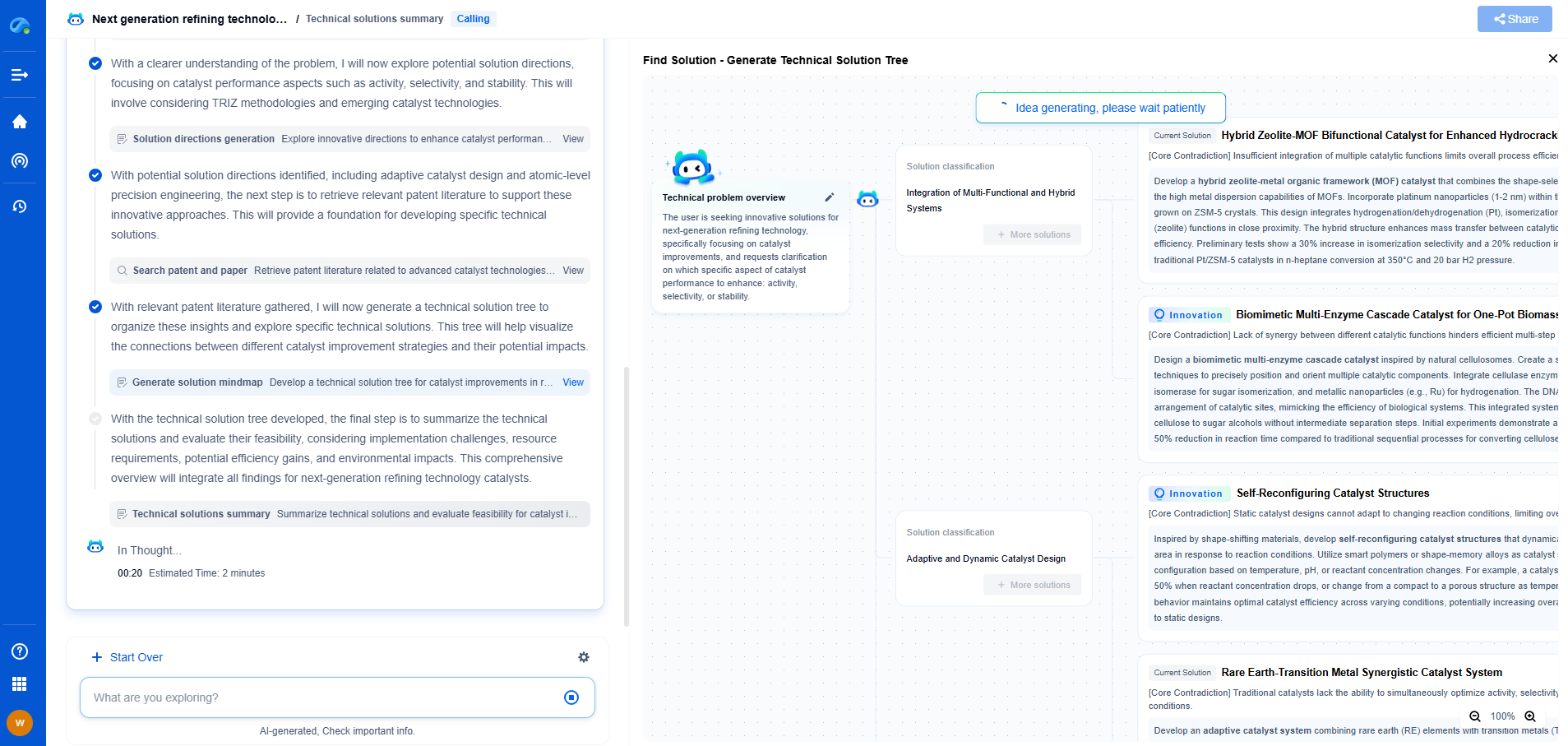
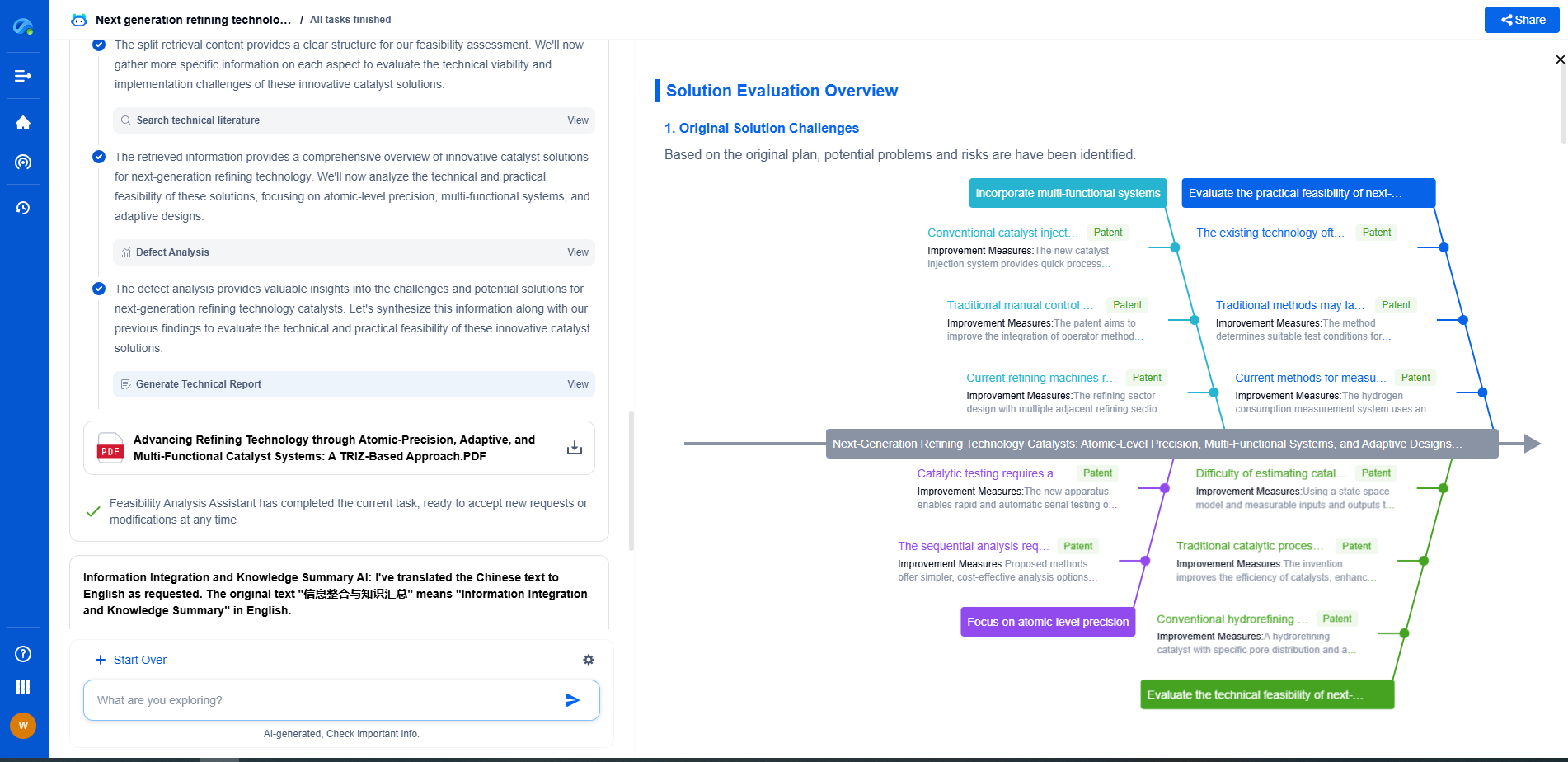
Piezoelectric vs. MEMS Vibration Sensors: Which One Fits Your Application?
JUL 16, 2025 |
In today's rapidly advancing technological landscape, selecting the right sensor for vibration monitoring is crucial for ensuring the efficiency and reliability of various applications. Two popular types of vibration sensors often considered are piezoelectric and MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) sensors. Each technology brings its own unique advantages and potential limitations. Understanding these differences can help you make an informed decision on which sensor best suits your specific needs.
What Are Piezoelectric Vibration Sensors?
Piezoelectric sensors are devices that utilize the piezoelectric effect to measure changes in pressure, acceleration, temperature, or force by converting them into an electrical charge. These sensors are renowned for their high sensitivity, broad frequency range, and ability to handle extreme conditions. The core component of a piezoelectric sensor is a piezoelectric material, often a crystal or ceramic, which generates an electrical voltage in response to mechanical stress.
Advantages of Piezoelectric Sensors
1. High Sensitivity and Accuracy: Piezoelectric sensors offer exceptional sensitivity, making them ideal for capturing minute vibrations or high-frequency signals. This makes them a preferred choice for laboratory and industrial applications requiring precise measurements.
2. Wide Frequency Range: These sensors are capable of operating effectively over a broad frequency range, from a few hertz to several kilohertz, making them versatile for various applications.
3. Robustness and Durability: Piezoelectric sensors are known for their robustness, capable of operating in harsh environments with high levels of shock and vibration. They can withstand significant temperature variations and are often used in aerospace and automotive industries.
Limitations of Piezoelectric Sensors
1. Cost: Piezoelectric sensors can be more expensive than other types of sensors, which might be a consideration for budget-sensitive projects.
2. Size: They are generally larger and bulkier, which might not be suitable for applications where space is a constraint.
What Are MEMS Vibration Sensors?
MEMS vibration sensors are a type of sensor technology that combines mechanical and electronic components on a microscopic scale using microfabrication technology. These sensors are known for their small size, low power consumption, and cost-effectiveness. MEMS sensors work by detecting changes in capacitance caused by the movement of a micro-machined structure within the sensor.
Advantages of MEMS Sensors
1. Compact Size: MEMS sensors are extremely small, making them an excellent choice for applications where space is limited. This compact size also allows for easy integration into portable devices.
2. Cost-Effective: Generally, MEMS sensors are less expensive due to mass-production capabilities and the use of silicon-based manufacturing processes.
3. Low Power Consumption: They consume significantly less power compared to piezoelectric sensors, which makes them ideal for battery-operated devices.
Limitations of MEMS Sensors
1. Limited Frequency Range: MEMS sensors typically have a narrower frequency range compared to piezoelectric sensors, which might restrict their use in high-frequency applications.
2. Sensitivity: While MEMS sensors are improving in sensitivity, they may not yet match the high sensitivity provided by piezoelectric sensors, potentially limiting their application in scenarios requiring extreme precision.
Choosing the Right Sensor for Your Application
When deciding between piezoelectric and MEMS sensors, several factors should be considered:
1. Application Requirements: Consider the specific requirements of your application, such as the frequency range, environmental conditions, and size constraints. For high-frequency and extreme environments, piezoelectric sensors might be a better fit. For compact and cost-sensitive applications, MEMS sensors could be more appropriate.
2. Budget Considerations: Assess the total cost of ownership, including the initial purchase price, installation, and maintenance costs. MEMS sensors may offer a cost advantage for projects with tight budgets.
3. Power Consumption: If your application is power-sensitive, such as in portable or battery-operated devices, MEMS sensors are likely the better choice due to their low power consumption.
Conclusion
Both piezoelectric and MEMS vibration sensors offer unique advantages, and the choice between them should be dictated by the specific demands of your application. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each technology, you can ensure optimal performance and efficiency in your vibration monitoring tasks. Whether you need the high sensitivity and durability of piezoelectric sensors or the compactness and cost-effectiveness of MEMS, there is a sensor solution that will meet your requirements.
In the world of vibration damping, structural health monitoring, and acoustic noise suppression, staying ahead requires more than intuition—it demands constant awareness of material innovations, sensor architectures, and IP trends across mechanical, automotive, aerospace, and building acoustics.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚙️ Bring Eureka into your vibration intelligence workflow—and reduce guesswork in your R&D pipeline. Start your free experience today.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com