ISO 10816 Vibration Severity Standards: Interpreting Machinery Thresholds
JUL 16, 2025 |
Machinery vibration analysis plays a pivotal role in predictive maintenance and the early detection of potential equipment failures. Among the various standards developed to aid in this, the ISO 10816 series stands out as a comprehensive guide for assessing the mechanical vibration of non-rotating and rotating machinery. Understanding these standards is crucial for maintenance professionals, engineers, and technicians involved in machinery health monitoring.
What is ISO 10816?
The ISO 10816 standard provides a framework for evaluating the severity of mechanical vibrations in a wide range of machines. Primarily, it focuses on vibration measurements taken at the bearing points of machines to determine their structural integrity and operational efficiency. The standard is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operations, reducing downtime, and preventing unexpected equipment failures.
Key Components of ISO 10816
ISO 10816 is divided into several parts, each addressing different types of machinery and specific conditions. The standard categorizes machinery into different groups based on power, speed, and construction, and provides guidelines for interpreting vibration severity.
1. Measurement Locations and Conditions
ISO 10816 specifies the measurement locations on a machine, typically at the bearings, where vibrations are most pronounced. It is vital to ensure that measurements are taken under normal operating conditions to obtain accurate and reliable data.
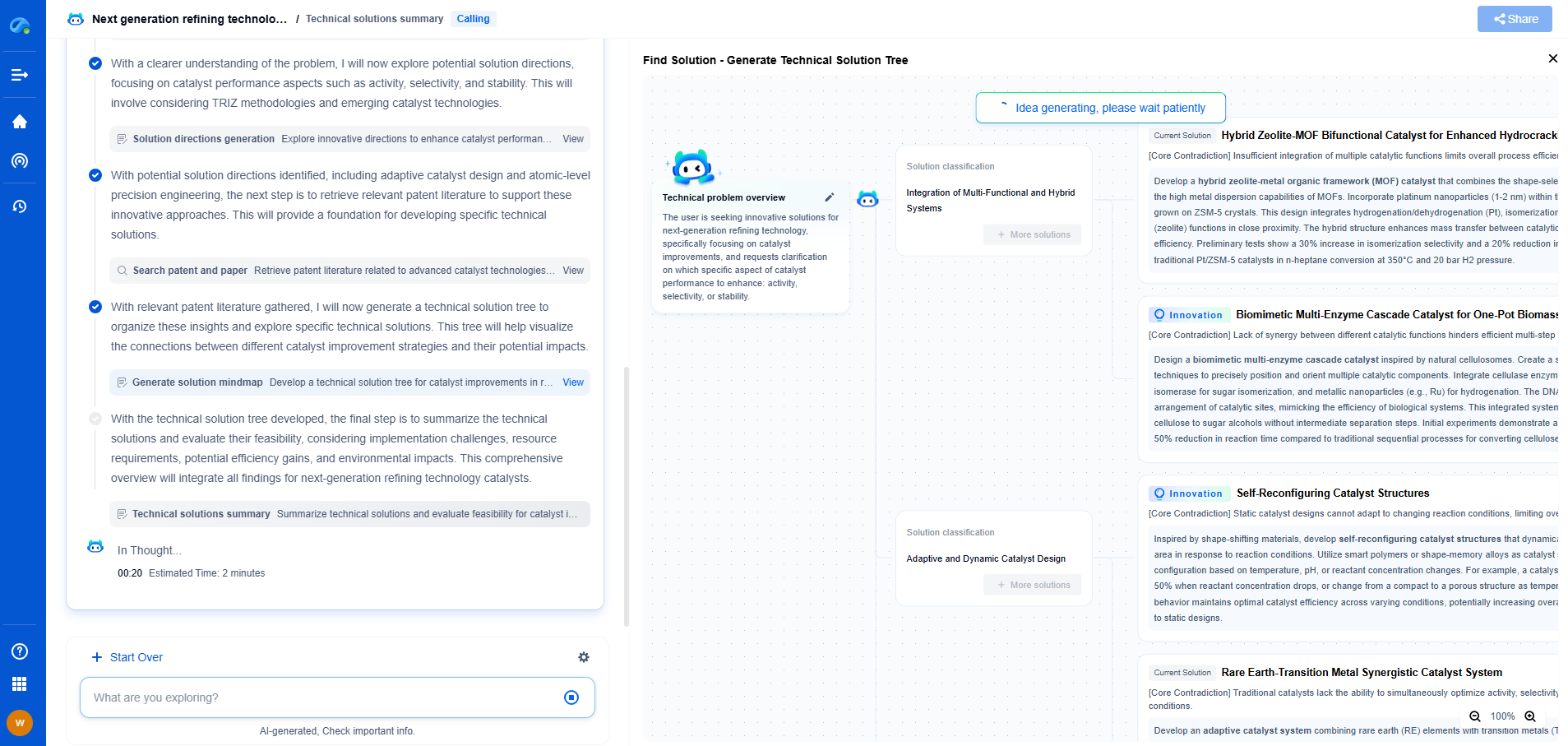
2. Vibration Severity Zones
One of the core aspects of ISO 10816 is the classification of vibration levels into four severity zones. These zones help in interpreting the vibration measurements and determining the condition of the machinery:
- Zone A: Good Condition – The machine is in excellent operational condition, with no immediate concerns.
- Zone B: Satisfactory Condition – The machine is operating satisfactorily, but some monitoring is advised.
- Zone C: Unsatisfactory Condition – The machine may be at risk of failure; maintenance should be scheduled.
- Zone D: Unacceptable Condition – Immediate action is required to address significant risk of failure.
Interpreting Vibration Thresholds
Understanding and interpreting vibration thresholds is critical for maintenance decisions and ensuring machinery reliability. Each machine type and operational condition will have specific thresholds defined in the ISO 10816 standard. By comparing the measured vibration values against these thresholds, maintenance teams can make informed decisions.
For example, a pump operating under normal conditions with vibration measurements within Zone A might require no immediate action. However, the same pump showing Zone C vibration levels may need immediate attention to avoid costly downtime or potential damage.
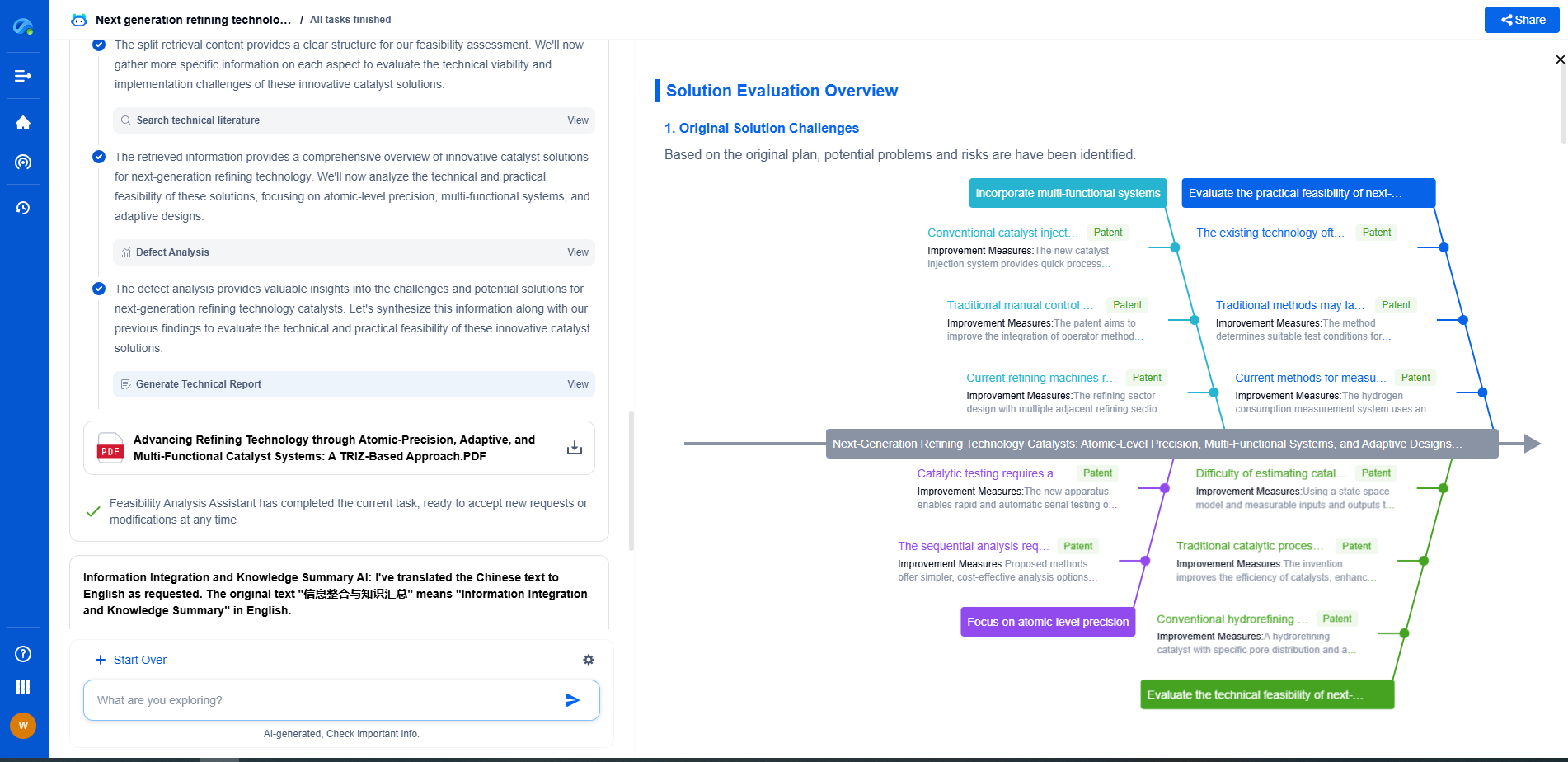
Applications Across Industries
The ISO 10816 standard is applicable across various industries, including manufacturing, energy, and transportation. In manufacturing, maintaining optimal vibration levels is crucial for ensuring product quality and minimizing machine wear. In the energy sector, particularly for large rotating equipment like turbines, adhering to vibration guidelines is essential for maintaining efficiency and safety.
In transportation, the standard helps in monitoring the health of engines and other rotating components, ensuring reliability and longevity. By applying ISO 10816 guidelines, industries can enhance machinery lifespan, improve safety, and reduce maintenance costs.
Benefits of Adhering to ISO 10816
Adhering to the ISO 10816 standard offers several advantages. It helps in the early detection of mechanical issues, reducing the risk of catastrophic failures. By identifying problems early, companies can plan maintenance activities more effectively, minimizing unscheduled downtime.
Moreover, the standard provides a common language for discussing vibration issues, facilitating better communication among engineers, technicians, and management. This shared understanding helps in prioritizing maintenance tasks and allocating resources efficiently.
Conclusion
ISO 10816 serves as an essential tool in the field of machinery maintenance and reliability. By providing clear guidelines for measuring and interpreting vibration severity, it enables industries to maintain equipment health and optimize operational efficiency. Understanding and applying these standards can lead to significant cost savings and enhanced safety, making it a valuable asset for any maintenance program.
In the world of vibration damping, structural health monitoring, and acoustic noise suppression, staying ahead requires more than intuition—it demands constant awareness of material innovations, sensor architectures, and IP trends across mechanical, automotive, aerospace, and building acoustics.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚙️ Bring Eureka into your vibration intelligence workflow—and reduce guesswork in your R&D pipeline. Start your free experience today.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com