Passive Cooling vs. Active Cooling in Solar Systems: Which Is Better?
JUL 22, 2025 |
As the demand for renewable energy sources grows, solar power systems are becoming increasingly popular. One of the critical factors to consider when designing or choosing a solar system is the cooling mechanism. Cooling is essential to maintain the efficiency and longevity of solar panels and inverters. There are two primary types of cooling systems used in solar power installations: passive cooling and active cooling. This article delves into both methods, comparing their advantages and disadvantages to help you determine which might be better suited for your needs.
Understanding Passive Cooling
Passive cooling relies on natural processes and materials to manage the temperature of solar systems without the use of mechanical devices. It typically involves design strategies that optimize the flow of air, reduce heat gain, and enhance heat dissipation. Common techniques for passive cooling include:
1. **Natural Ventilation**: Arranging solar panels or inverters to take advantage of prevailing winds can enhance air circulation, reducing heat buildup.
2. **Thermal Mass**: Using materials with high thermal mass can absorb excess heat during the day and release it slowly when temperatures drop.
3. **Reflective Surfaces**: Coating surfaces with reflective materials can help deflect sunlight, reducing the heat absorbed by solar components.
4. **Shading**: Employing strategic shading devices or trees can decrease direct sunlight exposure, thus lowering temperatures.
Advantages of Passive Cooling
One of the main benefits of passive cooling is its low cost. Since it doesn't require mechanical components, there's minimal maintenance required, and no electricity is consumed. This makes passive cooling an environmentally friendly option that aligns well with the principles of sustainability. Furthermore, passive systems are generally more reliable as they have fewer parts that could fail over time.
Disadvantages of Passive Cooling
Despite its benefits, passive cooling has some limitations. It is highly dependent on the climate and environmental conditions, which can vary greatly. Additionally, passive methods may not be sufficient in areas with extremely high temperatures, potentially leading to reduced solar system efficiency and lifespan.
Understanding Active Cooling
Active cooling involves the use of mechanical systems and devices to regulate temperature. This might include fans, liquid cooling systems, or even advanced technologies like phase change materials. Active cooling systems are designed to remove excess heat more aggressively than passive methods.
1. **Fans and Air Conditioning**: Mechanical fans and air conditioning units can be employed to circulate cool air and remove hot air from around solar panels or inverters.
2. **Liquid Cooling**: This involves circulating a coolant through a system of pipes to absorb heat from the solar components, which is then dissipated elsewhere.
3. **Phase Change Materials (PCMs)**: These materials absorb and release thermal energy during the process of melting and solidifying, maintaining a stable temperature range.
Advantages of Active Cooling
Active cooling provides a more consistent and controlled cooling environment, making it suitable for areas with high ambient temperatures. These systems can significantly enhance the efficiency of solar panels and inverters by maintaining optimal operating conditions, which can lead to increased energy output and longer system life.
Disadvantages of Active Cooling
The primary downside of active cooling is that it requires additional energy to operate, which can reduce the overall efficiency and sustainability of the solar system. Moreover, active cooling systems are typically more complex and costly, both in terms of installation and ongoing maintenance. There is also a higher risk of mechanical failure due to the moving parts involved.
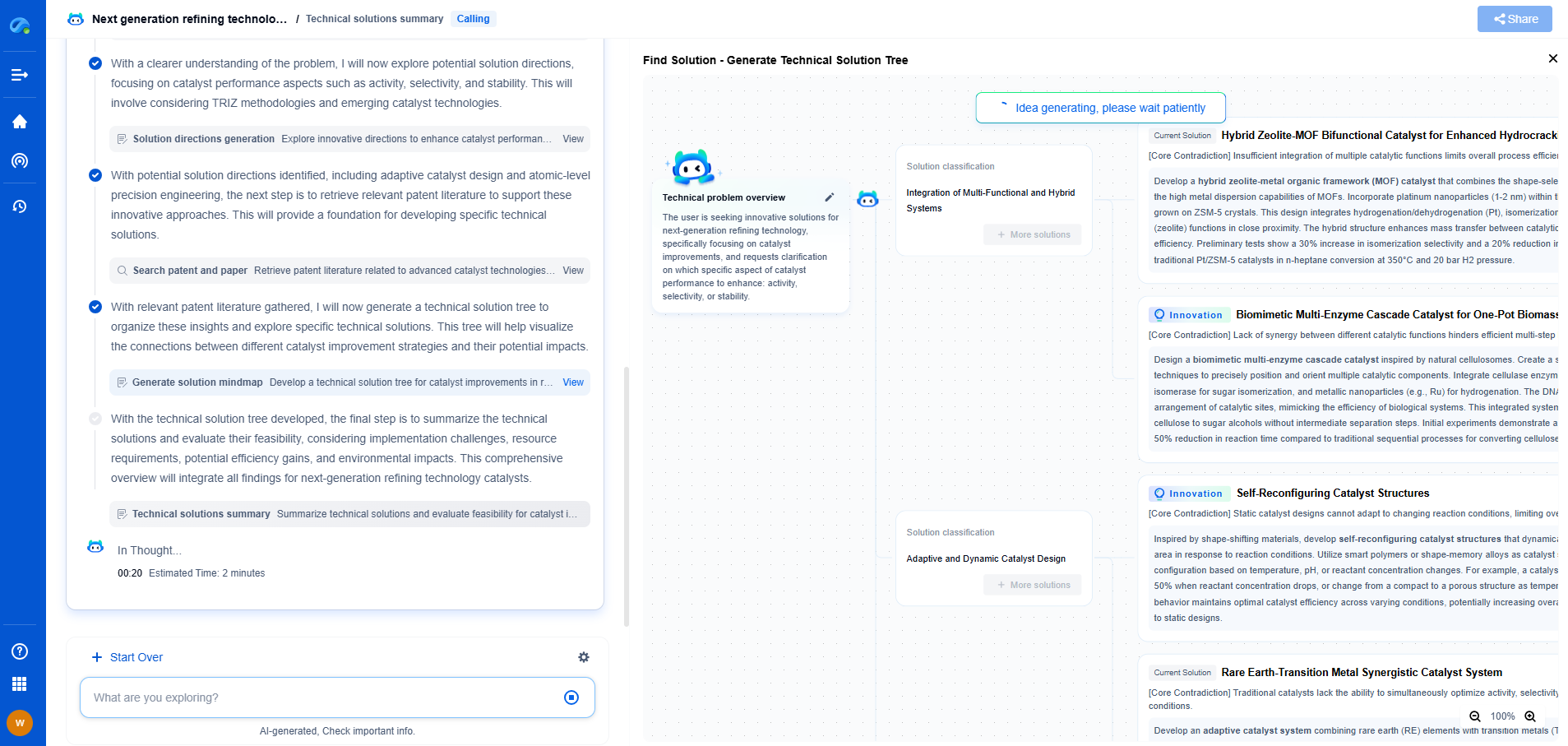
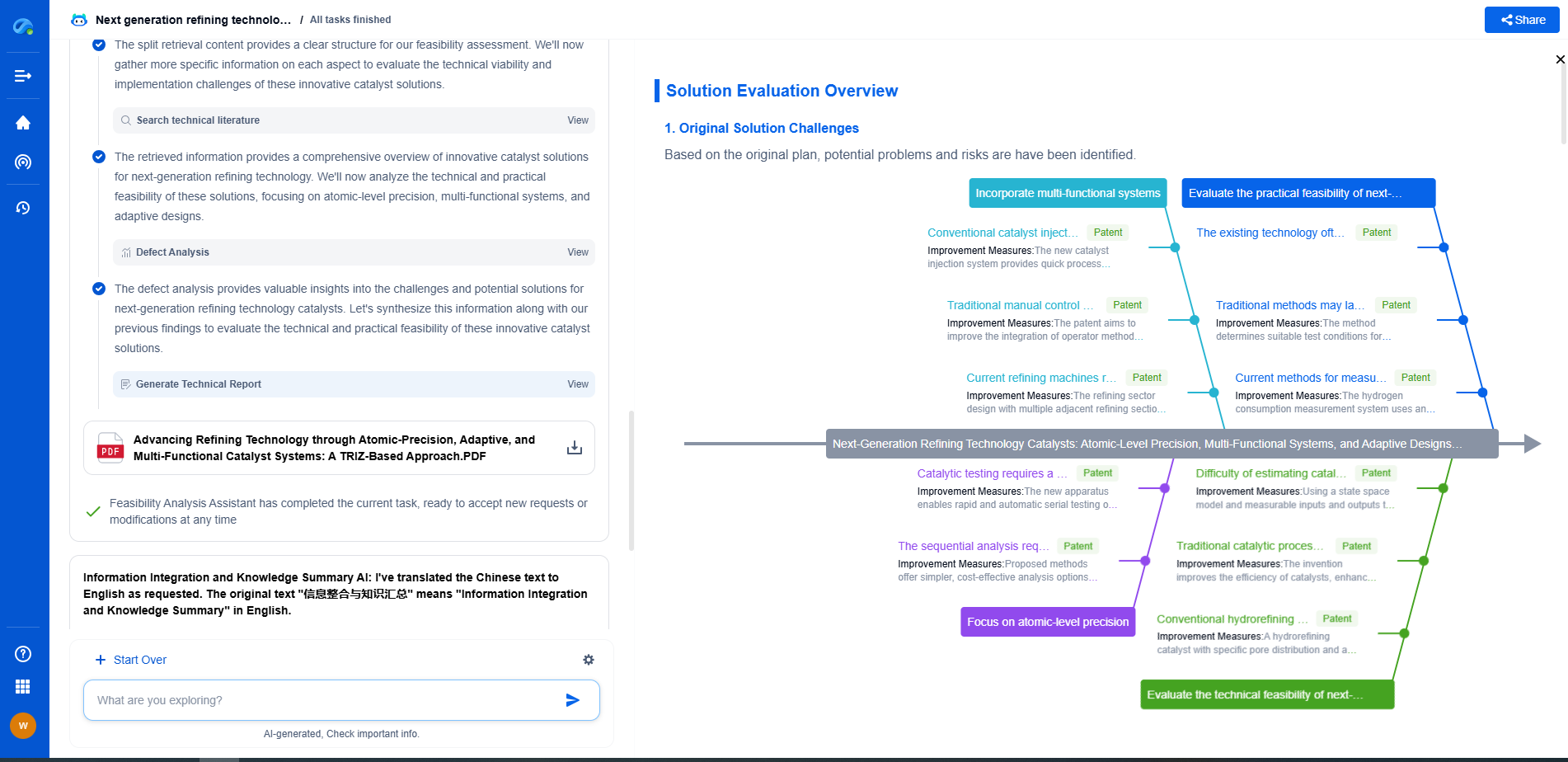
Conclusion: Which Is Better?
The choice between passive and active cooling largely depends on the specific conditions and requirements of your solar installation. For those in milder climates looking to minimize costs and maintenance, passive cooling might be the ideal solution. However, in hotter regions where maintaining optimal performance is crucial, investing in an active cooling system could prove beneficial despite the higher upfront and operational costs.
In essence, both cooling methods have their place in solar systems. Consider your environmental conditions, budget, and performance expectations when deciding which cooling strategy to implement. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can ensure your solar system operates efficiently and sustainably for many years to come.
As solar technology races ahead—from perovskite cells to tandem architectures, from anti-reflective coatings to transparent electrodes—staying on top of fast-moving innovation has become a strategic imperative.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚡ Ready to accelerate your solar innovation journey? Try Patsnap Eureka today and let AI help you harness the full power of the sun—and your IP strategy.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com