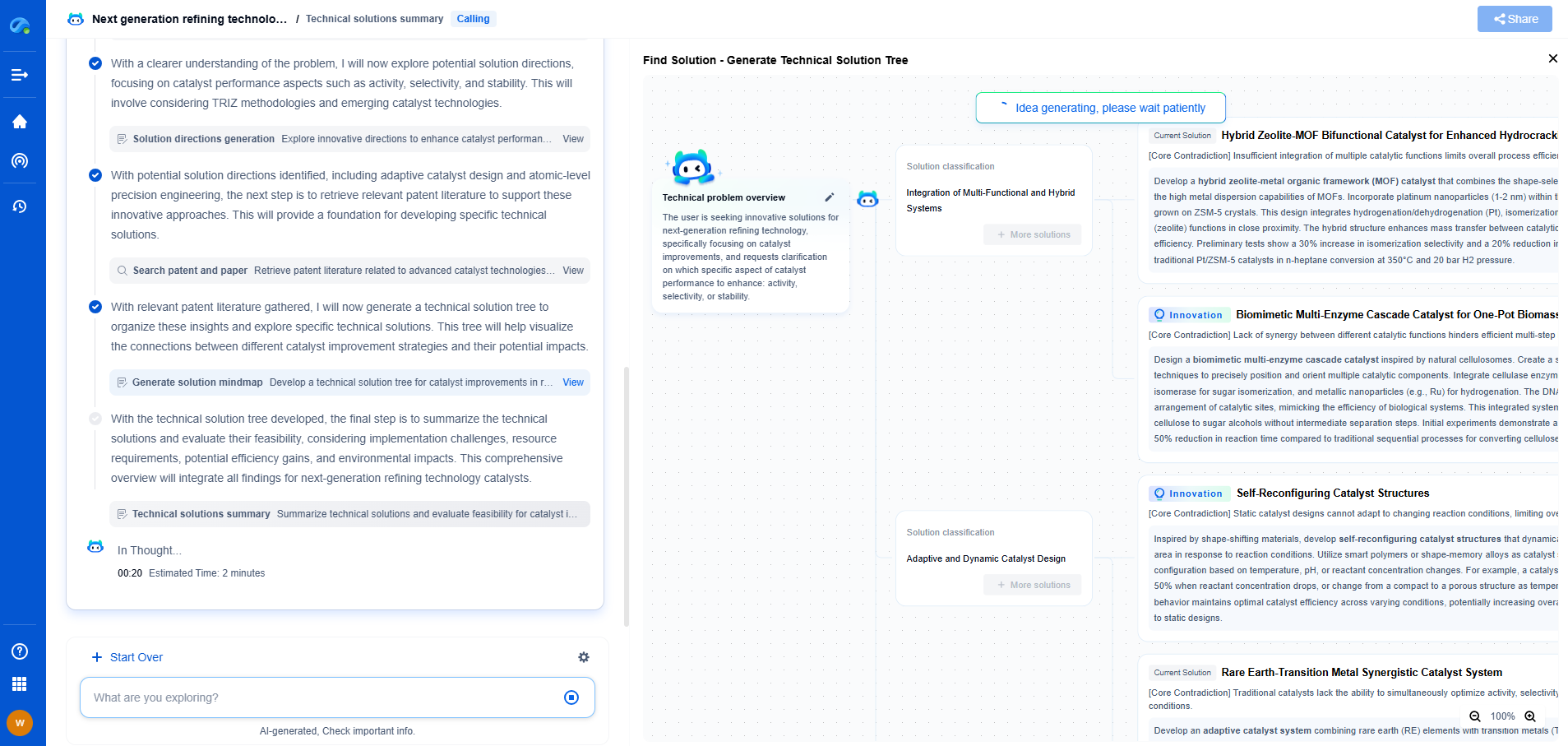
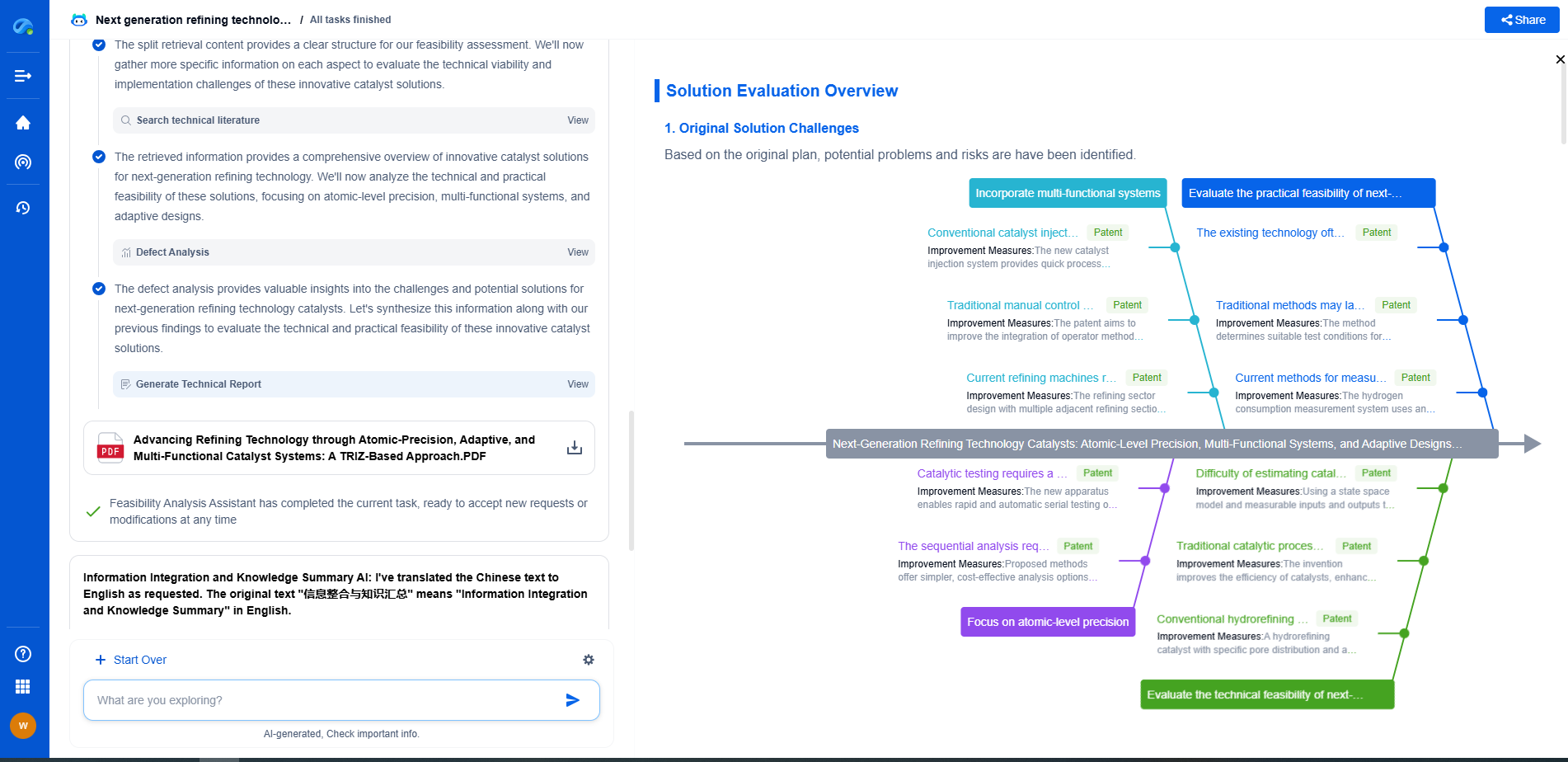
How the Current Transformer Method Works for High-Current Measurements
JUL 9, 2025 |
In the world of electrical engineering, the measurement of high currents is a critical task. To achieve this safely and accurately, a device known as a current transformer (CT) is employed. Current transformers are specially designed transformers used to transform high current levels into a smaller, more manageable current that can be easily measured with standard instruments. This allows for the monitoring and recording of electrical currents in a variety of applications, such as power generation, transmission, and distribution.
The Basic Principle of Operation
The operation of a current transformer is based on the principles of electromagnetic induction, much like any other transformer. It consists of a primary winding, which carries the current to be measured, and a secondary winding, which produces a current proportional to the primary current but at a reduced magnitude. The primary winding is connected in series with the load, and the secondary winding is connected to a measuring instrument, like an ammeter or a relay.
When current flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field around it. This magnetic field induces a current in the secondary winding. The number of turns in the secondary winding is much greater than that in the primary winding, which allows the large primary current to be transformed into a smaller secondary current. This transformation makes it possible to measure high currents safely without having to directly handle the high-voltage circuit.
Types of Current Transformers
Current transformers come in various types, each suited for different applications and operating conditions. The most common types include:
1. Wound Current Transformers: These transformers have separate windings for both the primary and secondary sides. The primary winding is wound on the core, providing excellent accuracy and is often used in precision measurement applications.
2. Toroidal Current Transformers: These transformers lack a primary winding. Instead, the conductor carrying the current to be measured passes through a window or hole in the core, acting as a single-turn primary winding. These are widely used due to their simplicity and ease of installation.
3. Bar-Type Current Transformers: In these transformers, the primary winding is a busbar or a cable carrying the current. The secondary winding is wound around this bar. They are suitable for high-current applications due to their robust construction.
Applications of Current Transformers
Current transformers are indispensable in various electrical systems and applications. Some of the key areas where they are used include:
1. Power System Protection: CTs are crucial components in protective relays, which detect abnormal conditions and initiate circuit breakers to protect electrical systems from damage due to overloads or short circuits.
2. Energy Metering: In substations and industrial settings, CTs are used alongside voltage transformers to measure the power consumed. This information is essential for billing and energy management.
3. Monitoring and Control: CTs are used to monitor the current flow in electrical systems, providing data for load analysis, system optimization, and preventive maintenance.
4. Ground Fault Detection: CTs are employed in detecting ground faults by measuring the difference between the current entering and leaving a system, helping to ensure system safety.
Advantages of Using Current Transformers
The use of current transformers offers several advantages, especially in high-current applications:
1. Safety: CTs allow for the measurement of high currents without requiring direct contact with the high-voltage circuit, significantly reducing the risk of electrical shock.
2. Accuracy: Modern CTs are highly accurate and can provide precise measurements over a wide range of current levels, which is crucial for both metering and protective applications.
3. Versatility: With various types of CTs available, they can be adapted to suit different installations and operating conditions, making them flexible tools in electrical engineering.
4. Cost-Efficiency: By enabling the use of standard measuring instruments, CTs reduce the need for expensive high-current measuring devices, thus offering a cost-effective solution for current measurement.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their advantages, the use of current transformers also involves certain challenges and considerations. It is essential to ensure proper installation and maintenance to prevent issues such as saturation, which can affect the accuracy of the measurements. The burden, or the load connected to the CT's secondary, should also be within specified limits to ensure optimal performance.
Conclusion
Current transformers play a vital role in the safe and accurate measurement of high currents in electrical systems. By understanding their operation, types, applications, and benefits, engineers and technicians can better utilize these devices to enhance the reliability and efficiency of electrical systems. Whether for protection, monitoring, or control, current transformers remain an indispensable tool in modern electrical engineering practices.
Navigating the evolving world of electrical measurement—from high-precision signal integrity to advanced test protocols like BERT or TDR—demands more than just expertise; it demands smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka empowers you to keep up—by turning complex patent data, technical parameters, and industry signals into actionable insight. It’s your AI partner for exploring what’s next in test, measurement, and electrical diagnostics.
💡 Try Patsnap Eureka for free and see how it transforms the way you work with electrical measurement technologies.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com