How to Replace Tantalum Capacitors with Polymer Capacitors Safely
JUL 9, 2025 |
When it comes to electronic circuits, components play a significant role in determining the performance and reliability of the system. Tantalum capacitors, known for their excellent capacitance stability and reliability, have been a staple in many applications. However, with the rise of advanced technology and the need for environmentally friendly solutions, polymer capacitors are becoming a popular alternative. This article will guide you through the process of safely replacing tantalum capacitors with polymer capacitors.
Understanding Capacitor Types
Before diving into the replacement process, it's crucial to understand the differences between tantalum and polymer capacitors. Tantalum capacitors are known for their high volumetric efficiency and reliability, making them suitable for various applications, especially where space is a constraint. However, they can be prone to failure, especially under conditions like voltage spikes.
On the other hand, polymer capacitors offer a lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) and improved performance at higher frequencies. They also boast better stability and reliability, particularly in challenging environmental conditions. Notably, polymer capacitors are less likely to catch fire in case of failure, making them a safer choice for many applications.
Benefits of Replacing Tantalum with Polymer Capacitors
Switching to polymer capacitors brings several advantages. Firstly, they present enhanced safety due to their non-ignitable failure mode. Secondly, their lower ESR translates to better efficiency and performance in high-frequency applications. Furthermore, they are environmentally friendly, reducing the reliance on tantalum, which is a conflict mineral, and thus supporting sustainable electronic design practices.
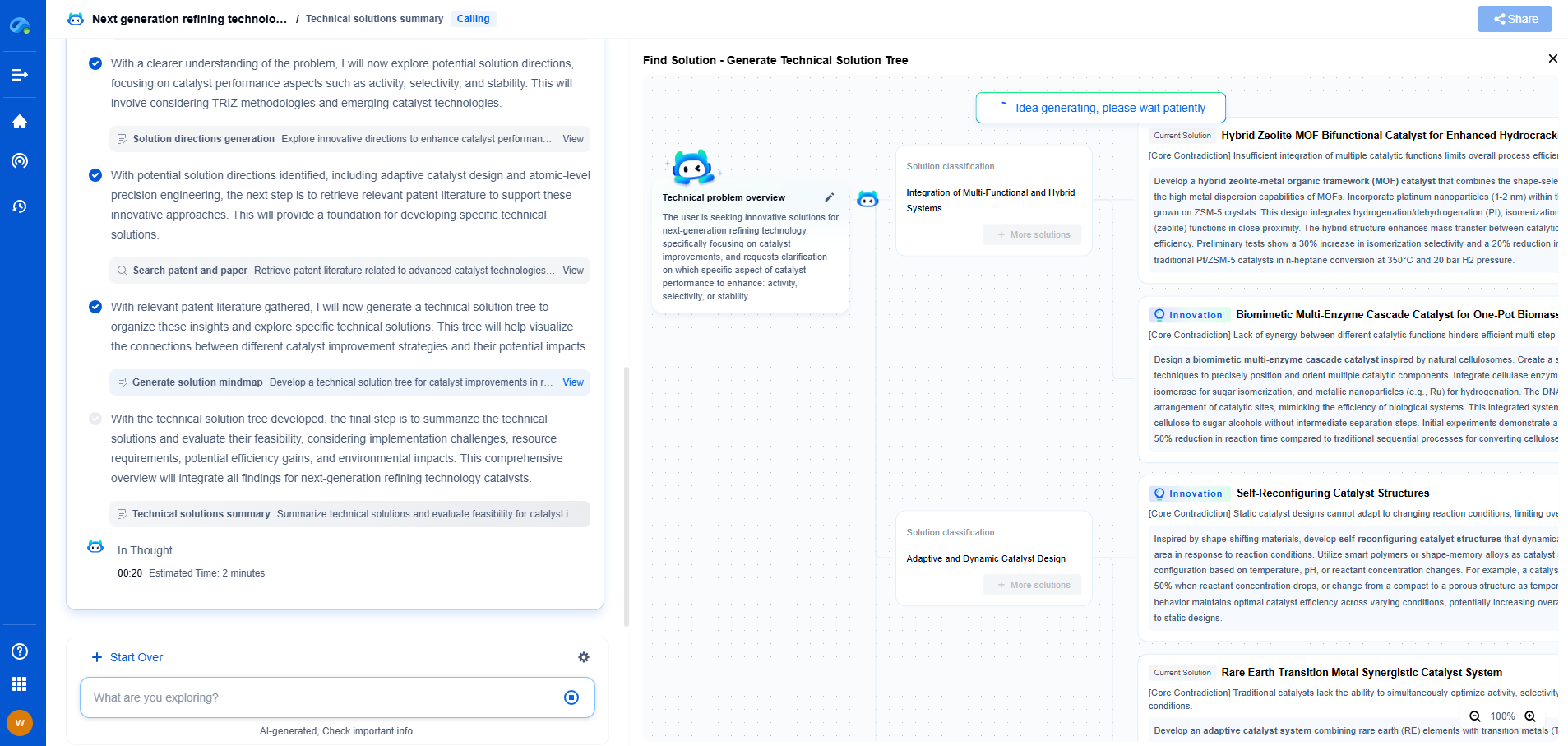
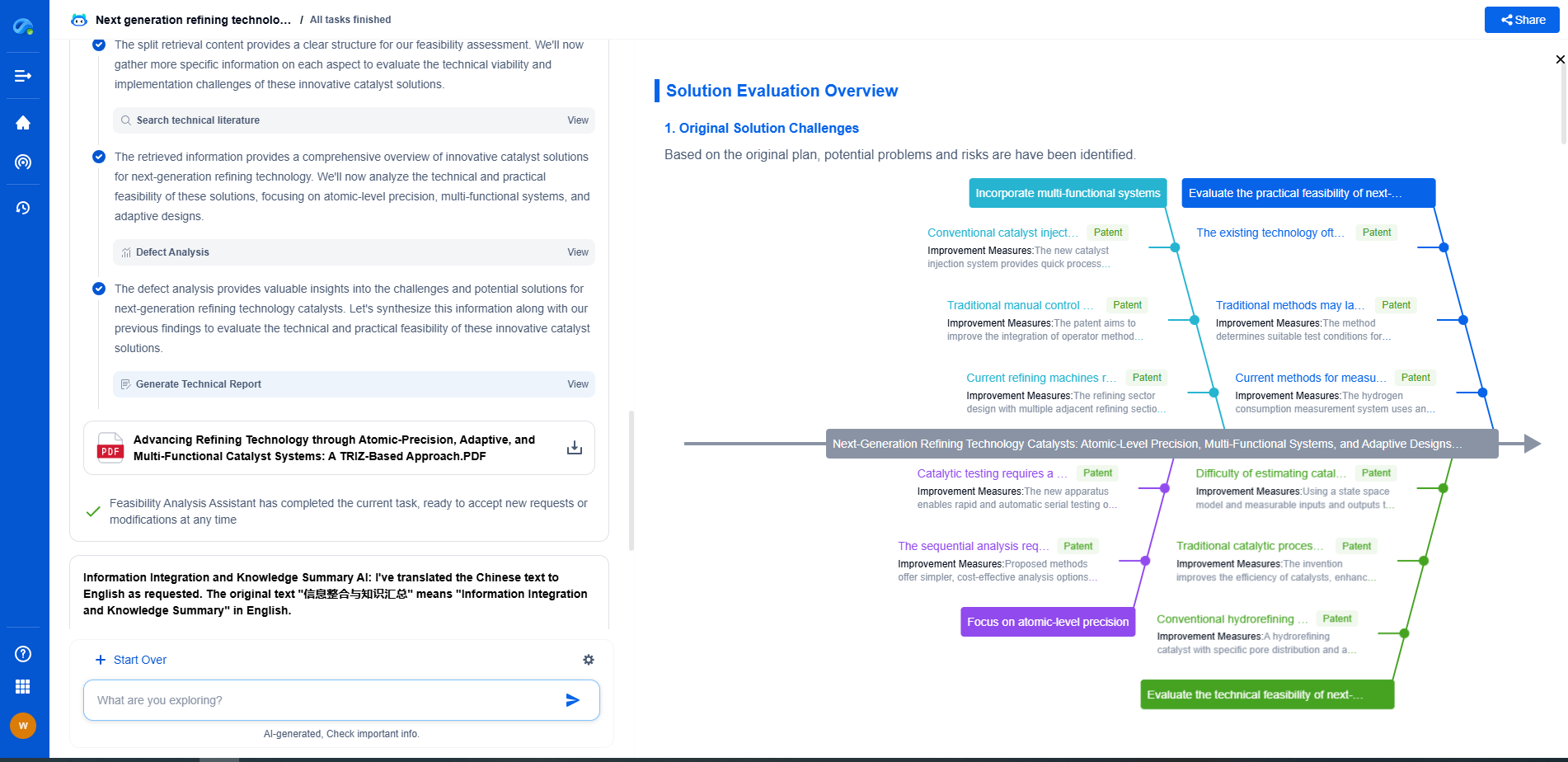
Steps to Safely Replace Tantalum Capacitors with Polymer Capacitors
1. Identify the Right Polymer Capacitor
The first step in replacing a tantalum capacitor is to identify the suitable polymer capacitor that matches the required specifications. This involves verifying parameters like capacitance, voltage rating, and physical size to ensure compatibility with the circuit design.
2. Evaluate Electrical Requirements
Analyze the circuit's electrical requirements, focusing on aspects like the ripple current, frequency response, and temperature stability. Polymer capacitors generally perform better in these areas, but it's crucial to ensure they meet the specific needs of your application.
3. Check Voltage Ratings and Derating
Polymer capacitors typically have different voltage ratings compared to tantalum capacitors. Ensure that the chosen polymer capacitor can handle the operating voltage with an adequate safety margin. Implement derating practices to enhance reliability, ensuring the capacitor operates well below its maximum voltage capacity.
4. Analyze Size and Form Factor
While polymer capacitors often offer similar or superior performance in a smaller package, the physical size must be compatible with your existing circuit board layout. Confirm that the new capacitor fits within the design without causing interference with other components.
5. Consider Environmental Factors
Consider the environmental conditions the capacitors will be exposed to, such as temperature fluctuations and humidity. Polymer capacitors generally perform well under a wide range of conditions, but it's essential to ensure they will be reliable in your specific application environment.
6. Perform Testing and Validation
Before fully integrating the polymer capacitors into your system, conduct thorough testing to validate their performance. This includes checking for stability, efficiency, and overall compatibility with the circuit. Any anomalies should be addressed to avoid potential issues down the line.
7. Implement Gradual Transition
If you're replacing multiple tantalum capacitors in a large system, consider a phased approach. This allows for monitoring and evaluation of the performance of polymer capacitors in smaller segments before a complete transition. It also reduces the risk of widespread issues and provides an opportunity for troubleshooting.
Conclusion
Replacing tantalum capacitors with polymer capacitors can significantly enhance the safety, performance, and environmental impact of electronic systems. By carefully selecting the right polymer capacitors and following a structured replacement process, you can ensure a seamless transition while maintaining the reliability and efficiency of your applications. Always prioritize thorough testing and validation to safeguard against potential issues, and embrace the benefits of modern capacitor technology.
Looking to accelerate your capacitor innovation pipeline?
As capacitor technologies evolve—from miniaturized MLCCs for smartphones to grid-scale energy storage devices—so must the way your team accesses critical knowledge.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Try Patsnap Eureka now and discover a faster, smarter way to research and innovate in capacitor technology.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com