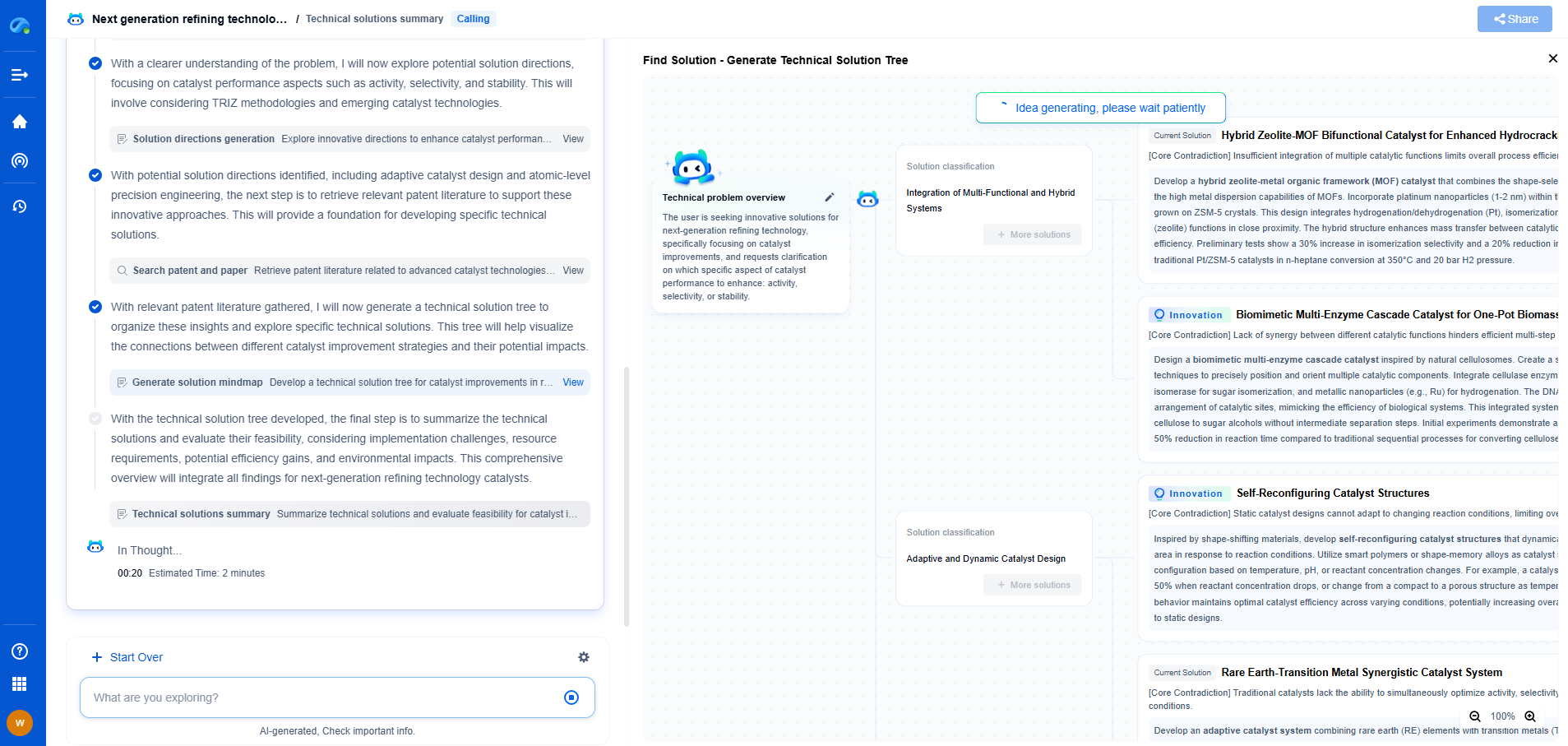
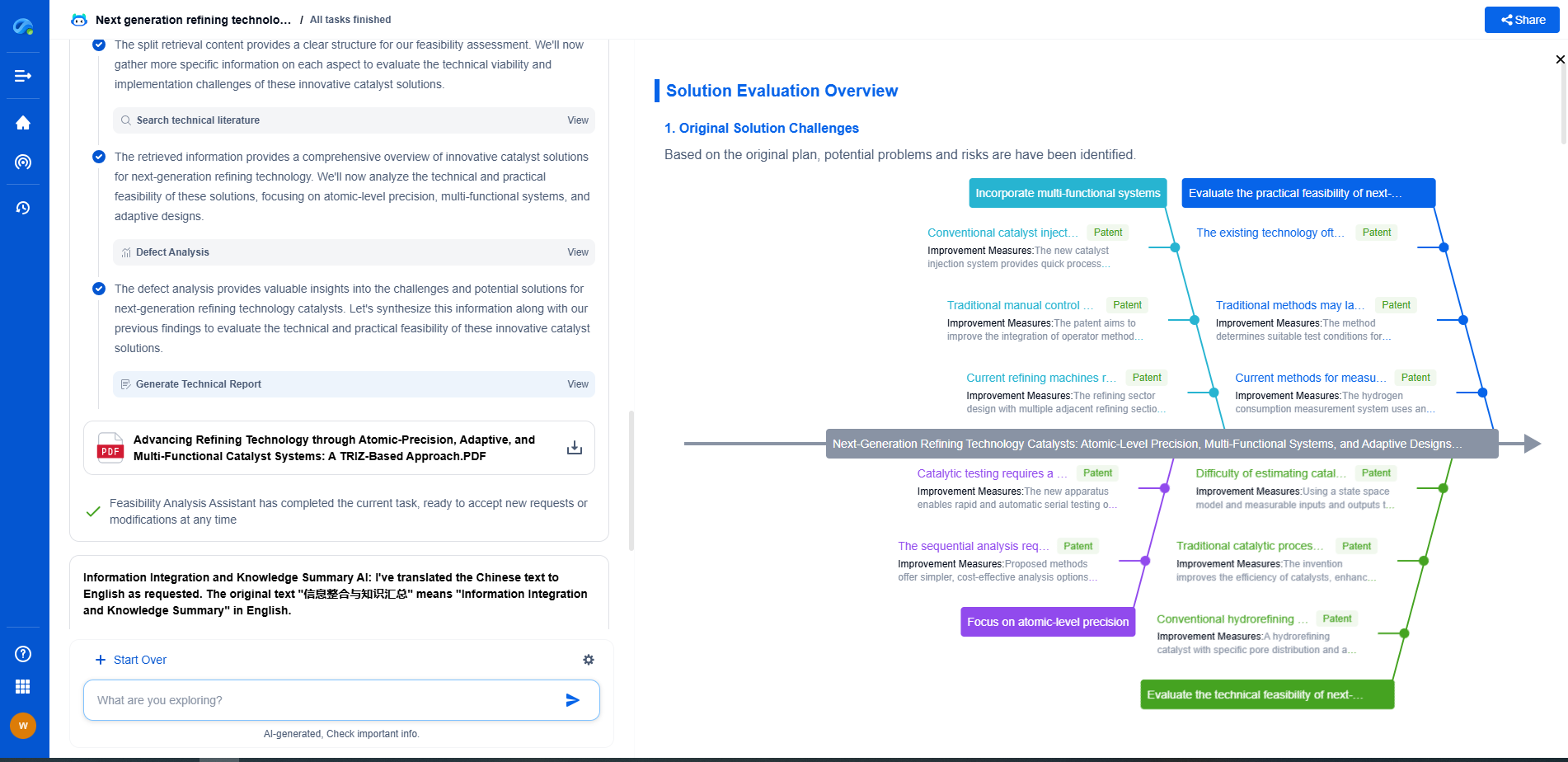
Passive RFID Sensors vs BLE: Range and Data Rate for Industrial IoT
JUL 14, 2025 |
In the rapidly evolving landscape of Industrial IoT (IIoT), choosing the right technology for specific applications is crucial. Two widely used technologies in IIoT are Passive RFID Sensors and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE). Each has its strengths and limitations, particularly concerning range and data rate, which are critical factors in industrial settings. This article delves into the capabilities of Passive RFID Sensors and BLE to help you make informed decisions for your industrial IoT applications.
Understanding Passive RFID Sensors
Passive RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) sensors are a popular choice for asset tracking and identification in industrial environments. These sensors do not have an internal power source; instead, they leverage the energy from RFID readers. This characteristic grants them the benefit of long-term deployment without battery replacements. However, this feature also affects their range and data rate capabilities.
Range and Data Rate of Passive RFID
Passive RFID sensors typically have a shorter range compared to active RFID systems. The range is generally up to a few meters, depending on the frequency used and environmental factors. For example, UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID systems can achieve a range of up to 12 meters under optimal conditions. The data rate for Passive RFID is relatively low, as it primarily transmits simple identification data, such as unique IDs, rather than complex datasets.
Applications of Passive RFID in Industrial IoT
Despite their limitations in range and data rate, Passive RFID sensors excel in applications where identification and tracking of assets are essential. They are used extensively in supply chain management, inventory control, and production line monitoring. The advantage of not needing a power source makes them ideal for environments where maintenance access is limited or where cost is a concern.
Exploring Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Bluetooth Low Energy, or BLE, is a wireless technology designed for short-range communication. It is characterized by its low power consumption, making it suitable for battery-operated devices. BLE has gained popularity in IIoT due to its versatility and ability to transmit more complex data than Passive RFID sensors.
Range and Data Rate of BLE
BLE devices typically have a range of up to 100 meters in open environments, although this can decrease in industrial settings with obstacles and interference. BLE offers higher data rates compared to Passive RFID, supporting complex data transmissions such as sensor readings, control information, and real-time alerts. The higher data rate makes BLE suitable for applications requiring detailed monitoring and control.
Applications of BLE in Industrial IoT
BLE is widely used in applications where more than just identification is needed. It is suitable for condition monitoring, predictive maintenance, and real-time location systems in industrial environments. The ability to transmit detailed data makes BLE ideal for environments where a comprehensive understanding of processes and assets is necessary.
Comparative Analysis: Passive RFID vs. BLE
When considering range and data rate, it is clear that BLE provides a broader range and higher data rates compared to Passive RFID sensors. However, the choice between the two should be based on specific application requirements. Passive RFID is advantageous for simple asset tracking where power availability is a concern, and the data to be transmitted is minimal. In contrast, BLE is preferred for applications that require more detailed data transmission and where power management can be addressed through battery-powered devices.
Conclusion
In the realm of Industrial IoT, both Passive RFID Sensors and BLE have their unique places. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each technology in terms of range and data rate is essential for selecting the right solution. By carefully assessing the specific needs of your industrial application, you can make an informed choice that optimizes performance, cost, and efficiency.
From 5G NR to SDN and quantum-safe encryption, the digital communication landscape is evolving faster than ever. For R&D teams and IP professionals, tracking protocol shifts, understanding standards like 3GPP and IEEE 802, and monitoring the global patent race are now mission-critical.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
📡 Experience Patsnap Eureka today and unlock next-gen insights into digital communication infrastructure, before your competitors do.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com