Introduction to Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems (TPMS): Sensors and Signals
JUL 14, 2025 |
As vehicles become more advanced, so too do the technologies designed to keep drivers safe. One such innovation is the Tire Pressure Monitoring System (TPMS), a crucial safety feature in modern vehicles. This article delves into the fundamentals of TPMS, exploring how these systems work, the types of sensors involved, and the signals they use to communicate crucial information to drivers.
The Importance of Tire Pressure
Before diving into TPMS specifics, it's vital to understand why maintaining proper tire pressure is so important. Incorrect tire pressure can lead to a host of problems, including reduced fuel efficiency, increased tire wear, and compromised vehicle handling. In extreme cases, it can even cause tire blowouts, leading to dangerous situations on the road. TPMS helps mitigate these risks by alerting drivers to any significant changes in tire pressure.
Types of TPMS
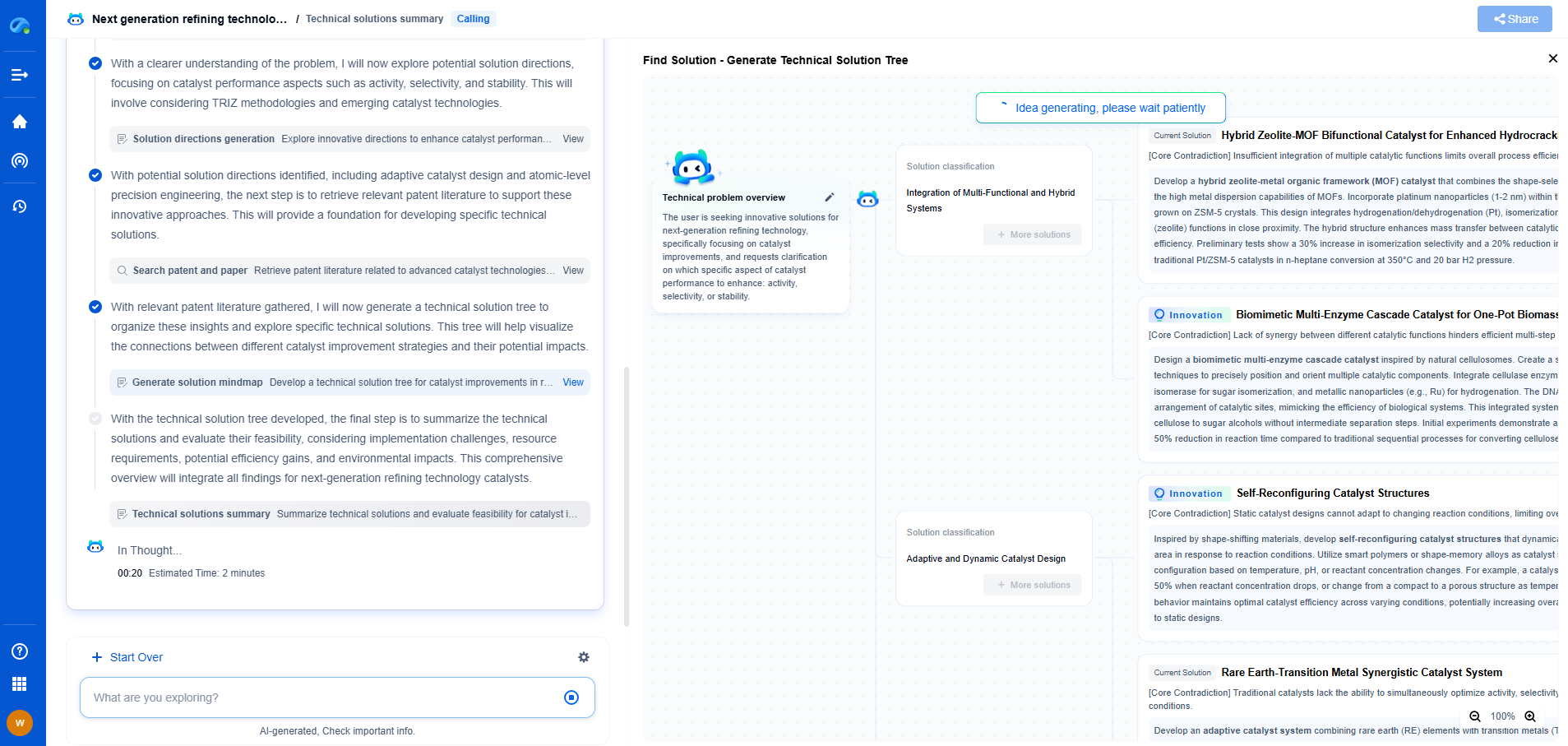
There are generally two types of TPMS: Direct and Indirect systems. Each type has its own unique approach to monitoring tire pressure.
Direct TPMS
Direct TPMS uses sensors mounted inside each tire to directly measure air pressure. These sensors transmit data to a central control module, which then displays the information on the vehicle's dashboard. If the pressure in any tire falls below a certain threshold, the system triggers a warning light to alert the driver. Direct TPMS provides accurate, real-time tire pressure data, making it a reliable choice for monitoring tire condition.
Indirect TPMS
Indirect TPMS, on the other hand, does not measure air pressure directly. Instead, it uses data from the vehicle's anti-lock braking system (ABS) to monitor wheel speed. Since under-inflated tires rotate at a different speed compared to properly inflated ones, the system can infer potential pressure issues. While indirect TPMS can be less accurate than direct systems, it is generally more cost-effective and easier to maintain.
How TPMS Sensors Work
The heart of any TPMS is the sensor. In direct systems, each sensor is typically attached to the tire's valve stem or mounted inside the tire itself. These sensors are powered by small batteries and consist of a pressure sensor, a transmitter, and a microcontroller.
The pressure sensor measures the tire's air pressure and converts this information into an electrical signal. The microcontroller processes this signal and sends it via radio frequency (RF) to the vehicle's central receiver. The receiver then interprets the data and communicates it to the driver through the dashboard display.
In indirect systems, the sensors are part of the vehicle’s existing ABS, measuring wheel rotation speeds to detect discrepancies that may indicate pressure issues.
Interpreting TPMS Signals
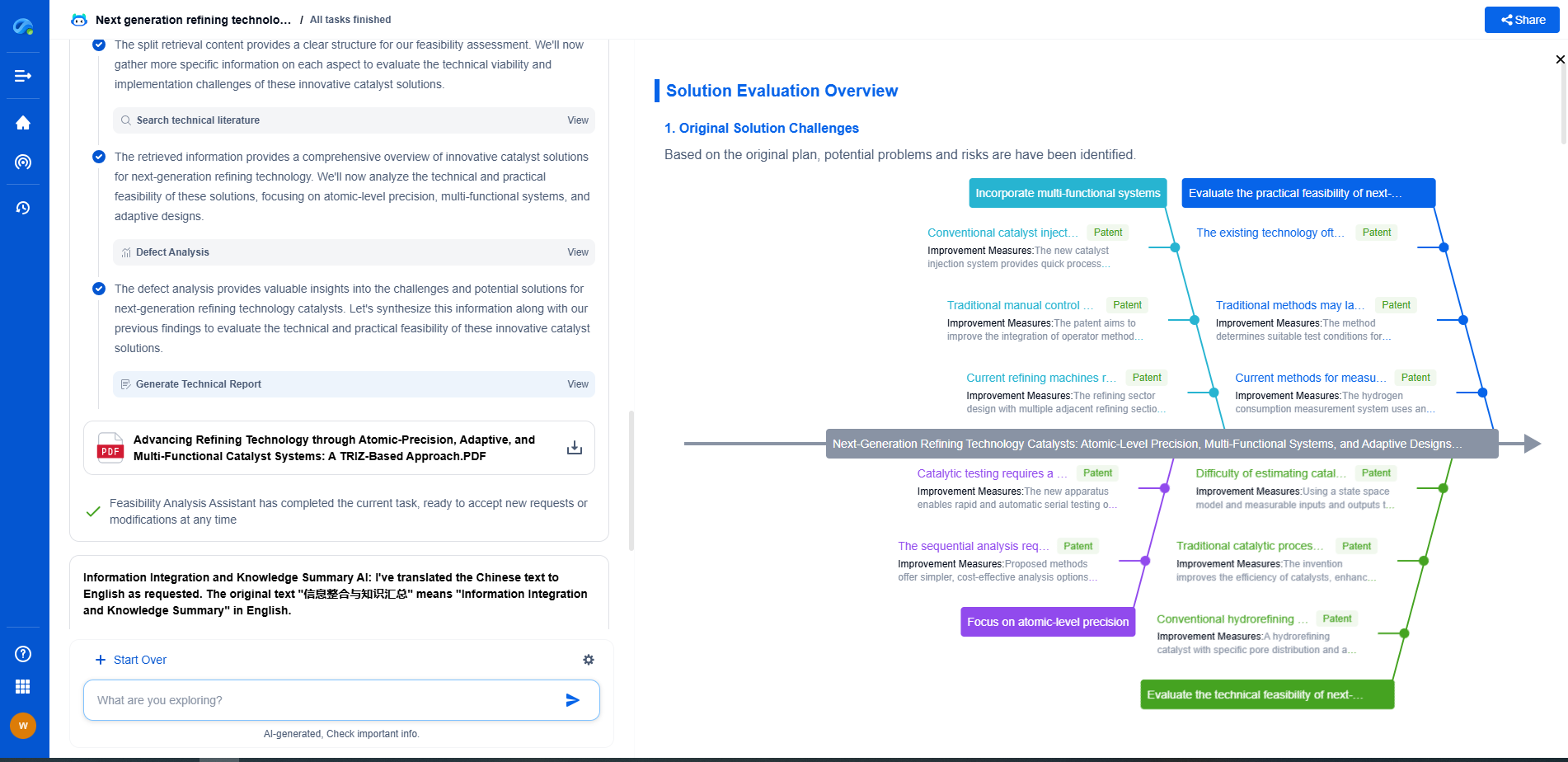
Understanding the signals sent by your TPMS is crucial for vehicle safety. When the TPMS warning light illuminates on your dashboard, it’s essential to confirm which tire is affected and address the issue promptly. Some systems provide additional information, such as the current pressure of each tire, allowing for more precise adjustments.
Regular maintenance and timely replacement of TPMS components, especially the sensors, are necessary to ensure the system's accuracy and reliability. Over time, sensor batteries can deplete, and components may wear out, necessitating replacement to maintain optimal function.
Conclusion
TPMS is an invaluable tool for modern drivers, enhancing road safety and vehicle efficiency by keeping track of tire pressure. Whether through direct or indirect systems, TPMS offers critical real-time alerts that help prevent potential tire-related issues. Understanding how these systems work and the importance of maintaining them can make a significant difference in your driving experience, ensuring both safety and peace of mind every time you hit the road.
From 5G NR to SDN and quantum-safe encryption, the digital communication landscape is evolving faster than ever. For R&D teams and IP professionals, tracking protocol shifts, understanding standards like 3GPP and IEEE 802, and monitoring the global patent race are now mission-critical.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
📡 Experience Patsnap Eureka today and unlock next-gen insights into digital communication infrastructure, before your competitors do.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com