How to Develop a Pipeline Safety Management System (PSMS)
JUN 20, 2025 |
Pipeline Safety Management Systems (PSMS) are essential frameworks that help organizations manage the safety of their pipeline operations efficiently and effectively. These systems are designed to reduce risks, prevent accidents, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards, while promoting a culture of safety throughout the organization. Developing a PSMS involves a strategic approach and commitment from all levels of the organization. This article provides a comprehensive guide on how to develop a robust Pipeline Safety Management System.
Assessing Your Current Safety Practices
The first step in developing a PSMS is to assess your current safety practices. This involves evaluating existing policies, procedures, and safety measures to identify gaps and areas for improvement. Conduct a thorough review of incident reports, audits, and safety assessments to understand the current state of your pipeline operations. Gather input from employees at all levels to gain a comprehensive understanding of the safety culture within your organization.
Defining Safety Objectives and Goals
Once you have assessed your current safety practices, the next step is to define clear safety objectives and goals. These should be aligned with your organization's overall mission and values, as well as industry standards and regulatory requirements. Clearly defined objectives will guide the development and implementation of your PSMS, ensuring that all efforts are focused on achieving specific outcomes. Consider both short-term and long-term goals to address immediate needs and build a sustainable safety culture.
Designing the PSMS Framework
Designing the PSMS framework involves establishing the structure and components of your safety management system. This includes defining roles and responsibilities, developing policies and procedures, and setting up communication channels. Ensure that the framework is scalable and adaptable to accommodate changes in technology, regulations, and business objectives. Incorporate best practices from industry standards, such as API RP 1173, to ensure a comprehensive and effective PSMS design.
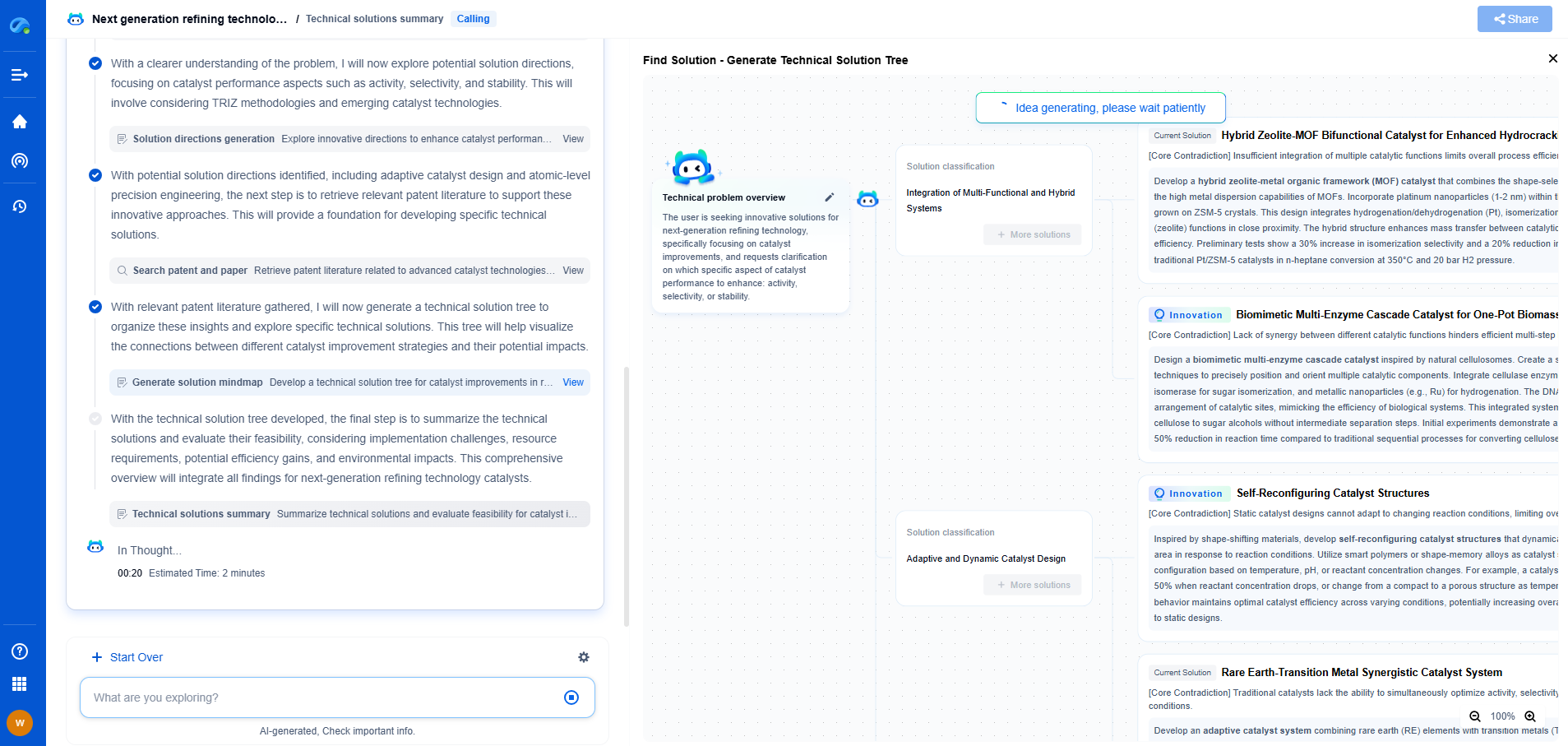
Implementing Risk Management Strategies
Risk management is a core component of a PSMS. Implementing risk management strategies involves identifying potential hazards, assessing risks, and establishing controls to mitigate them. Use tools such as hazard analysis, risk assessment matrices, and failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA) to systematically evaluate risks and prioritize actions. Develop emergency response plans and training programs to ensure preparedness in the event of incidents or accidents.
Fostering a Safety Culture
A successful PSMS requires a strong safety culture, where safety is prioritized and valued by everyone in the organization. Encourage open communication, reporting of safety concerns, and proactive involvement in safety initiatives. Leadership commitment is crucial for fostering a safety culture, as it sets the tone for the organization and influences employee attitudes toward safety. Provide continuous education and training to reinforce safety awareness and skills.
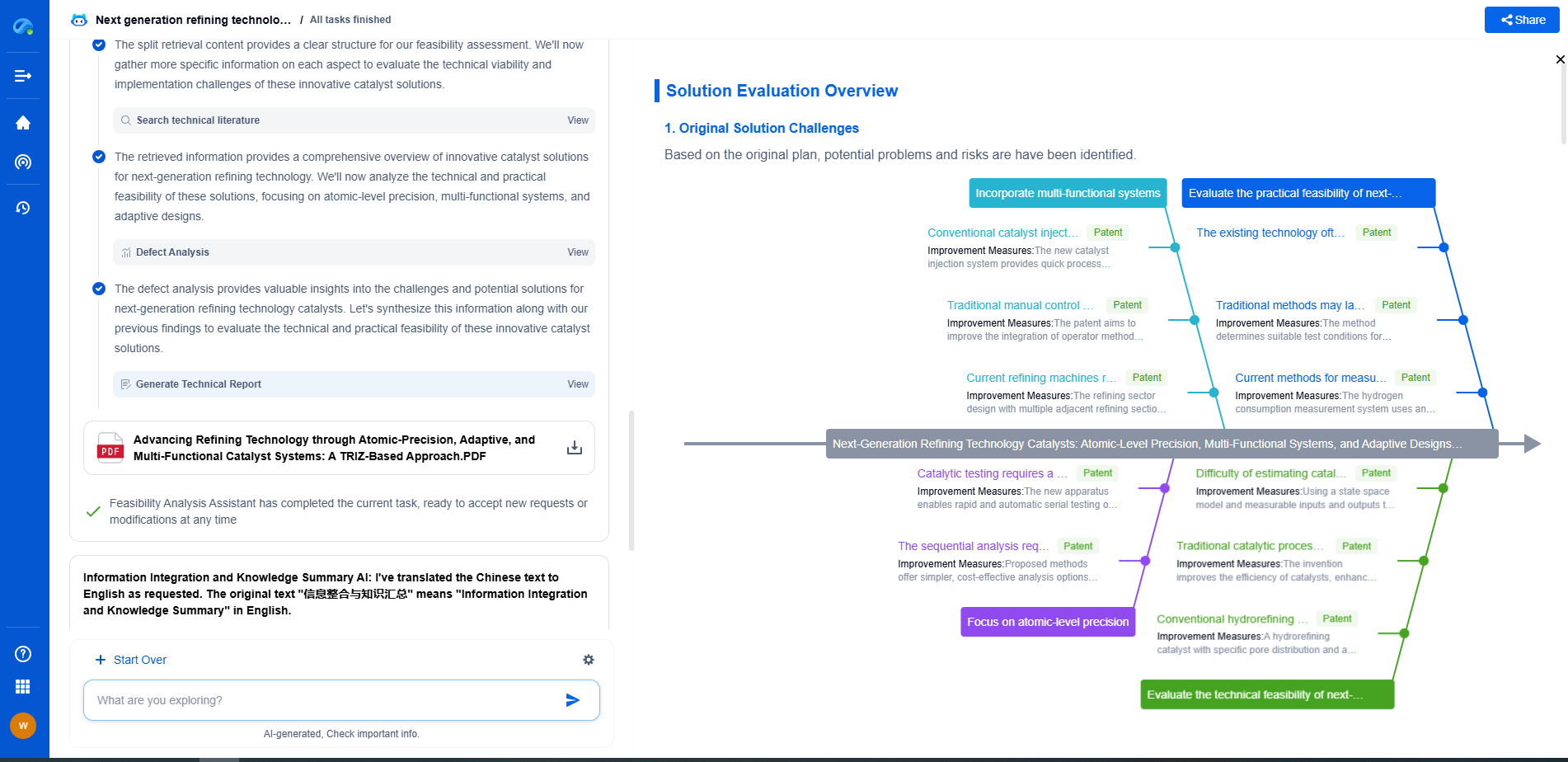
Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
Monitoring and continuous improvement are essential for the ongoing effectiveness of a PSMS. Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure safety performance and track progress toward objectives. Conduct regular audits, inspections, and reviews to identify areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments. Encourage feedback and suggestions from employees to drive innovation and enhance safety practices.
Ensuring Compliance with Regulations
Compliance with regulations is a critical aspect of a PSMS. Stay updated with the latest regulatory requirements and industry standards to ensure your system remains compliant. Establish processes for monitoring changes in regulations and implement necessary updates to your PSMS. Engage with industry groups and participate in workshops and seminars to stay informed and share best practices.
Conclusion
Developing a Pipeline Safety Management System is a comprehensive process that requires commitment, strategic planning, and continuous improvement. By assessing current practices, defining objectives, designing a robust framework, implementing risk management strategies, fostering a safety culture, and ensuring compliance, organizations can build a PSMS that enhances safety performance and protects both people and the environment. Embrace the journey of developing a PSMS as an opportunity to create a safer and more resilient pipeline operation.
Transform the Way You Innovate in Pipeline Technology—with AI-Powered Intelligence
From corrosion-resistant materials to smart monitoring systems and advanced flow control mechanisms, the pipeline industry is undergoing rapid technological transformation. Yet keeping up with evolving engineering solutions, regulatory landscapes, and competitive patents can be a major bottleneck for R&D and IP teams.
Patsnap Eureka is your AI-powered research companion—built specifically for professionals in high-tech and infrastructure domains like pipeline technology. Whether you're designing high-pressure transport systems, assessing trenchless installation innovations, or safeguarding proprietary flow assurance solutions, Eureka provides real-time insights into global patent trends, emerging technologies, and R&D intelligence—all in one intuitive interface.
Empower your team to innovate faster, reduce technical blind spots, and stay ahead of industry shifts. Discover Patsnap Eureka today and bring clarity and confidence to your pipeline technology decisions.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com