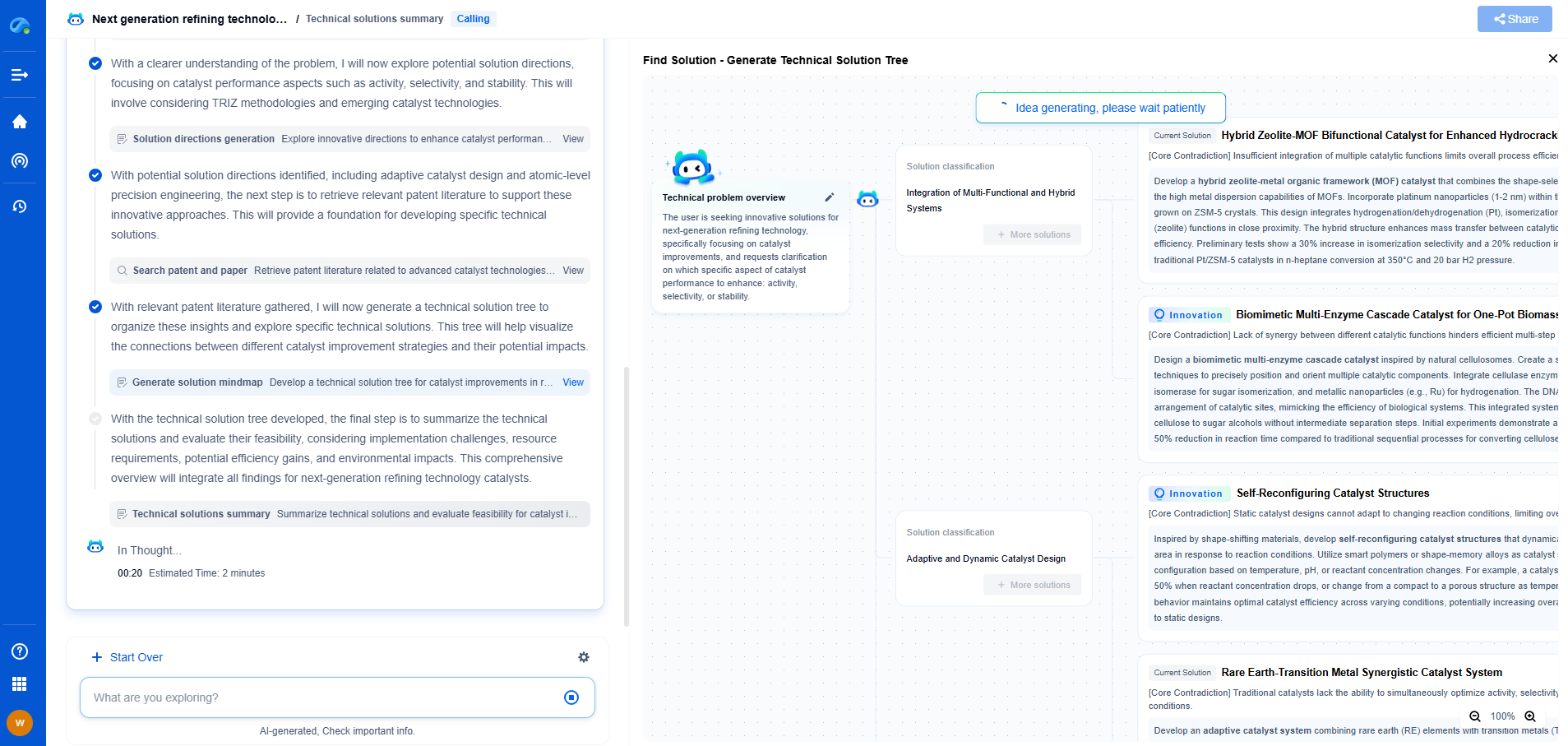
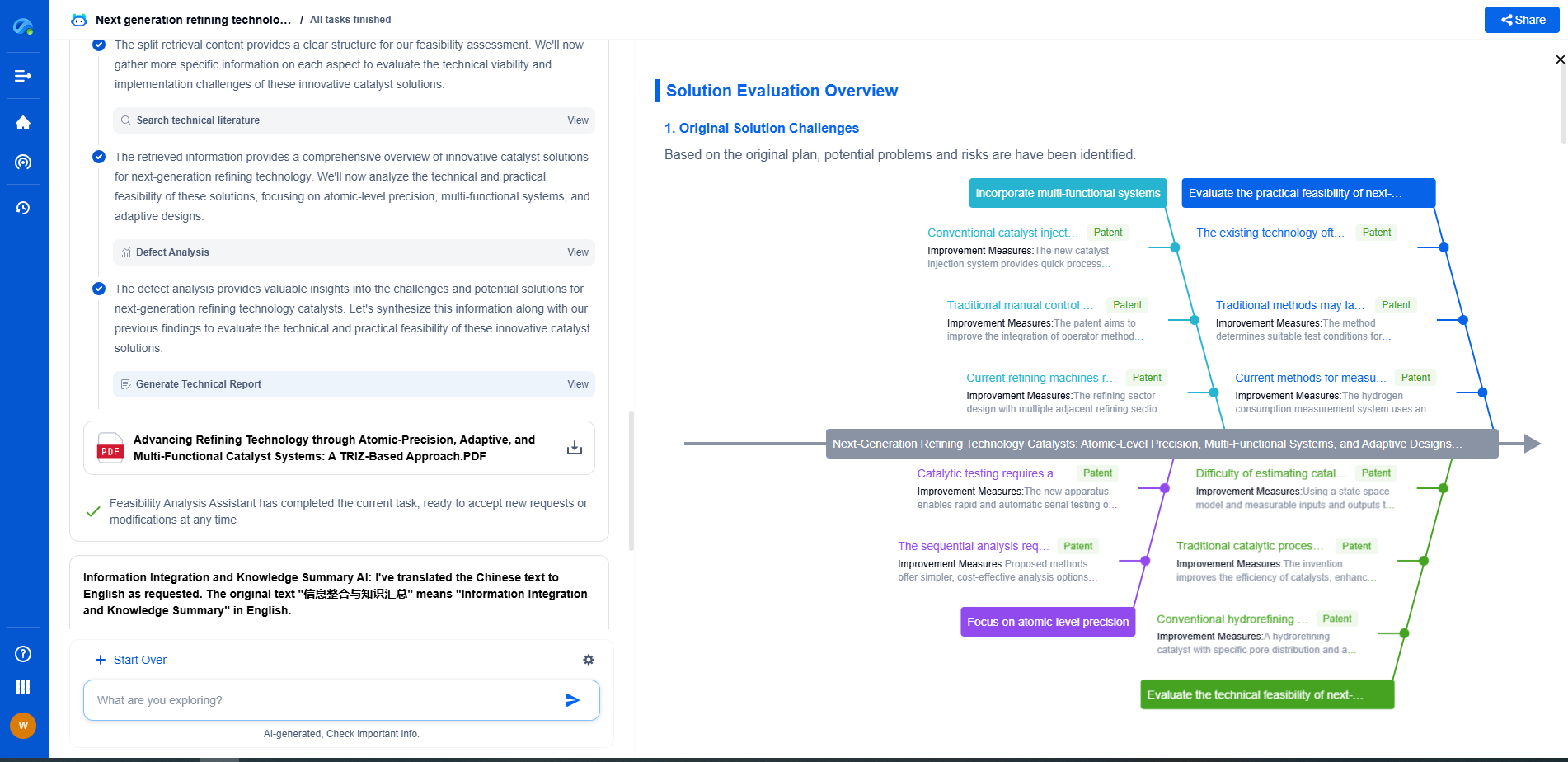
How to Use a Laser Doppler Vibrometer for Non-Contact Vibration Analysis
JUL 16, 2025 |
Laser Doppler Vibrometry (LDV) is a sophisticated technique employed for non-contact vibration measurement and analysis. This method is renowned for its precision and ability to analyze vibrations without physically contacting the object. Whether it's in the aerospace industry, automotive sector, or even in civil engineering, understanding how to effectively use an LDV can greatly enhance your vibration analysis capabilities. This article will guide you through the process of using a Laser Doppler Vibrometer for non-contact vibration analysis, from understanding its components to interpreting the results.
Understanding the Basics of Laser Doppler Vibrometry
At its core, a Laser Doppler Vibrometer consists of a laser source, an optical system, and a photodetector. The laser source emits a beam of laser light, which is directed towards the surface of the vibrating object. As the light reflects off the moving surface, the frequency of the reflected light shifts slightly due to the Doppler effect. This frequency shift is proportional to the velocity of the surface's vibration. The photodetector captures the reflected light, and the system then analyzes the frequency shift to calculate the vibration velocity.
Setting Up the Equipment
Setting up an LDV for vibration measurement involves several important steps:
1. Positioning the LDV: Ensure the LDV is securely mounted on a stable tripod or a fixed structure to prevent any movement during measurement. Align the laser head precisely with the surface of the object under study. The laser beam should strike the surface perpendicularly to obtain accurate measurements.
2. Adjusting the Focus: Use the focusing mechanism to ensure that the laser beam is sharply focused on the target surface. This helps in maximizing the signal quality and accuracy of the measurement.
3. Calibration: Before starting the measurement, calibrate the LDV system according to the manufacturer's instructions. Calibration involves setting the system's sensitivity and ensuring that the measurements are accurate.
Conducting the Vibration Measurement
Once the LDV is set up, you can begin the measurement process:
1. Select the Measurement Parameters: Determine the parameters you need to measure, such as vibration velocity, displacement, or acceleration. Configure the LDV system to capture these parameters.
2. Start the Measurement: Initiate the data acquisition process. The LDV will continuously monitor the surface vibrations and record the data. Ensure that environmental factors, like temperature and humidity, are within acceptable limits to prevent interference with the measurements.
3. Monitoring the Measurement: During the measurement, observe the real-time data to ensure there is no loss of signal or unexpected anomalies. This can help in making necessary adjustments on the spot.
Analyzing and Interpreting the Data
After data collection, the next step is analysis:
1. Data Processing: Use specialized software provided by the LDV manufacturer to process the raw data. This software helps in converting the frequency shifts into meaningful vibration information.
2. Interpreting the Results: Analyze the processed data to understand the vibration characteristics of the object. Look for patterns, peak frequencies, and any abnormalities that might indicate issues with the object being tested.
3. Reporting: Compile the results into a comprehensive report. Include graphs, charts, and any other visual aids that can help in conveying the findings effectively.
Applications and Benefits of LDV
Laser Doppler Vibrometry offers several advantages over traditional contact-based vibration measurement techniques:
1. Non-Contact Measurement: LDV allows for the measurement of delicate or difficult-to-reach objects without physical contact, reducing the risk of altering the object's natural vibration characteristics.
2. High Precision: The laser-based approach provides highly accurate and repeatable measurements, making it ideal for detailed vibration analysis.
3. Versatility: LDV can be used across various industries and applications, from testing mechanical components to monitoring large structures like bridges and buildings.
Conclusion
Using a Laser Doppler Vibrometer for non-contact vibration analysis provides unparalleled precision and convenience. By following the outlined steps for setting up, measuring, and analyzing vibrations, you can harness the full potential of LDV technology. Whether you're troubleshooting mechanical systems or conducting advanced research, mastering LDV can significantly enhance your vibration analysis endeavors.
In the world of vibration damping, structural health monitoring, and acoustic noise suppression, staying ahead requires more than intuition—it demands constant awareness of material innovations, sensor architectures, and IP trends across mechanical, automotive, aerospace, and building acoustics.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚙️ Bring Eureka into your vibration intelligence workflow—and reduce guesswork in your R&D pipeline. Start your free experience today.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com