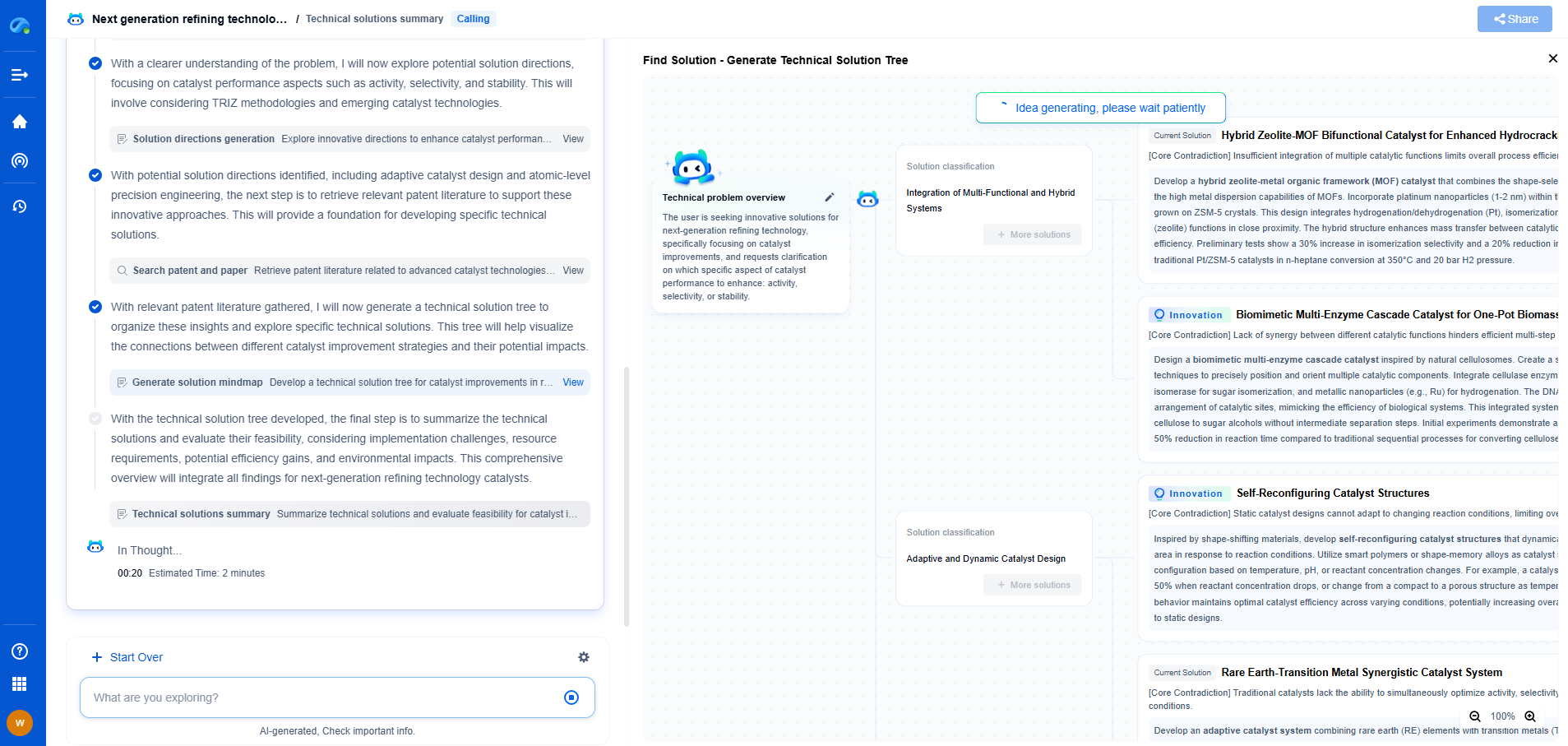
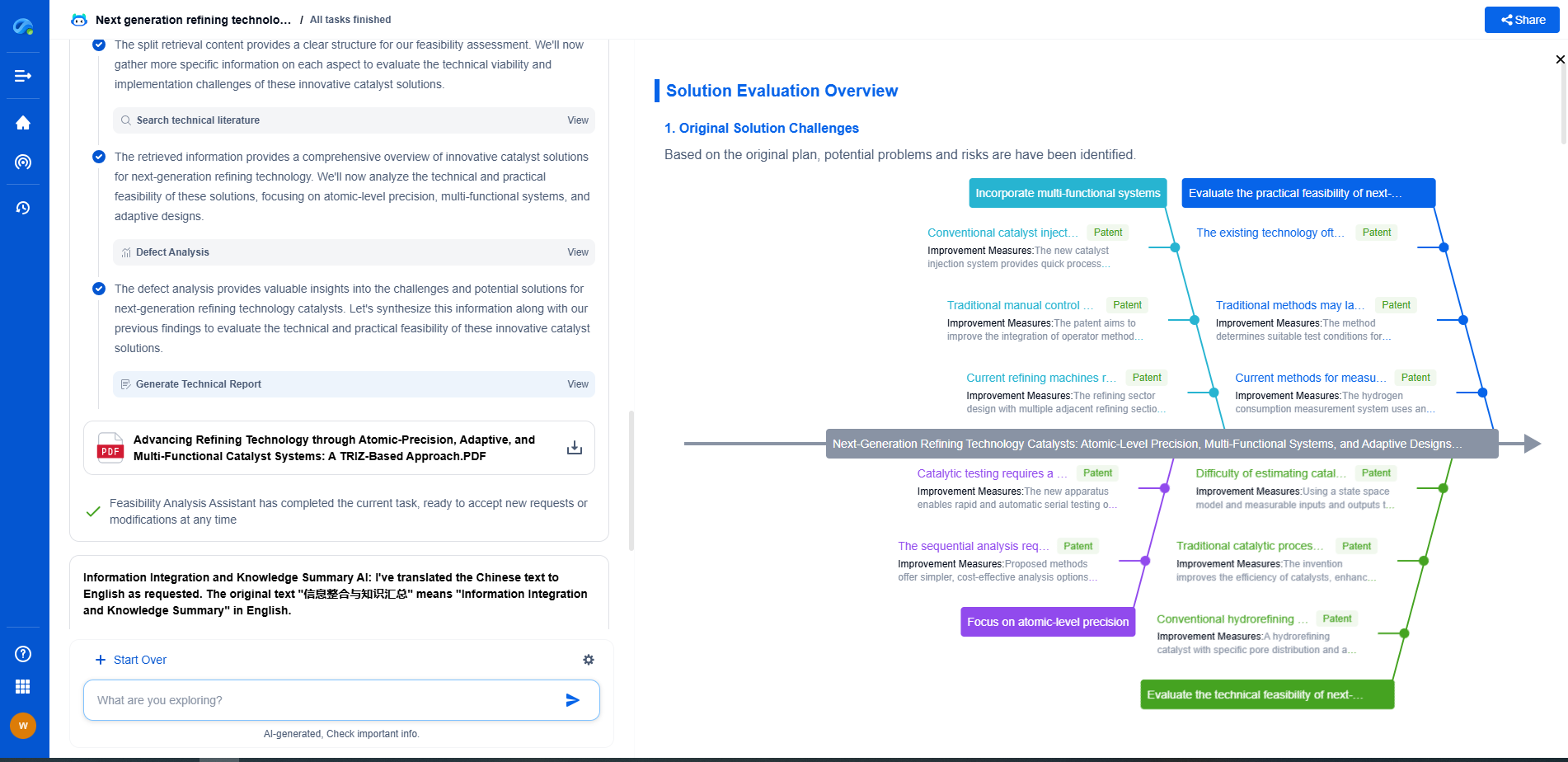
Pressure sensors are devices that measure the force exerted by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface, converting this physical pressure into an electrical signal for monitoring or control purposes. They operate based on various principles such as piezoresistive, capacitive, and piezoelectric effects. Pressure sensors are critical in applications like industrial automation, automotive systems, medical devices, and aerospace. Accuracy, stability, and environmental compatibility are key performance criteria.
Understanding Self-Powered Pressure Sensors
Self-powered pressure sensors generate their own power through energy harvesting techniques. These sensors typically use piezoelectric materials or other mechanisms to convert mechanical energy from pressure changes into electrical energy. This self-sufficiency makes them a compelling choice for certain applications.
Pros of Self-Powered Pressure Sensors
1. Long-Term Cost Efficiency: Since self-powered sensors do not rely on external power sources like batteries, they eliminate the recurring costs associated with battery replacement. This can lead to significant savings over time, especially in large-scale applications.
2. Environmental Friendliness: With no need for batteries, self-powered sensors reduce electronic waste, contributing to environmentally sustainable practices.
3. Maintenance-Free Operation: The absence of batteries means reduced maintenance, as there is no need for regular battery checks or replacements. This simplifies the upkeep of systems in remote or hard-to-reach locations.
4. Adaptability: These sensors are well-suited for applications where power sources are limited or unavailable, such as in remote environmental monitoring stations.
Cons of Self-Powered Pressure Sensors
1. Limited Energy Output: The energy generated by self-powered sensors may be insufficient for certain applications requiring high power or continuous data transmission.
2. Design Complexity: Incorporating energy harvesting mechanisms can complicate the sensor design, potentially increasing initial development costs and time.
3. Sensitivity to Environmental Changes: The efficiency of energy harvesting can be affected by environmental conditions, such as temperature or humidity, which may impact sensor reliability.
Exploring Battery-Based Pressure Sensors
Battery-based pressure sensors rely on batteries as their primary power source. These sensors are widely used due to their straightforward design and reliable performance.
Pros of Battery-Based Pressure Sensors
1. Consistent Power Supply: Batteries provide a steady and reliable power source, ensuring consistent sensor performance over time.
2. Simplified Design: The use of batteries simplifies sensor design and integration, making battery-based sensors a popular choice for many applications.
3. High Power Output: Battery-based sensors can deliver higher power levels, supporting advanced functionalities such as wireless data transmission and real-time monitoring.
4. Versatile Application: These sensors are suitable for a wide range of applications, from industrial automation to medical devices, due to their reliable power supply.
Cons of Battery-Based Pressure Sensors
1. Maintenance Requirements: Regular battery replacement or recharging is necessary, leading to additional maintenance efforts and costs.
2. Environmental Impact: The disposal of batteries contributes to electronic waste, posing environmental challenges and requiring proper waste management.
3. Limited Lifespan: Battery lifespan can be a limiting factor, particularly in long-term applications where continuous operation is essential.
Making the Right Choice
Choosing between self-powered and battery-based pressure sensors depends on various factors, including the application requirements, environmental conditions, and budget constraints. Self-powered sensors are ideal for applications where maintenance-free operation and environmental sustainability are priorities. In contrast, battery-based sensors offer consistent power supply and higher energy output, making them suitable for applications demanding advanced functionalities.
Conclusion
Both self-powered and battery-based pressure sensors have their own set of advantages and limitations. Understanding these can help you select the right sensor type for your specific needs. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further advancements in sensor design and energy solutions, ultimately broadening the range of applications and enhancing performance across industries.
Self-Powered vs. Battery-Based Pressure Sensors: Pros and Cons
JUL 14, 2025 |
From 5G NR to SDN and quantum-safe encryption, the digital communication landscape is evolving faster than ever. For R&D teams and IP professionals, tracking protocol shifts, understanding standards like 3GPP and IEEE 802, and monitoring the global patent race are now mission-critical.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
📡 Experience Patsnap Eureka today and unlock next-gen insights into digital communication infrastructure, before your competitors do.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com