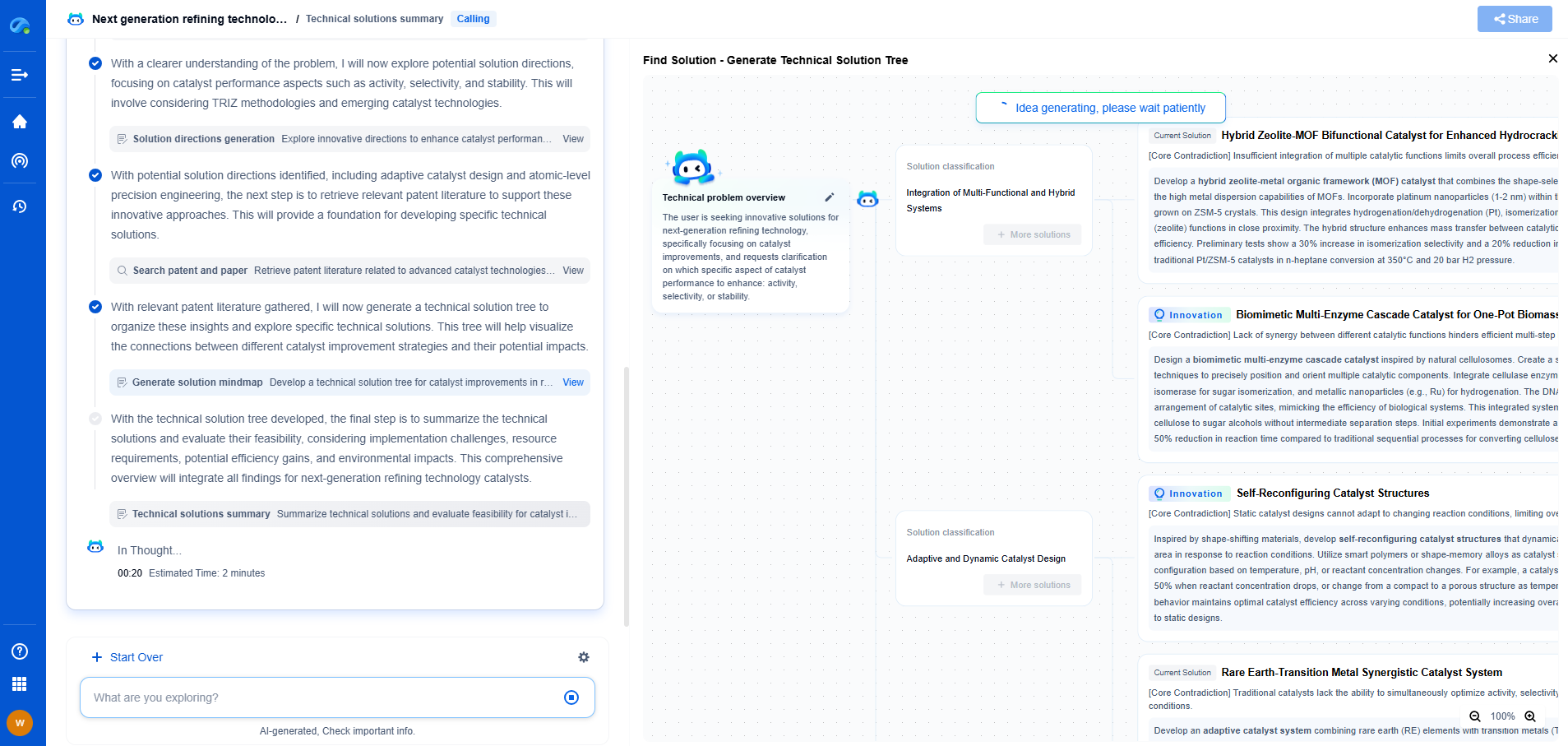
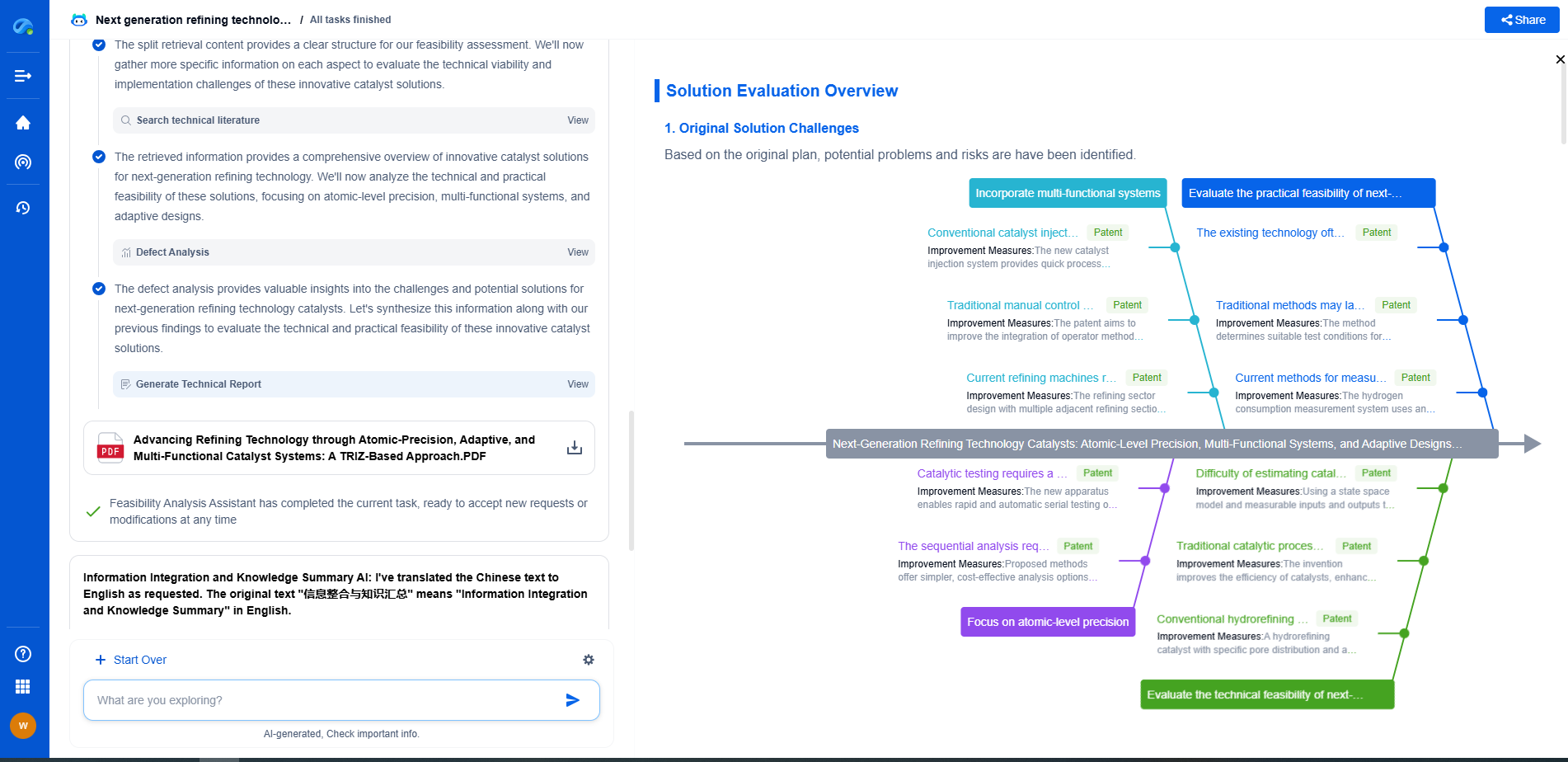
MQTT/OPC UA in IoT Metering: Protocols for Industrial Data Streaming
JUL 9, 2025 |
Understanding MQTT and OPC UA
Before delving into their applications, it's important to understand what MQTT and OPC UA fundamentally offer. MQTT is a lightweight messaging protocol designed for efficient communication between devices with limited resources and networks with low bandwidth. Its publish/subscribe model is particularly suited for scenarios where numerous devices need to send data to a central server or cloud application, making it a popular choice in IoT environments.
On the other hand, OPC UA is a more complex protocol designed for comprehensive, secure, and reliable data exchange in industrial automation systems. Unlike MQTT, which is simpler and more focused on data transmission, OPC UA offers a rich set of features including data modeling, semantic interoperability, and secure communication. This makes it ideal for industries with stringent requirements for data integrity and security.
Applications in IoT Metering
In the context of IoT metering—where devices collect and transmit data on energy consumption, water flow, and other metrics—both MQTT and OPC UA have distinct roles.
MQTT is often favored for its simplicity and efficiency. It is capable of handling large volumes of data with minimal overhead, facilitating real-time monitoring and control. For instance, smart meters deployed in residential or commercial settings can use MQTT to send data to a centralized system for analysis and billing purposes. Its lightweight nature means that it can operate effectively even in scenarios where network bandwidth is limited or variable.
Conversely, OPC UA shines in complex industrial environments where detailed data exchange is crucial. It allows for seamless integration of devices and systems from different manufacturers, thanks to its standardized data models. This is particularly useful in large-scale industrial metering applications, such as in manufacturing plants or utilities where data must be shared across different systems while maintaining high levels of security and consistency. OPC UA’s ability to provide context and semantics to data makes it indispensable for those seeking to leverage advanced data analytics and machine learning models.
Security and Reliability Considerations
Both MQTT and OPC UA prioritize security and reliability, albeit in different ways. MQTT has built-in mechanisms such as username/password authentication and SSL/TLS encryption to secure data in transit. However, its simplicity means that additional measures may be needed to ensure robustness in highly sensitive applications.
In contrast, OPC UA was designed with security as a core feature. It provides comprehensive security features including user authentication, authorization, encryption, and integrity checking. This makes OPC UA particularly suitable for environments where data security is non-negotiable.
Potential Synergies and Integration
One of the exciting prospects in the IoT landscape is the potential integration of MQTT and OPC UA. These protocols can complement each other, leveraging the strengths of both to create robust and flexible data communication strategies. For instance, MQTT can be used for efficient data collection and initial transmission from edge devices, while OPC UA can handle the more complex aspects of data processing, integration, and security at higher levels of the system architecture.
In practice, such a hybrid approach allows organizations to tailor their IoT solutions to specific needs, optimizing for both performance and security. This flexibility is especially valuable as industries continue to digitize and integrate IoT technologies into their operations.
Conclusion
MQTT and OPC UA are pivotal in the advancement of IoT metering, each offering unique advantages that cater to different industrial needs. While MQTT excels in simplicity and efficiency, OPC UA provides depth and security. By understanding and leveraging the strengths of both protocols, industries can create robust, scalable, and secure IoT solutions that meet the demands of modern industrial operations. As the IoT ecosystem continues to expand, the role of these protocols will only become more critical, paving the way for smarter, more connected systems.
Navigating the evolving world of electrical measurement—from high-precision signal integrity to advanced test protocols like BERT or TDR—demands more than just expertise; it demands smart tools.
Patsnap Eureka empowers you to keep up—by turning complex patent data, technical parameters, and industry signals into actionable insight. It’s your AI partner for exploring what’s next in test, measurement, and electrical diagnostics.
💡 Try Patsnap Eureka for free and see how it transforms the way you work with electrical measurement technologies.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com