How to Combine GIS and SCADA for Smart Pipeline Management
JUN 20, 2025 |
In recent years, the integration of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems has revolutionized pipeline management. Both technologies have their distinct advantages: GIS provides spatial context, enabling precise mapping and analysis of pipeline networks, while SCADA offers real-time monitoring and control capabilities. When combined, they create a robust smart pipeline management system that enhances efficiency, safety, and sustainability.
Understanding GIS and Its Role in Pipeline Management
GIS is a powerful tool that captures, stores, manipulates, analyzes, and presents spatial or geographic data. For pipeline management, GIS allows operators to visualize their infrastructure overlaid on maps with various layers of information, such as topography, land use, and environmental constraints. This spatial perspective enables better planning, decision-making, and resource allocation.
With GIS, pipeline companies can identify optimal routes, assess risk factors, and monitor environmental impact. The spatial analysis capabilities help in identifying potential threats like landslides or floods that could affect pipeline integrity. Moreover, GIS supports asset management by maintaining an up-to-date database of pipeline components and their conditions.
The Role of SCADA in Pipeline Management
SCADA systems are integral for pipeline operations, providing real-time data acquisition, processing, and control. They enable operators to monitor pipeline conditions, such as pressure, temperature, flow rate, and valve status, from a centralized location. This real-time monitoring is crucial for maintaining pipeline integrity and ensuring safe operations.
SCADA systems can trigger alarms in case of anomalies, facilitating prompt response to potential hazards like leaks or ruptures. Furthermore, they support automation by allowing remote control of valves and pumps, optimizing flow rates, and reducing manual intervention.
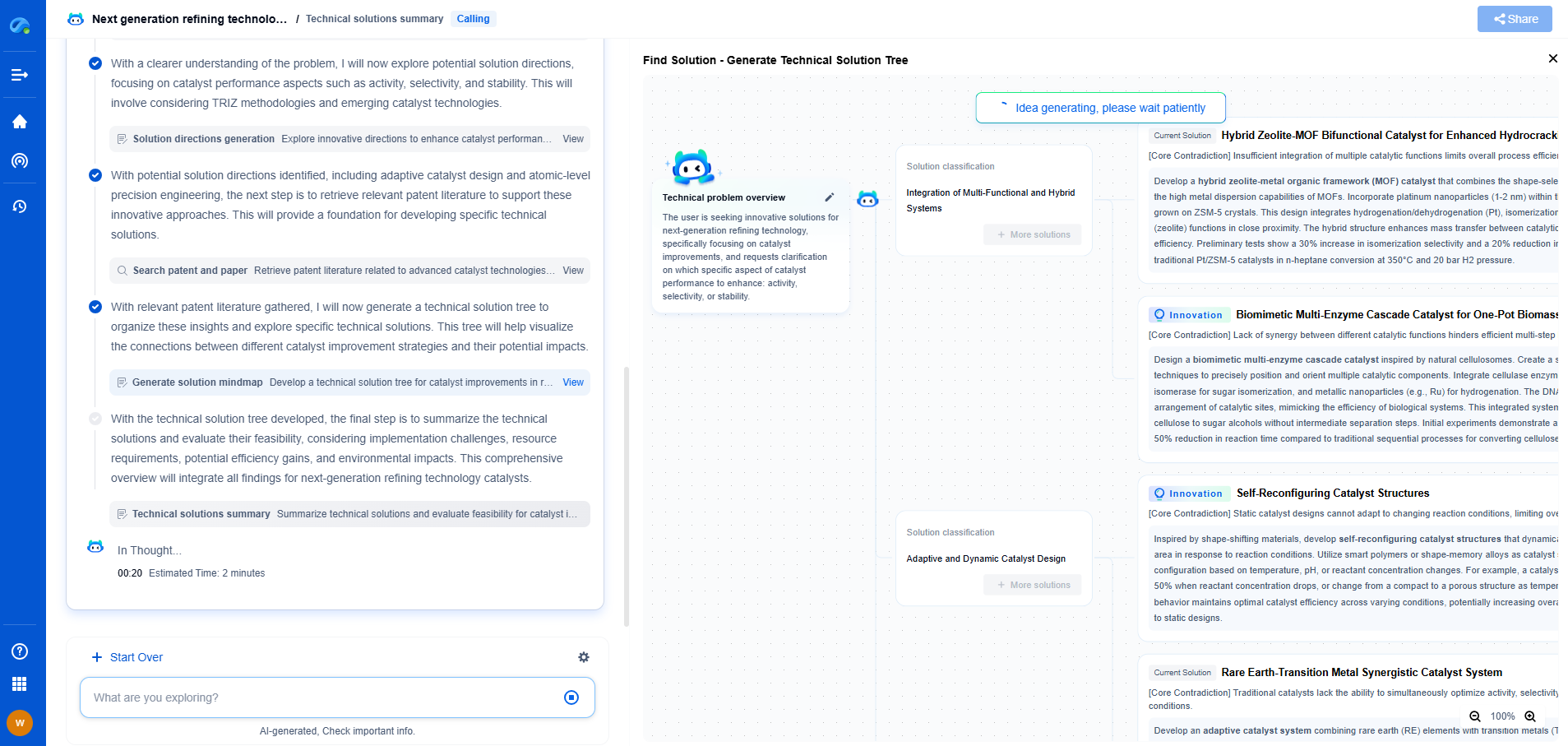
The Synergy of GIS and SCADA
The integration of GIS and SCADA creates a comprehensive smart pipeline management system. This synergy allows for the spatial visualization of real-time data, enabling operators to see both the physical layout of the pipeline and its current operational status. The combination enhances situational awareness and facilitates more informed decision-making.
For instance, when a SCADA system detects a pressure drop, the integrated GIS can help pinpoint the exact location and context of the issue, whether it’s due to a leak in a flood-prone area or a mechanical failure near a construction site. This spatially-aware data can significantly reduce response times and improve the accuracy of maintenance operations.
Benefits of GIS and SCADA Integration
The integration of GIS and SCADA offers numerous benefits to pipeline management:
1. Enhanced Safety: By providing real-time monitoring and spatial analysis, operators can quickly identify and address safety risks, reducing the likelihood of accidents and environmental hazards.
2. Improved Efficiency: The ability to remotely monitor and control pipeline operations leads to optimized performance and reduced operational costs.
3. Proactive Maintenance: Predictive analytics can be applied to combined GIS and SCADA data, allowing for proactive maintenance scheduling, which minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of pipeline assets.
4. Regulatory Compliance: The comprehensive data and reports generated through this integration aid in meeting regulatory requirements and demonstrating compliance with safety and environmental standards.
5. Better Decision-Making: The rich insights derived from combining geographic and operational data support more informed strategic planning and decision-making.
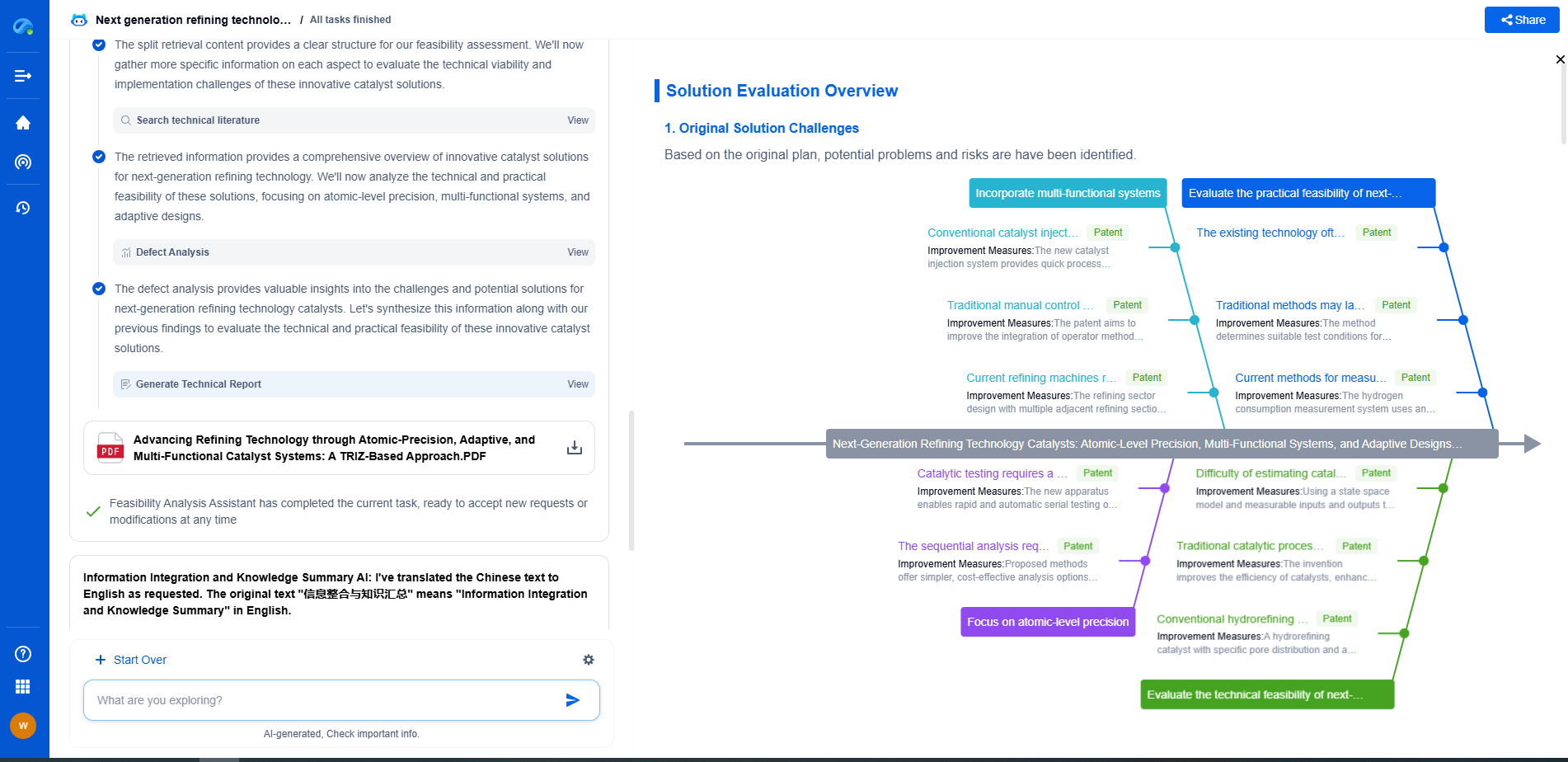
Implementation Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits are clear, integrating GIS and SCADA systems can pose challenges. It requires careful planning, investment in technology, and a skilled workforce capable of managing and interpreting complex data. Compatibility between existing systems, data security, and ensuring uninterrupted data flow are other critical considerations.
Pipeline operators need to collaborate with technology providers to develop customized solutions that address specific needs. Training staff to effectively use these integrated systems is essential for maximizing their potential.
Conclusion
The integration of GIS and SCADA systems marks a significant advancement in smart pipeline management. By harnessing the spatial visualization of GIS with the real-time monitoring capabilities of SCADA, operators can achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, safety, and reliability. As technology continues to evolve, the potential for these systems to further transform pipeline management is immense, offering promising solutions for the industry’s future challenges.
Transform the Way You Innovate in Pipeline Technology—with AI-Powered Intelligence
From corrosion-resistant materials to smart monitoring systems and advanced flow control mechanisms, the pipeline industry is undergoing rapid technological transformation. Yet keeping up with evolving engineering solutions, regulatory landscapes, and competitive patents can be a major bottleneck for R&D and IP teams.
Patsnap Eureka is your AI-powered research companion—built specifically for professionals in high-tech and infrastructure domains like pipeline technology. Whether you're designing high-pressure transport systems, assessing trenchless installation innovations, or safeguarding proprietary flow assurance solutions, Eureka provides real-time insights into global patent trends, emerging technologies, and R&D intelligence—all in one intuitive interface.
Empower your team to innovate faster, reduce technical blind spots, and stay ahead of industry shifts. Discover Patsnap Eureka today and bring clarity and confidence to your pipeline technology decisions.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com