Lifecycle Assessment of PZT Ceramics: Environmental Impact of Lead-Based Materials
JUL 16, 2025 |
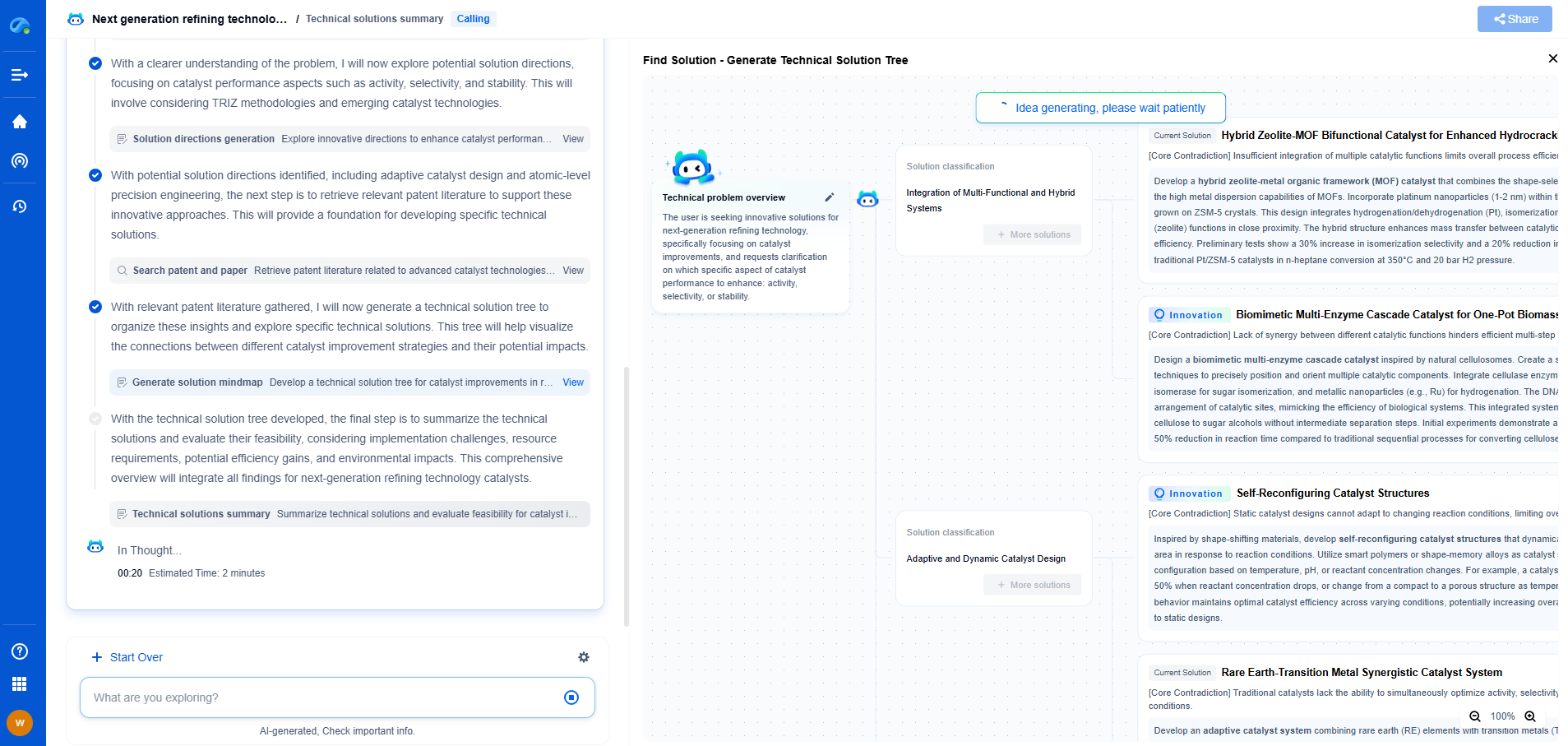
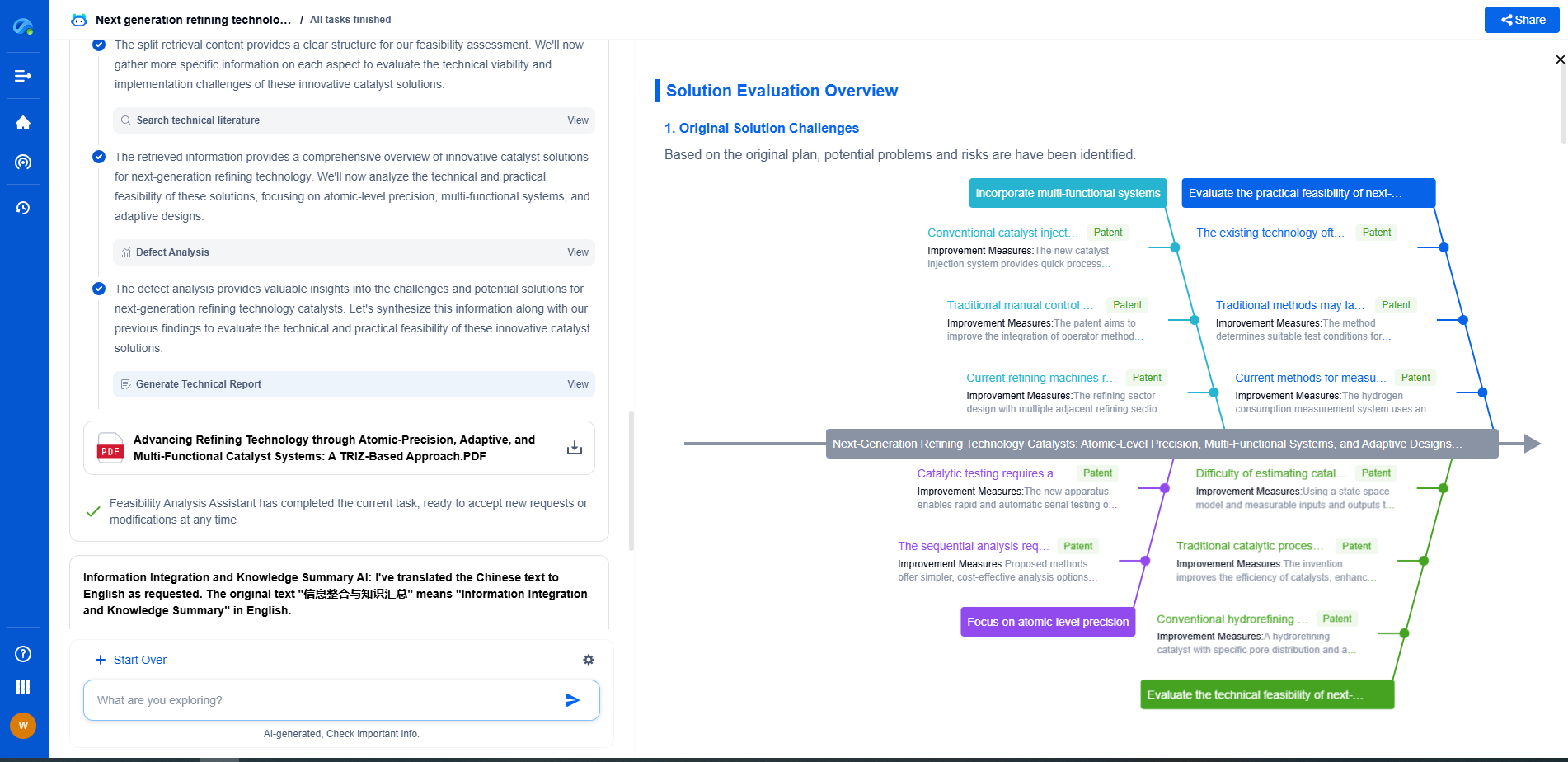
Piezoelectric materials have become indispensable in various technological applications, from everyday consumer electronics to advanced medical devices. Among these, lead zirconate titanate (PZT) ceramics stand out for their remarkable efficiency and adaptability. However, the reliance on lead-based materials raises critical environmental and health concerns that necessitate a comprehensive lifecycle assessment to understand their impact and explore sustainable alternatives.
Production and Raw Material Extraction
The lifecycle of PZT ceramics begins with raw material extraction, where the environmental footprint is significant. Mining lead, zirconium, and titanium involves energy-intensive processes that result in substantial greenhouse gas emissions and habitat disruption. Lead, a core component of PZT, poses particular challenges due to its toxicity. During extraction and refinement, lead can leach into the soil and waterways, posing risks to ecosystems and human health in surrounding communities. It’s crucial to monitor and mitigate these impacts through stricter regulatory frameworks and improved extraction technologies.
Manufacturing and Processing
The manufacturing process of PZT ceramics involves high-temperature sintering and precise compositional control, which consumes large amounts of energy and materials. The handling of lead during manufacturing requires stringent safety protocols to protect workers from exposure. Despite advances in technology, dust and waste generated during production can still pose environmental risks. Implementing closed-loop systems and recycling initiatives can help reduce waste and lower the environmental burden associated with manufacturing.
Usage and Performance
In their operational phase, PZT ceramics are lauded for their efficiency and reliability, contributing to energy savings in devices they power. However, considering the entire lifecycle, their environmental benefits during usage do not offset the negative impacts accrued during earlier stages. Moreover, the potential for lead leaching remains a concern, particularly in applications where PZT materials are subjected to mechanical stress or high temperatures. Continued research into encapsulation techniques and alternative materials is vital to enhance safety and sustainability during use.
End-of-Life Disposal
The end-of-life stage of PZT ceramics presents significant environmental challenges. Disposal often results in lead contamination, either through improper waste management practices or when devices are discarded in landfills. Recycling PZT ceramics is currently limited by the complexity and cost of separating lead from other constituents. Developing cost-effective recycling technologies and establishing comprehensive e-waste recycling programs can play a crucial role in mitigating environmental impacts.
Alternatives and Future Directions
In response to the environmental concerns associated with PZT ceramics, researchers are exploring lead-free alternatives such as bismuth sodium titanate (BNT) and potassium sodium niobate (KNN). These materials show promise in delivering similar piezoelectric properties while eliminating the risks associated with lead. Transitioning to these alternatives, however, faces challenges including material availability, processing costs, and performance optimization. Continued investment in research and development, combined with supportive policy measures, will be essential to facilitate this transition.
Conclusion
The lifecycle assessment of PZT ceramics highlights the considerable environmental impacts associated with lead-based materials. While PZT ceramics offer unmatched performance in numerous applications, the environmental and health risks posed by lead demand urgent attention and action. By advancing towards lead-free alternatives and adopting more sustainable practices across the lifecycle stages, we can strive towards a future where piezoelectric technologies are not only efficient but also environmentally responsible. As stakeholders in this ecosystem, manufacturers, researchers, policymakers, and consumers must collaborate to drive this transformation and ensure a sustainable path forward.
In the world of vibration damping, structural health monitoring, and acoustic noise suppression, staying ahead requires more than intuition—it demands constant awareness of material innovations, sensor architectures, and IP trends across mechanical, automotive, aerospace, and building acoustics.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚙️ Bring Eureka into your vibration intelligence workflow—and reduce guesswork in your R&D pipeline. Start your free experience today.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com