Molded vs. Hermetic Sealing: Which Offers Better Long-Term Reliability?
JUL 9, 2025 |
In the world of electronic and mechanical components, ensuring long-term reliability is crucial. The integrity and performance of these components can be significantly affected by environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and temperature fluctuations. To combat these issues, manufacturers often employ sealing techniques to protect their products. Two popular methods are molded and hermetic sealing. But which one offers better long-term reliability? In this blog post, we will explore both methods in detail, examining their advantages and disadvantages to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding Molded Sealing
Molded sealing involves encasing a component in a protective layer, typically made from materials like silicone, epoxy, or rubber. This method is widely used due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. Molded seals can be customized to fit a variety of shapes and sizes, making them ideal for components with complex geometries.
Advantages of Molded Sealing
1. Flexibility: Molded sealing offers a high degree of customization, allowing manufacturers to tailor the seal to fit specific components perfectly. This flexibility can be particularly beneficial for non-standard shapes and sizes.
2. Cost-effective: Compared to hermetic sealing, molded sealing is generally more affordable, making it an attractive option for budget-conscious projects.
3. Vibration and Shock Resistance: The materials used in molded sealing can absorb vibrations and shocks, providing additional protection for sensitive components.
Disadvantages of Molded Sealing
1. Limited Environmental Protection: While molded seals offer a certain level of protection against moisture and dust, they may not be as effective in extreme conditions, such as high-pressure environments or rapid temperature changes.
2. Wear and Tear: Over time, molded seals can degrade due to exposure to harsh environmental factors, potentially compromising their effectiveness.
Exploring Hermetic Sealing
Hermetic sealing involves creating an airtight and watertight seal around a component. This is typically achieved by using materials such as glass, metal, or ceramic. Hermetic seals are often employed in applications where maximum protection is necessary, such as aerospace, medical, and military devices.
Advantages of Hermetic Sealing
1. Superior Environmental Protection: Hermetic seals provide an airtight barrier that is highly effective in preventing moisture, dust, and other contaminants from reaching the component. This makes them ideal for use in harsh environments.
2. Longevity: Hermetic seals are known for their durability and ability to maintain their effectiveness over long periods, even in challenging conditions.
3. High-Temperature Tolerance: Hermetic seals can withstand extreme temperatures, making them suitable for applications where temperature fluctuations are a concern.
Disadvantages of Hermetic Sealing
1. Cost: The complexity and materials involved in hermetic sealing make it a more expensive option compared to molded sealing.
2. Limited Flexibility: Hermetic seals are less adaptable to non-standard shapes and sizes, which can limit their use in certain applications.
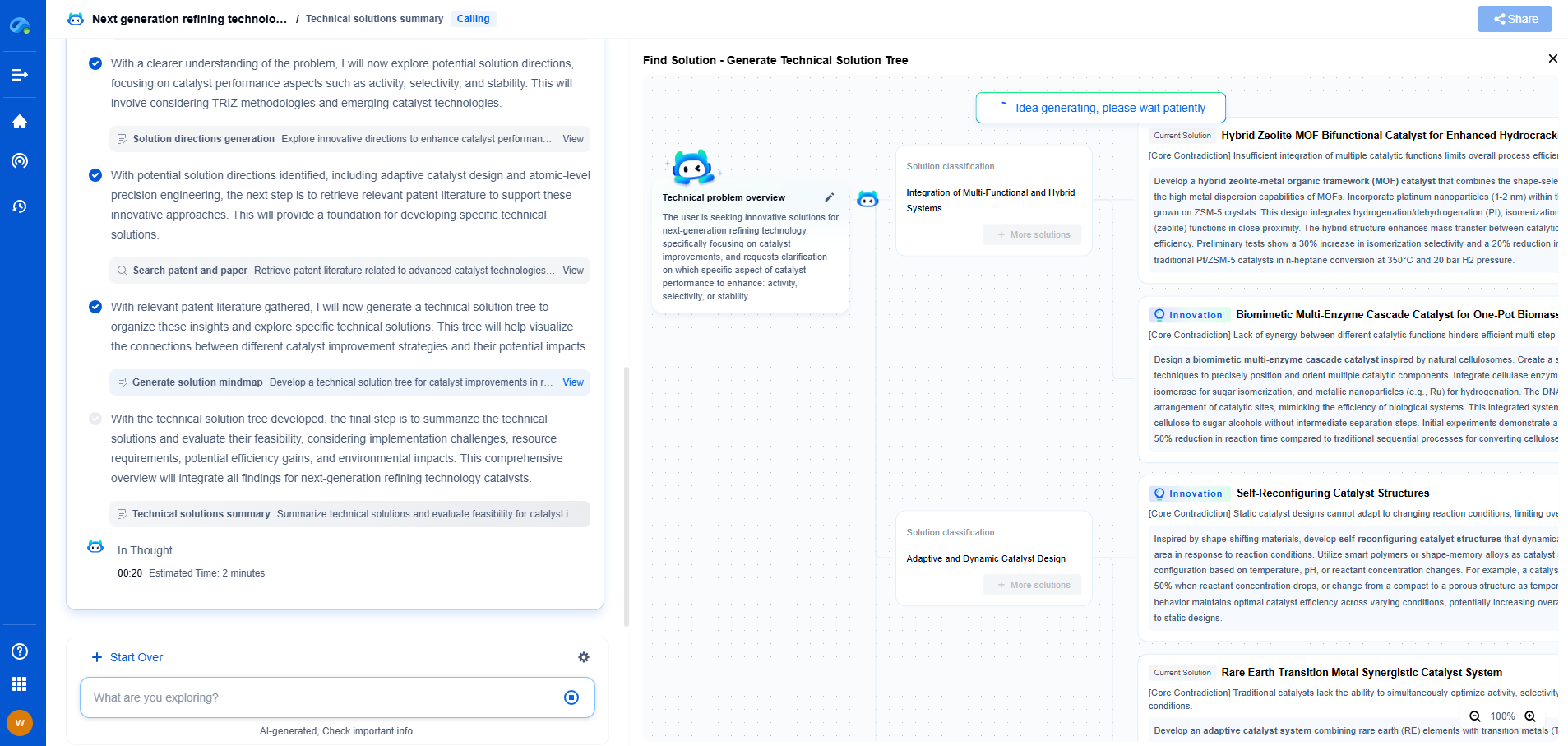
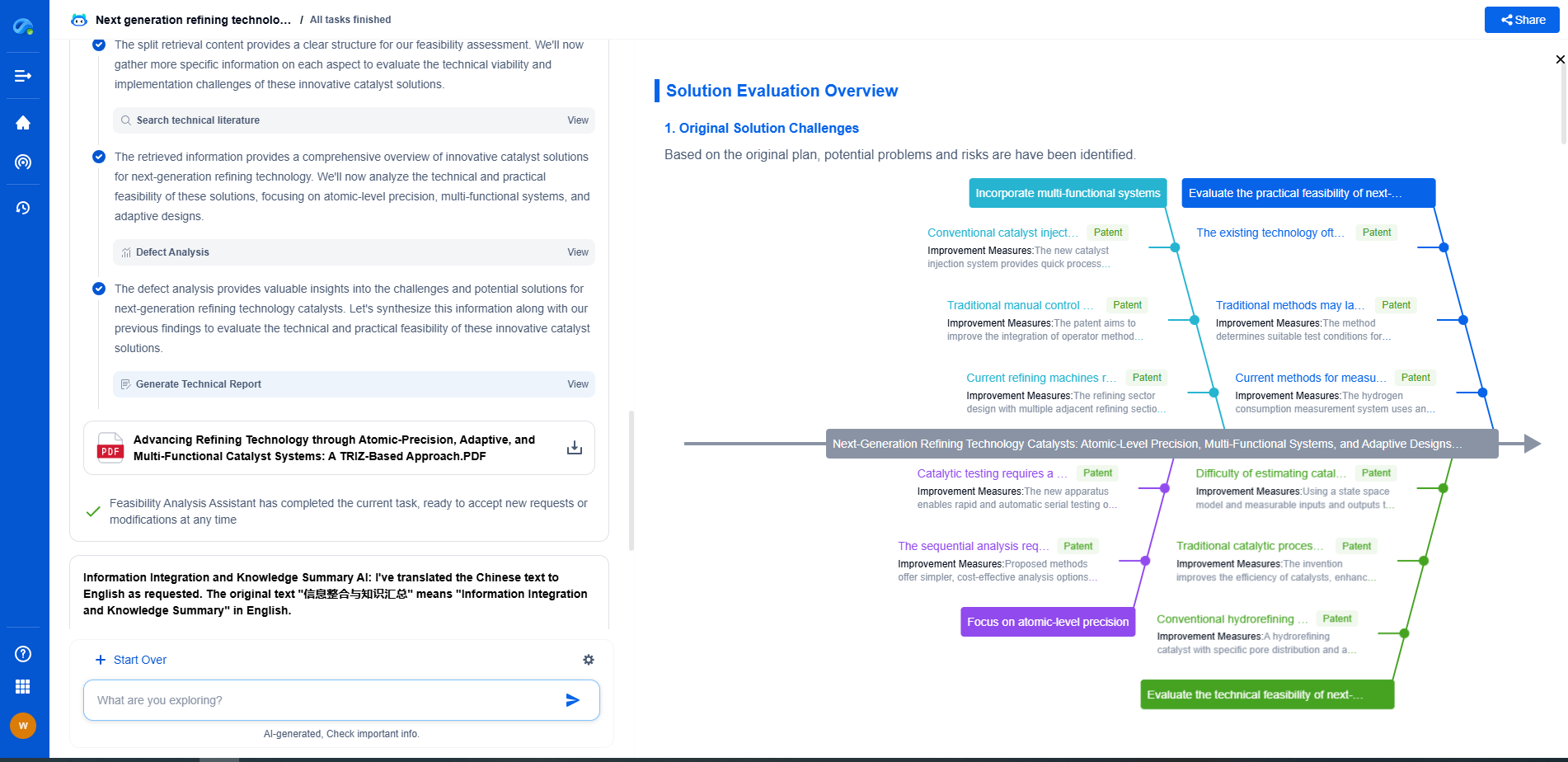
Comparing Long-Term Reliability
When it comes to long-term reliability, the choice between molded and hermetic sealing largely depends on the specific requirements of the application. Hermetic sealing offers superior protection and longevity, making it the preferred option for critical applications where failure is not an option. However, for less demanding environments, molded sealing can offer adequate protection at a lower cost.
Conclusion
Both molded and hermetic sealing have their unique strengths and weaknesses. Molded sealing is a flexible, cost-effective solution suitable for many general applications, while hermetic sealing provides unparalleled protection and durability for more demanding conditions. Understanding the specific needs of your application is key to determining which sealing method will offer the best long-term reliability. Ultimately, the right choice will depend on factors such as budget, environmental conditions, and the criticality of the component being protected.
Looking to accelerate your capacitor innovation pipeline?
As capacitor technologies evolve—from miniaturized MLCCs for smartphones to grid-scale energy storage devices—so must the way your team accesses critical knowledge.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Try Patsnap Eureka now and discover a faster, smarter way to research and innovate in capacitor technology.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com