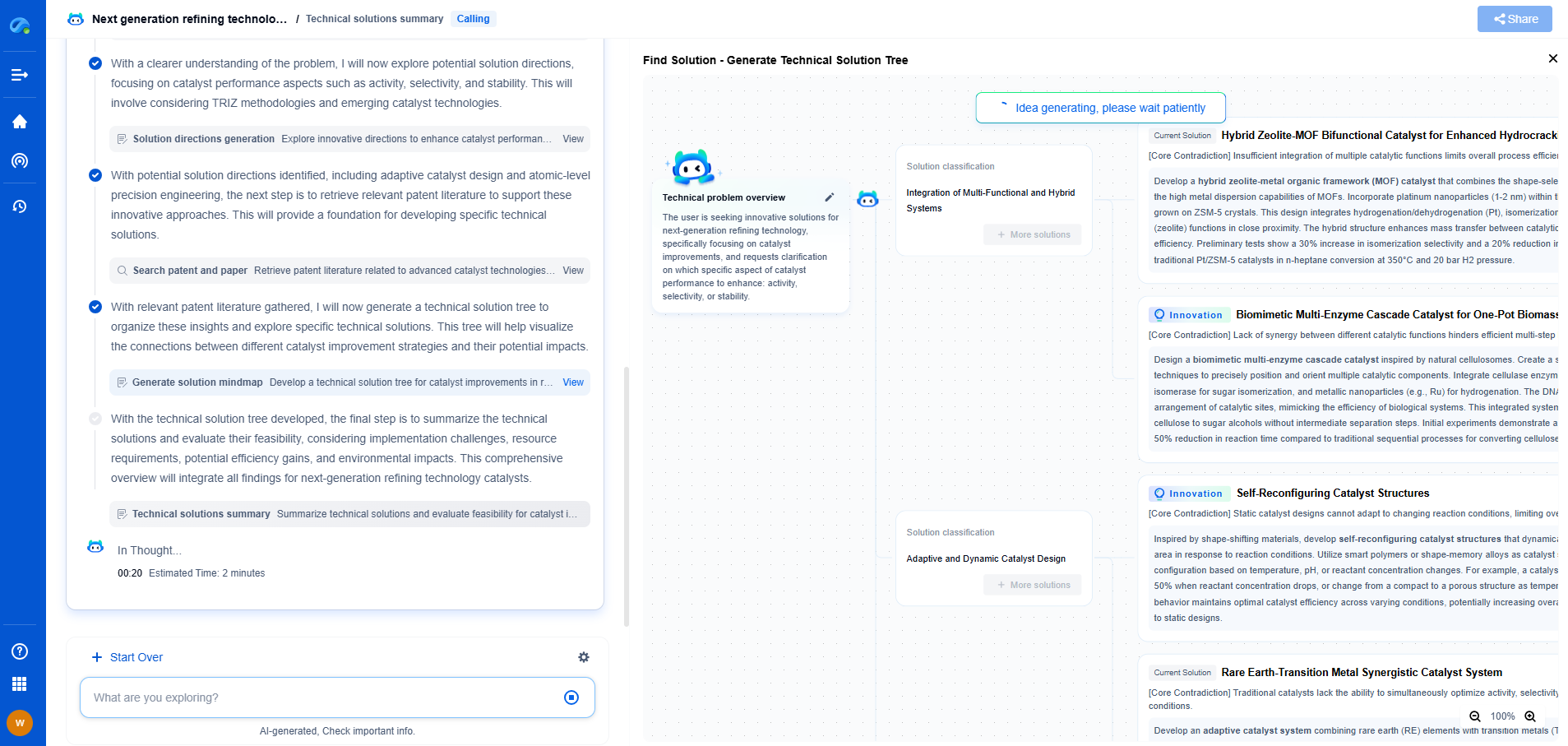
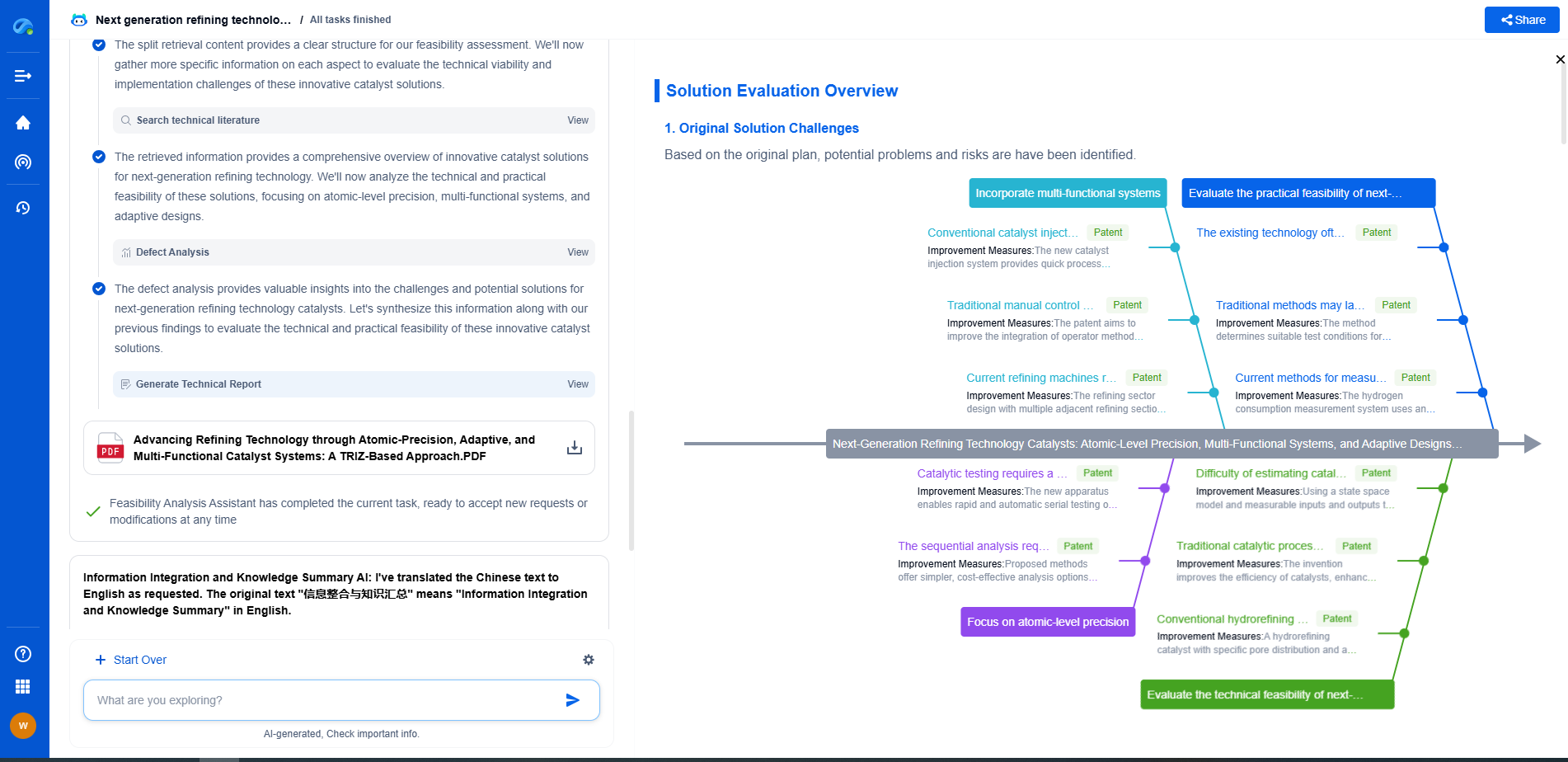
Printable Solar Cells vs. Thin-Film Solar Panels: What’s the Difference?
JUL 22, 2025 |
As the world shifts towards sustainable energy solutions, solar technology has emerged as a frontrunner in clean energy production. Among the varieties of solar technologies available, printable solar cells and thin-film solar panels are gaining attention for their unique attributes and potential applications. Both offer distinct advantages and have specific use cases, making them compelling options for different scenarios. In this article, we'll delve into the key differences between these two technologies, examining their materials, manufacturing processes, efficiencies, and potential impacts on the solar industry.
**Understanding Printable Solar Cells**
Printable solar cells, also known as organic photovoltaic (OPV) cells, represent a cutting-edge approach to solar technology. These cells are created using organic materials, including polymers and small organic molecules, which allow them to be printed onto flexible substrates. This is achieved through various printing techniques such as inkjet printing, screen printing, or roll-to-roll processing.
One of the main advantages of printable solar cells is their flexibility. This flexibility allows for innovative applications, including integration into clothing, windows, and even vehicles. The lightweight nature of these cells means they can be deployed in situations where traditional solar panels would be impractical. Additionally, the manufacturing process for printable solar cells is relatively low-cost and energy-efficient, making them a promising option for reducing the overall cost of solar energy.
However, printable solar cells currently face challenges in terms of efficiency and durability. Compared to traditional silicon-based solar cells, their efficiency rates are generally lower, and they tend to degrade faster when exposed to environmental conditions. Researchers are actively working on improving these aspects to make printable solar cells more viable for widespread use.
**Exploring Thin-Film Solar Panels**
Thin-film solar panels are another innovative approach to capturing solar energy. These panels are constructed by depositing one or more thin layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate. The most common types of thin-film solar materials include cadmium telluride (CdTe), amorphous silicon (a-Si), and copper indium gallium selenide (CIGS).
The primary advantage of thin-film solar panels is their versatility. They can be manufactured in various shapes and sizes, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from large-scale solar farms to building-integrated photovoltaics. Thin-film panels are also known for their aesthetic appeal, as they can be seamlessly integrated into building designs.
Thin-film solar panels typically have lower efficiency rates than crystalline silicon panels but are still higher than those of most printable solar cells. They also tend to have a longer lifespan and better performance in low-light conditions. The manufacturing process for thin-film solar panels is less energy-intensive than traditional silicon-based panels, which can lead to lower production costs.
**Comparing Efficiency and Cost**
When comparing printable solar cells and thin-film solar panels, efficiency is a key factor. Printable solar cells are still in the developmental stage, with efficiencies generally ranging from 3% to 10%. Thin-film solar panels, on the other hand, offer efficiencies between 10% and 20%, making them more suitable for applications where higher energy output is required.
Cost is another crucial consideration. Printable solar cells have the potential to be very cost-effective due to their simple production process and the use of abundant materials. Thin-film solar panels also promise lower costs than traditional silicon panels, but they require more advanced manufacturing facilities, which can offset some of the savings.
**Potential Applications and Future Prospects**
The potential applications for both printable solar cells and thin-film solar panels are vast and varied. Printable solar cells could revolutionize the integration of solar technology into everyday objects, potentially powering wearable electronics and providing portable energy solutions. Meanwhile, thin-film solar panels are well-suited for urban environments, where space is at a premium and architectural aesthetics are important.
The future prospects for both technologies are promising. Advances in material science and manufacturing techniques are likely to enhance the efficiency and durability of printable solar cells, making them a more competitive option in the solar market. For thin-film solar panels, continued improvements in efficiency and cost reduction could lead to broader adoption in both residential and commercial settings.
**Conclusion**
In summary, both printable solar cells and thin-film solar panels offer unique advantages and face specific challenges. Printable solar cells, with their flexibility and low-cost production, hold exciting potential for novel applications, while thin-film solar panels offer versatility and aesthetic integration. As research and development continue, both technologies are poised to play significant roles in the transition to a sustainable energy future. Understanding their differences helps in making informed decisions about their implementation based on specific needs and circumstances.
As solar technology races ahead—from perovskite cells to tandem architectures, from anti-reflective coatings to transparent electrodes—staying on top of fast-moving innovation has become a strategic imperative.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚡ Ready to accelerate your solar innovation journey? Try Patsnap Eureka today and let AI help you harness the full power of the sun—and your IP strategy.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com