Real-Time Neural Radiance Fields: Will They Replace Traditional Rendering?
JUL 10, 2025 |
In recent years, Neural Radiance Fields, or NeRFs, have emerged as a groundbreaking technology in the realm of computer graphics and 3D rendering. At their core, NeRFs utilize neural networks to generate photorealistic images by capturing the intricate details of how light interacts with surfaces. This method represents a significant departure from traditional rendering techniques that often rely on polygonal models and rasterization.
Understanding Traditional Rendering
Traditional rendering, particularly rasterization, has been the backbone of computer graphics for decades. It involves converting 3D models into 2D images by mapping objects in a scene onto a pixel grid. While this method is fast and efficient, especially with the aid of powerful GPUs, it often struggles with complex lighting scenarios like reflections, refractions, and global illumination.
The Emergence of NeRFs
NeRFs, however, approach the rendering problem from a fundamentally different perspective. Instead of working with explicit geometric representations, NeRFs encode a scene within a neural network. This network learns to approximate the volumetric effect of light, providing incredibly detailed renderings with realistic lighting and shadows. The result is a level of photorealism that can be difficult to achieve with traditional methods without significant computational overhead.
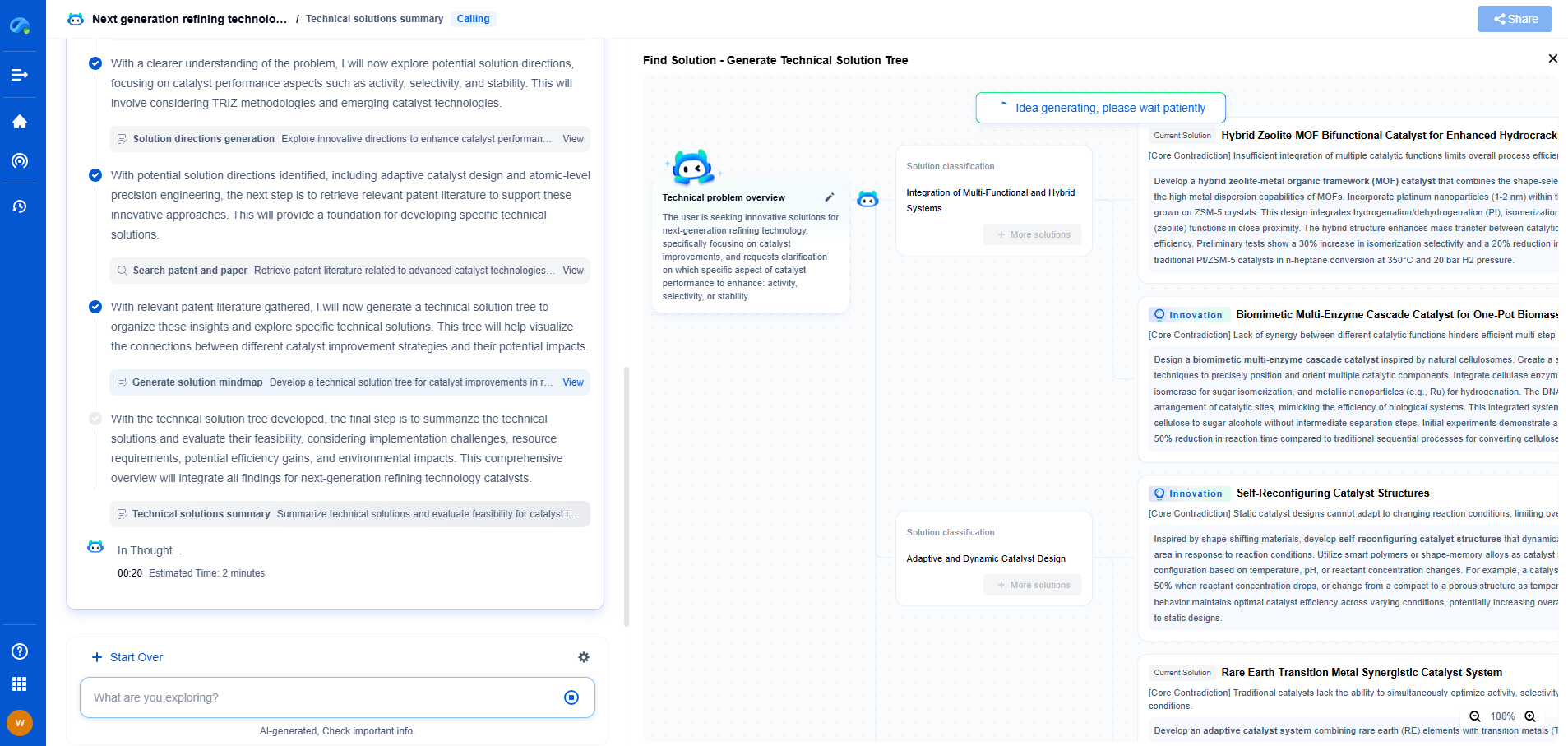
Real-Time NeRFs: A Game Changer?
Initially, NeRFs were computationally expensive, making them impractical for real-time applications. However, recent advancements have dramatically improved their efficiency. Researchers have been developing algorithms that significantly reduce the time required to train NeRF models and enhance their rendering speed. These improvements have paved the way for real-time applications, challenging the dominance of traditional real-time rendering techniques.
Benefits of Real-Time NeRFs
Real-time NeRFs hold several potential advantages over traditional rendering. One of the most significant is their ability to handle complex lighting scenarios naturally. NeRFs inherently account for subtle lighting effects, such as soft shadows and translucency, without the need for elaborate hacks or approximations. Moreover, NeRFs can render scenes with fewer artifacts, resulting in smoother and more realistic images.
Another advantage lies in the data efficiency of NeRFs. Since they encode scenes into neural networks, they can potentially reduce the storage requirements for high-quality 3D assets. This encoding capability can be particularly beneficial for applications involving large and complex environments.
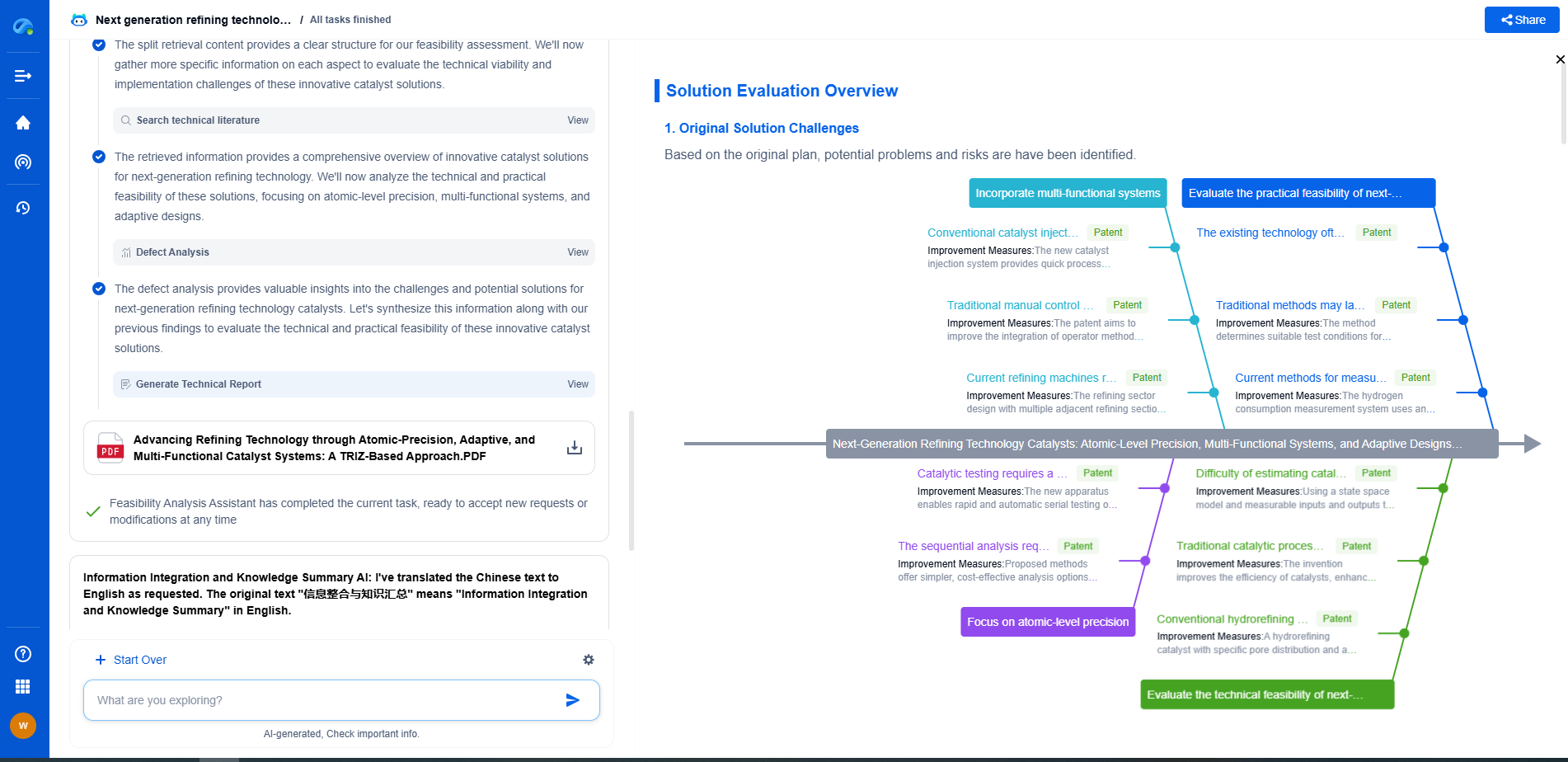
Challenges Facing NeRF Adoption
Despite their promise, NeRFs face several challenges that could hinder their widespread adoption. One of the primary concerns is the computational cost associated with training the neural networks. While real-time NeRFs have made strides in reducing these costs, they still require significant resources compared to traditional methods.
Moreover, the integration of NeRFs into existing pipelines poses another hurdle. The current infrastructure for game development and real-time applications is heavily invested in polygonal models and rasterization. Transitioning to a NeRF-based pipeline would require significant changes in tools, workflows, and potentially hardware.
The Future of Rendering: Coexistence or Replacement?
So, will real-time Neural Radiance Fields replace traditional rendering? The answer may not be straightforward. Instead of outright replacement, a more likely scenario is the coexistence of both technologies. Each has its strengths and weaknesses, and they may complement each other in different applications.
For instance, NeRFs could become a valuable tool for creating high-quality offline assets or enhancing visual effects in film and animation. On the other hand, traditional rendering might remain the preferred choice for applications requiring low latency and compatibility with existing hardware and software.
Conclusion
Real-time NeRFs represent a significant advancement in the field of rendering, offering a new paradigm for achieving photorealism. While they may not completely replace traditional rendering techniques in the near future, their potential cannot be underestimated. As technology continues to evolve, the line between these two approaches may blur, leading to innovative hybrid methods that leverage the strengths of both. Ultimately, the future of rendering is likely to be defined by the dynamic interplay between these groundbreaking technologies.
Image processing technologies—from semantic segmentation to photorealistic rendering—are driving the next generation of intelligent systems. For IP analysts and innovation scouts, identifying novel ideas before they go mainstream is essential.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
🎯 Try Patsnap Eureka now to explore the next wave of breakthroughs in image processing, before anyone else does.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com