Plasma ashing vs solvent resist strip: Pros and cons
JUL 28, 2025 |
In the semiconductor manufacturing industry, removing photoresist is a crucial step. Two common methods employed for this task are plasma ashing and solvent resist stripping. Each technique has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making it essential for manufacturers to understand the nuances of both processes to select the most suitable one for their specific needs.
Understanding Plasma Ashing
Plasma ashing is a dry process that utilizes plasma to remove photoresist from the surface of semiconductor wafers. This method involves exposing the wafers to a plasma field, where energized ions and electrons break down the resist into volatile compounds that are then evacuated from the chamber.
Pros of Plasma Ashing
1. Minimal Chemical Waste: One of the most significant advantages of plasma ashing is the reduction in chemical waste. Since it is a dry process, it eliminates the need for liquid chemicals, making it an environmentally friendly option.
2. Precision: Plasma ashing allows for high precision in removing photoresist, which is particularly advantageous for complex semiconductor designs that require meticulous attention to detail.
3. Uniformity: The process ensures uniform resist removal across the wafer, which is crucial for maintaining the integrity and performance of semiconductor devices.
Cons of Plasma Ashing
1. Equipment Cost: The initial investment in plasma ashing equipment can be substantial, which might be a barrier for smaller manufacturers with limited budgets.
2. Potential for Damage: Plasma ashing can sometimes cause damage to the underlying layers if not carefully controlled, which can affect the performance of the semiconductor device.
Exploring Solvent Resist Stripping
Solvent resist stripping is a wet process that uses chemical solvents to dissolve and remove the photoresist. This method is often used in conjunction with other cleaning processes to ensure complete removal of photoresist residues.
Pros of Solvent Resist Stripping
1. Cost-Effective: Solvent resist stripping is generally more cost-effective than plasma ashing, especially for manufacturers who do not require the high precision offered by plasma processes.
2. Gentle on Substrates: This method is less likely to cause damage to the underlying layers of the wafer, making it suitable for delicate substrates.
3. Simplicity: The process is relatively simple and does not require highly specialized equipment, making it accessible for a wide range of manufacturers.
Cons of Solvent Resist Stripping
1. Chemical Waste: This process generates a significant amount of chemical waste, which poses environmental and disposal challenges.
2. Incomplete Removal: There is a risk of incomplete resist removal, particularly for complex or densely packed semiconductor designs, which can impact device performance.
3. Variability: The effectiveness of solvent resist stripping can vary depending on the chemical formulation and process conditions, which may lead to inconsistencies in the final product.
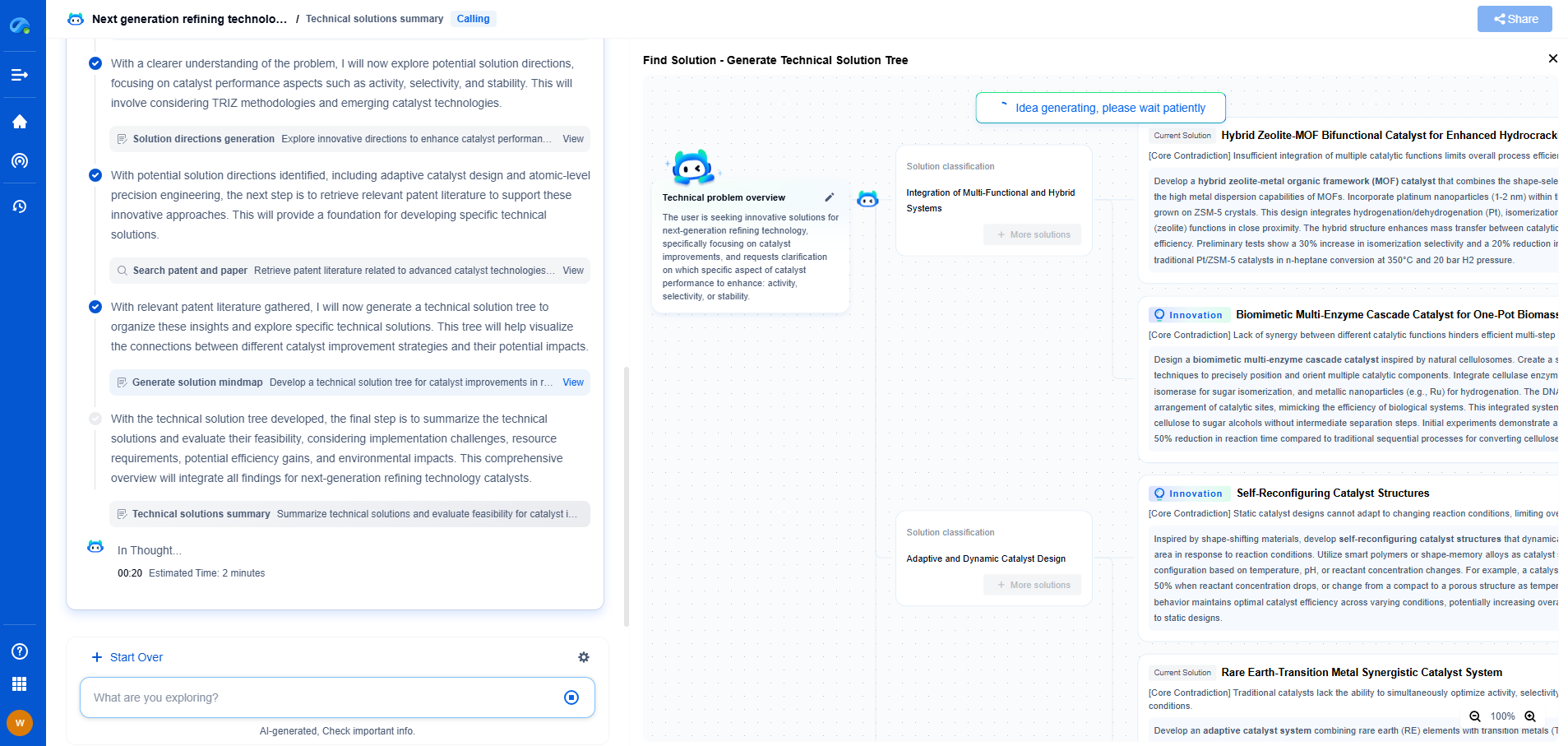
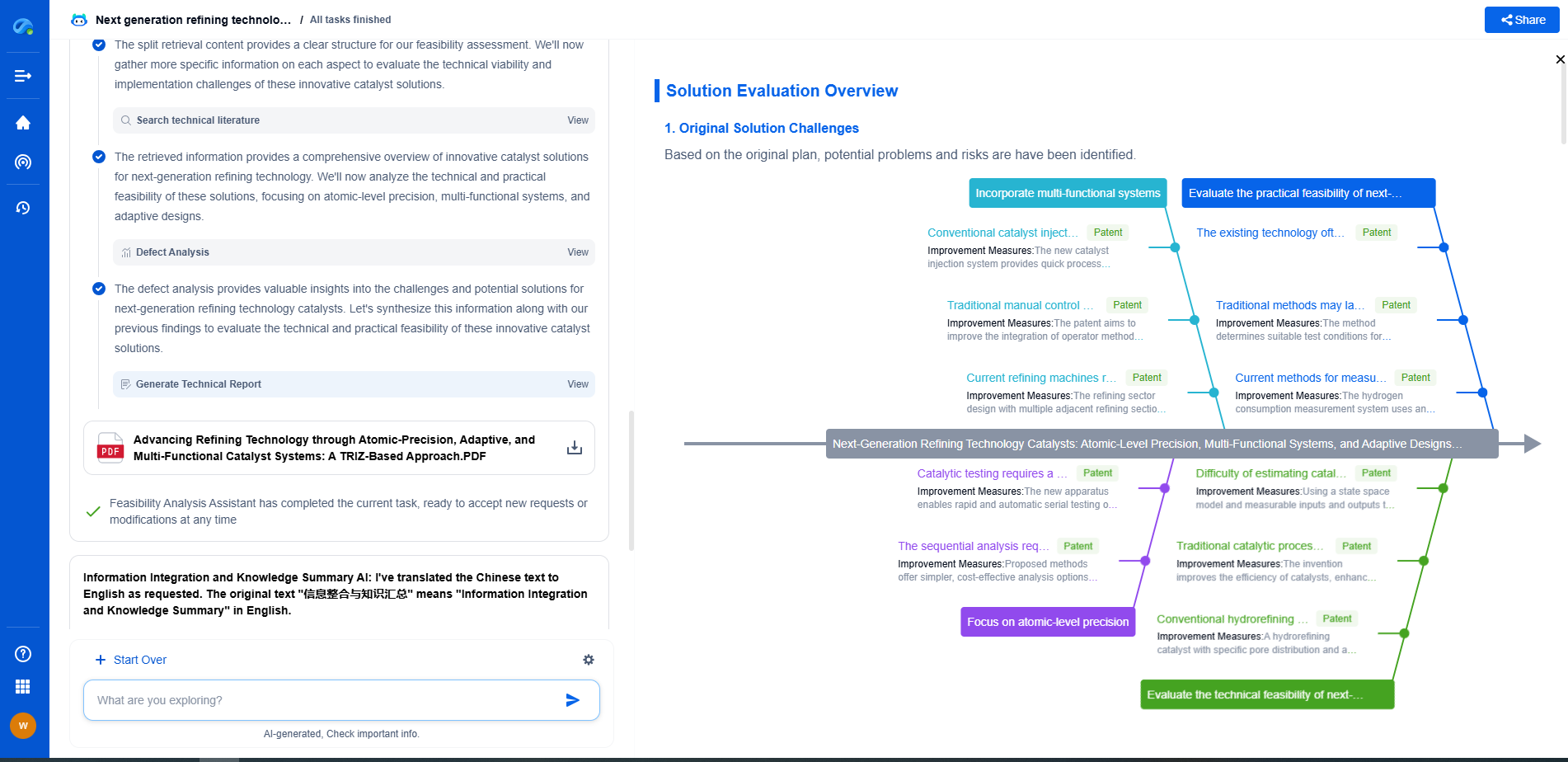
Conclusion
Both plasma ashing and solvent resist stripping have their own sets of advantages and disadvantages. Plasma ashing excels in precision and environmental friendliness but comes with higher costs and potential substrate damage. On the other hand, solvent resist stripping is cost-effective and substrate-friendly but poses challenges with chemical waste and removal completeness. Manufacturers must weigh these factors based on their specific needs, budget, and environmental considerations to make the best choice for their semiconductor manufacturing process.
As photolithography continues to push the boundaries of nanoscale patterning, from EUV and DUV advancements to multi-patterning and maskless lithography, innovation cycles are accelerating—and the IP landscape is becoming more complex than ever.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
Whether you're optimizing lithography depth of focus or exploring new materials for sub-3nm nodes, Patsnap Eureka empowers you to make smarter decisions, faster—combining AI efficiency with domain-specific insight.
💡 Start your free trial today and see how Eureka transforms how you discover, evaluate, and act on innovation in photolithography—from idea to impact.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com