MLCC vs. Tantalum Capacitors: Which Is Better for Medical Applications?
JUL 9, 2025 |
Capacitors are fundamental components in electronic circuits, serving functions such as energy storage, signal filtering, and power management. In medical devices, where reliability, precision, and safety are paramount, the choice of capacitor can significantly impact performance. Among the various types, Multi-Layer Ceramic Capacitors (MLCCs) and Tantalum Capacitors are commonly considered for medical electronics. Each type presents unique characteristics, advantages, and limitations, influencing their suitability for specific medical technologies.
Understanding MLCCs and Their Benefits
MLCCs are widely used in the electronics industry due to their compact size, high capacitance per unit volume, and excellent frequency characteristics. These capacitors are composed of multiple layers of ceramic dielectric material and metal electrodes. Their high volumetric efficiency makes them ideal for applications where space is limited, a frequent requirement in medical devices like pacemakers and hearing aids.
One of the primary benefits of MLCCs is their low Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR), which contributes to minimal loss and high efficiency in power applications. Additionally, MLCCs are less prone to failure due to their robust construction, offering a reliable choice for devices that require consistent performance over long periods. The absence of liquid electrolytes also means that MLCCs are free from risks related to leakage and corrosion, enhancing their longevity and reliability in critical medical applications.
Exploring Tantalum Capacitors and Their Advantages
Tantalum capacitors, on the other hand, are known for their high capacitance values and stability over a wide temperature range. They are constructed using a tantalum metal anode covered by a thin insulating oxide layer, which acts as the dielectric. This structure enables tantalum capacitors to deliver high capacitance in small package sizes, a valuable trait for complex medical devices that necessitate high power in a compact form factor.
Tantalum capacitors are particularly advantageous in applications requiring stable performance in varying environmental conditions, making them suitable for implantable devices that must operate reliably within the human body. Their self-healing properties also provide a level of resilience against dielectric breakdown, further enhancing their suitability for long-term medical use.
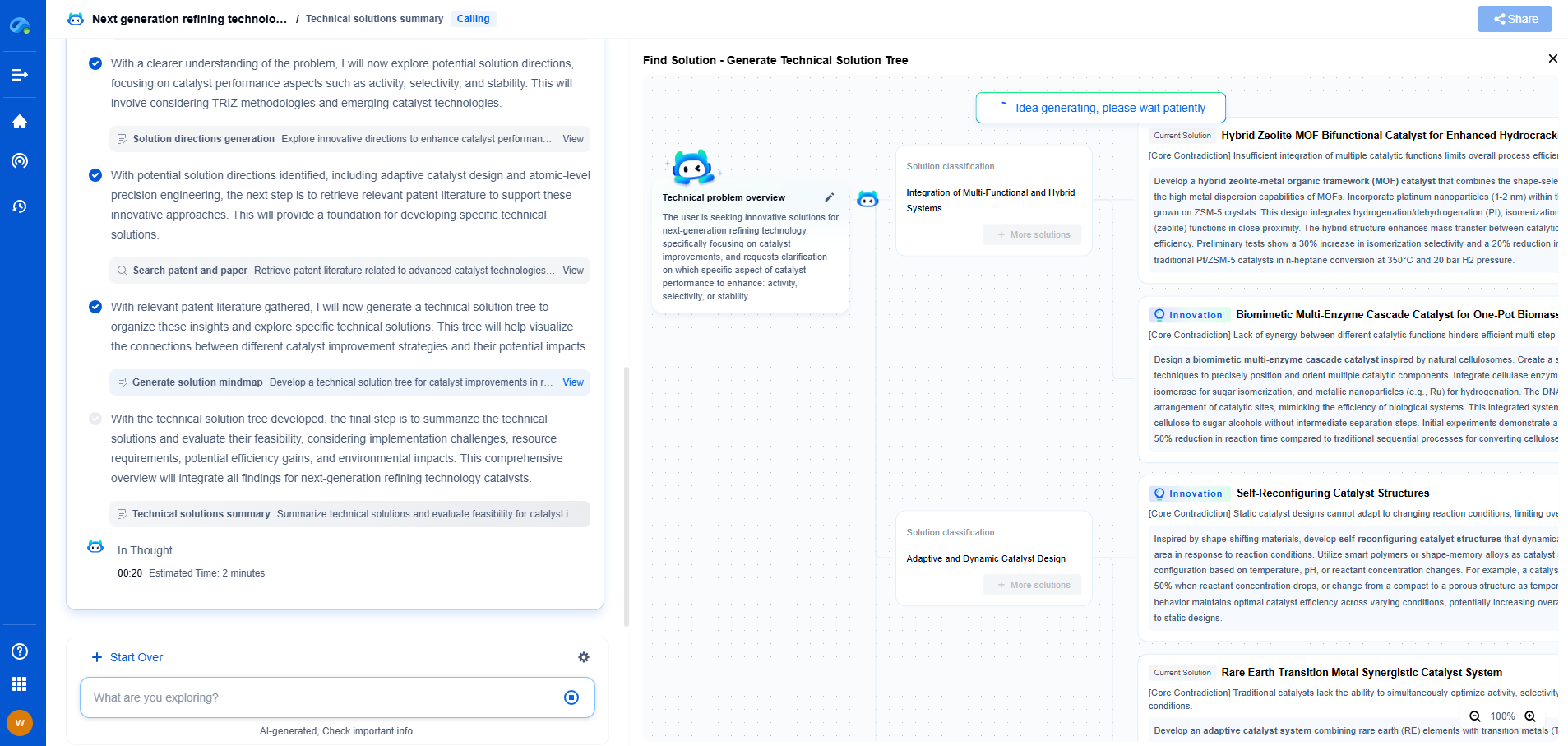
Comparative Analysis: MLCCs vs. Tantalum Capacitors
When comparing MLCCs and tantalum capacitors for medical applications, several factors must be considered, including reliability, size, performance, and cost.
Reliability is a critical factor in medical devices, where failures can have serious consequences. MLCCs offer high reliability due to their solid-state construction, while tantalum capacitors provide robustness with their self-healing dielectric. Each type's reliability must be assessed in the context of specific medical applications.
Size and form factor are also crucial, particularly in portable and implantable devices. MLCCs often provide smaller sizes for a given capacitance, but tantalum capacitors can achieve higher capacitance values in compact designs, making them suitable for high-power applications in tight spaces.
Performance considerations include frequency response and temperature stability. MLCCs excel in high-frequency applications due to their low ESR and wide temperature range. In contrast, tantalum capacitors offer better performance in applications requiring high capacitance and low leakage current over a broad temperature spectrum.
Cost is always a consideration in device manufacturing. MLCCs are generally more cost-effective due to their widespread production and use. However, the specific requirements of a medical device may justify the higher cost of tantalum capacitors if their benefits align with the device's needs.
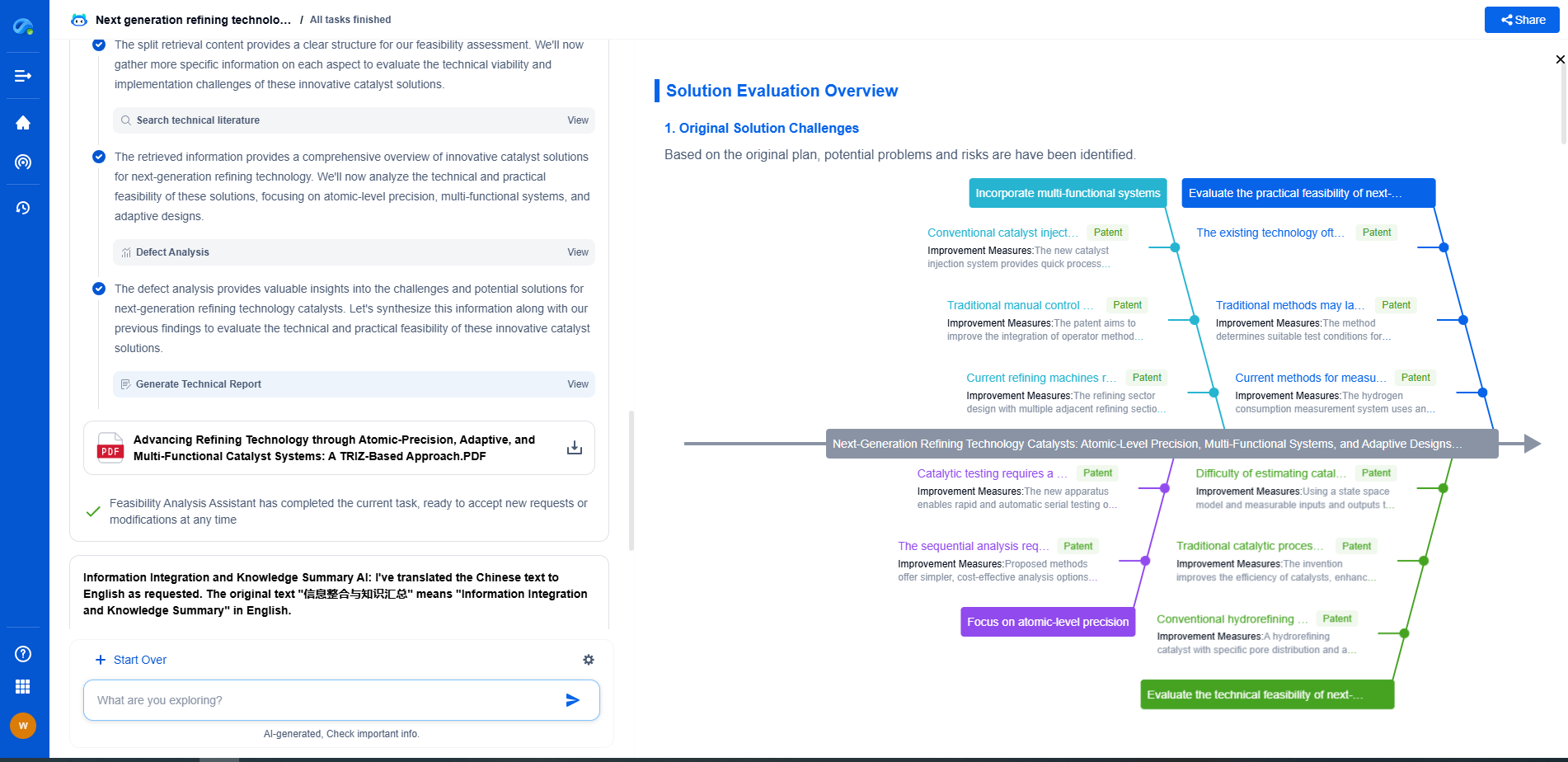
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Capacitor for Medical Devices
Ultimately, the choice between MLCCs and tantalum capacitors in medical applications depends on the specific requirements of the device. MLCCs are often preferred for their small size, low cost, and high frequency performance, making them suitable for a wide range of medical devices. Tantalum capacitors, while more expensive, provide high capacitance, stability, and reliability in demanding conditions, which may be necessary for certain critical applications.
In conclusion, the selection of capacitors for medical applications should be guided by a thorough understanding of the device's operational environment and requirements. Collaborating with experienced engineers and component suppliers can ensure the most appropriate capacitor choice, ultimately enhancing the performance and safety of medical technologies.
Looking to accelerate your capacitor innovation pipeline?
As capacitor technologies evolve—from miniaturized MLCCs for smartphones to grid-scale energy storage devices—so must the way your team accesses critical knowledge.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Try Patsnap Eureka now and discover a faster, smarter way to research and innovate in capacitor technology.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com