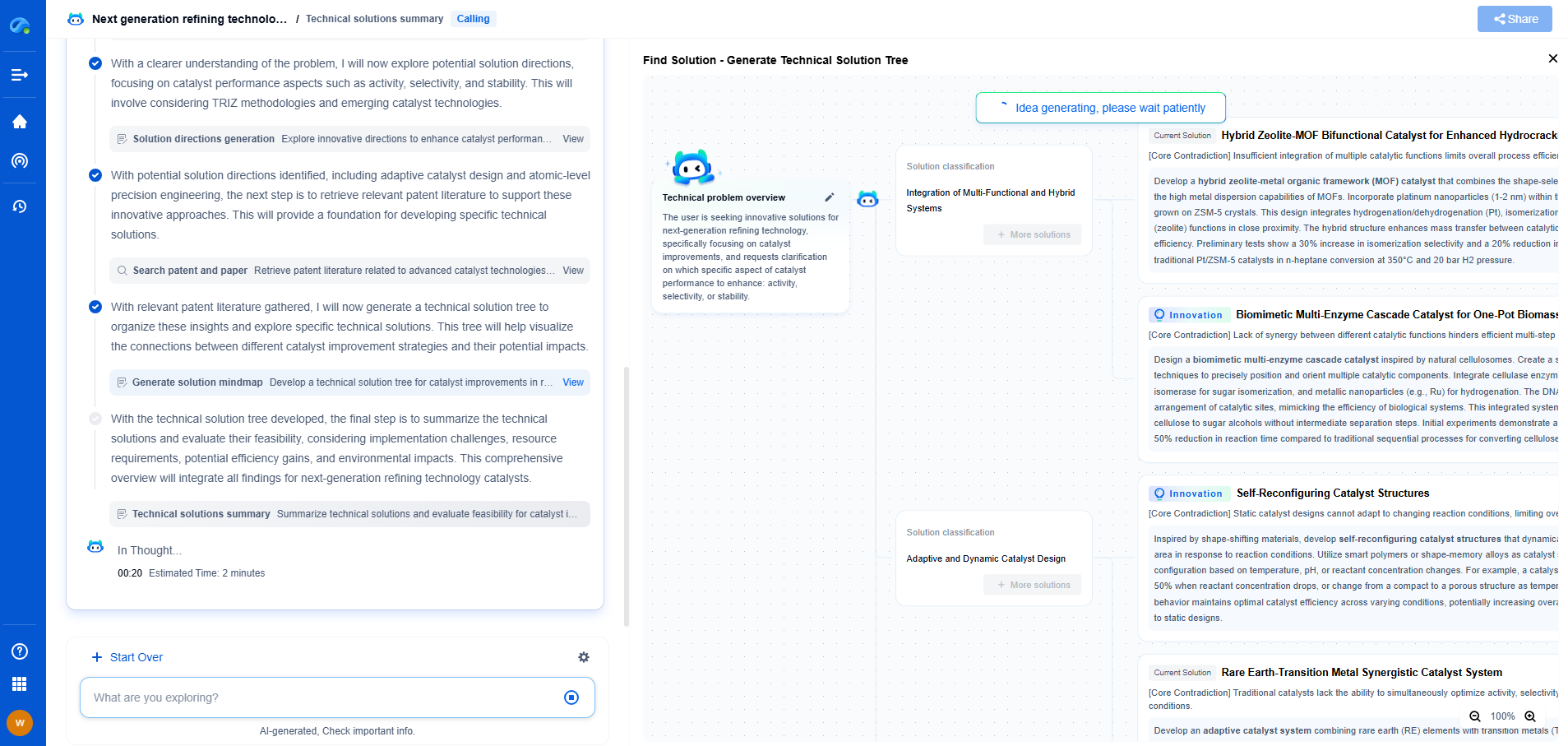
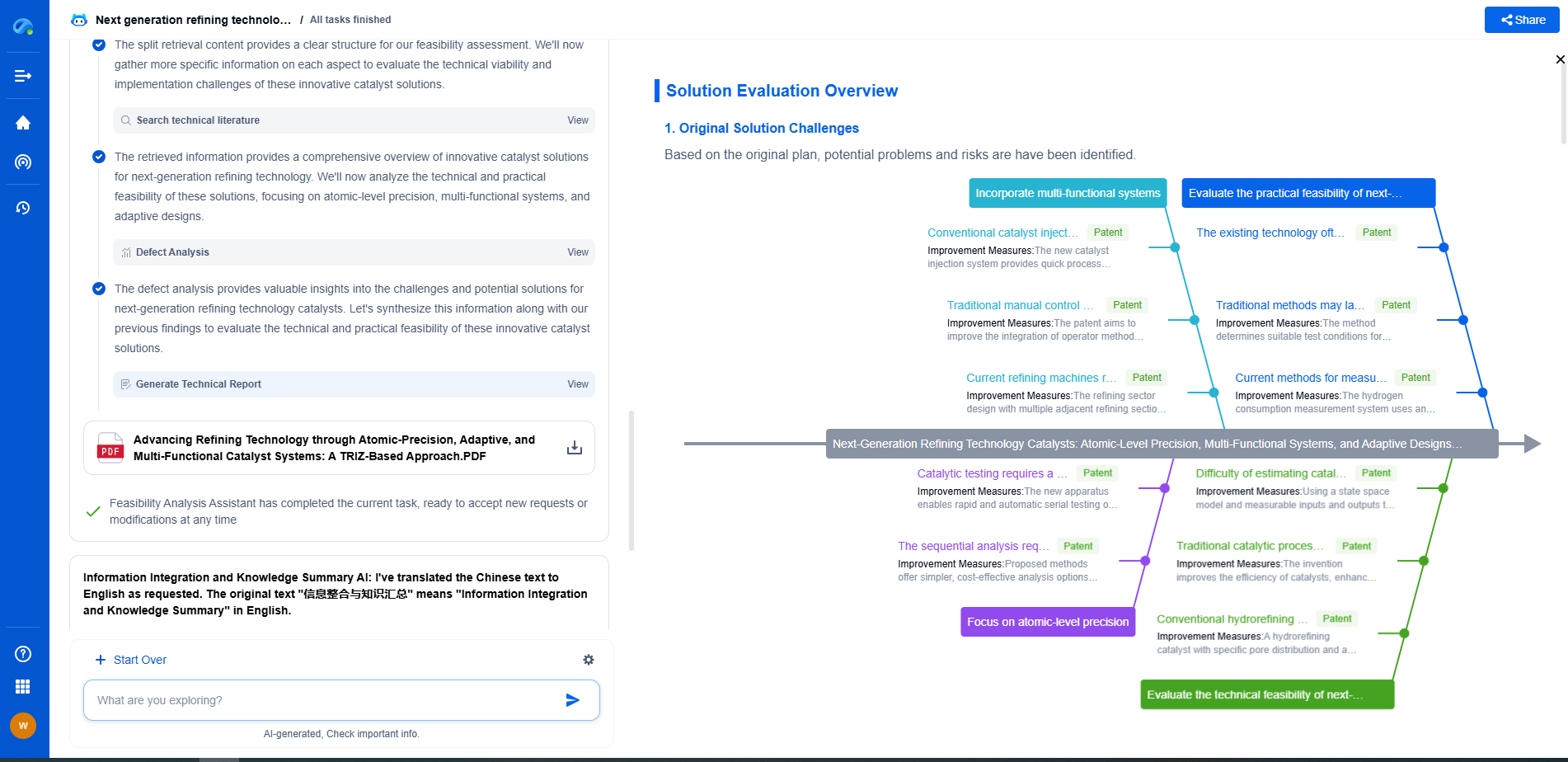
Recycling Drilling Waste: New Methods for Mud and Cuttings Reuse
JUN 20, 2025 |
Drilling operations, integral to oil and gas extraction, generate significant waste, primarily in the form of drilling mud and cuttings. Traditionally, these by-products have been discarded in landfills or subjected to costly treatments due to environmental regulations. However, with growing concerns over sustainability and environmental impact, the industry is exploring innovative methods to recycle and reuse drilling waste.
**Understanding Drilling Waste**
Before delving into new recycling methods, it's crucial to understand what constitutes drilling waste. Drilling mud, a complex mixture of water, clay, and chemicals, is used to lubricate and cool the drill bit, stabilize the wellbore, and carry cuttings to the surface. Cuttings are the broken bits of rock and soil extracted during drilling. Both materials can pose environmental hazards if not disposed of properly, due to potential contamination from hydrocarbons and heavy metals.
**Traditional Methods of Waste Disposal**
Historically, drilling waste has been managed through methods such as burial in onsite pits, landfarming, or incineration. While these techniques have been effective to a degree, they often involve significant environmental risks and costs. In recent years, stricter regulations have prompted the industry to look for more sustainable and cost-effective solutions.
**Innovative Recycling Techniques**
1. **Thermal Desorption**
Thermal desorption is a promising method for recycling drilling waste. It involves heating the waste to separate hydrocarbons from solids. The recovered hydrocarbons can be reintroduced into the drilling fluid system, while cleaned solids are safe for disposal or use in construction material. This approach not only minimizes environmental impact but also reduces the need for fresh drilling fluid.
2. **Bioremediation**
Bioremediation leverages microorganisms to break down contaminants in drilling waste. This natural process can effectively reduce the toxicity of mud and cuttings, making them suitable for safe disposal or repurposing. Bioremediation is particularly effective for oil-based muds, where hydrocarbons are the primary concern.
3. **Solidification and Stabilization**
Solidification and stabilization involve mixing drilling waste with binding agents such as cement, lime, or fly ash. This process transforms waste into solid blocks or aggregates, reducing leachability and potential environmental hazards. The stabilized waste can then be used in construction, such as in road bases or as fill material.
4. **Cuttings Reuse**
There are several innovative methods for reusing cuttings:
- **Construction Material**: Cuttings can be transformed into bricks or tiles, providing a sustainable alternative to traditional building materials.
- **Agricultural Applications**: When treated appropriately, cuttings can enhance soil structure and fertility, offering benefits for agriculture.
**Economic and Environmental Benefits**
Recycling drilling waste offers substantial economic advantages, reducing disposal costs and recovering valuable materials. Furthermore, these methods significantly decrease environmental impact, helping companies meet regulatory standards while contributing to global sustainability goals.
**Challenges and Future Prospects**
Despite the promise of these recycling methods, challenges remain. Technical limitations, high initial costs, and regulatory hurdles can impede widespread adoption. Continued research and development are essential to refine these techniques and expand their applicability. Collaboration between industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies will be vital in advancing sustainable drilling waste management practices.
**Conclusion**
The shift towards recycling drilling waste marks a significant advancement in environmental stewardship within the oil and gas industry. By embracing innovative methods such as thermal desorption, bioremediation, and solidification, companies can mitigate ecological risks while deriving economic benefits. As technology progresses and awareness grows, the potential for widespread implementation of these practices holds promise for a cleaner, more sustainable future in drilling operations.
Navigating the Complexities of Drilling Innovation? Let AI Do the Heavy Lifting
In an industry where subsurface conditions, materials science, and drilling dynamics evolve rapidly, staying ahead of technical innovation and protecting your intellectual property can be overwhelming.
Patsnap Eureka, our cutting-edge AI assistant, is built for R&D and IP professionals in high-tech industries like drilling technologies. Whether you're optimizing rotary steerable systems, evaluating high-temperature materials, or exploring next-gen automation in directional drilling, Eureka enables real-time analysis of the latest patents, technology landscapes, and competitive movements—all from one intelligent, intuitive platform.
Ready to accelerate your development cycle and make strategic decisions with confidence? Explore Patsnap Eureka today—where smart drilling starts with smarter insights.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com