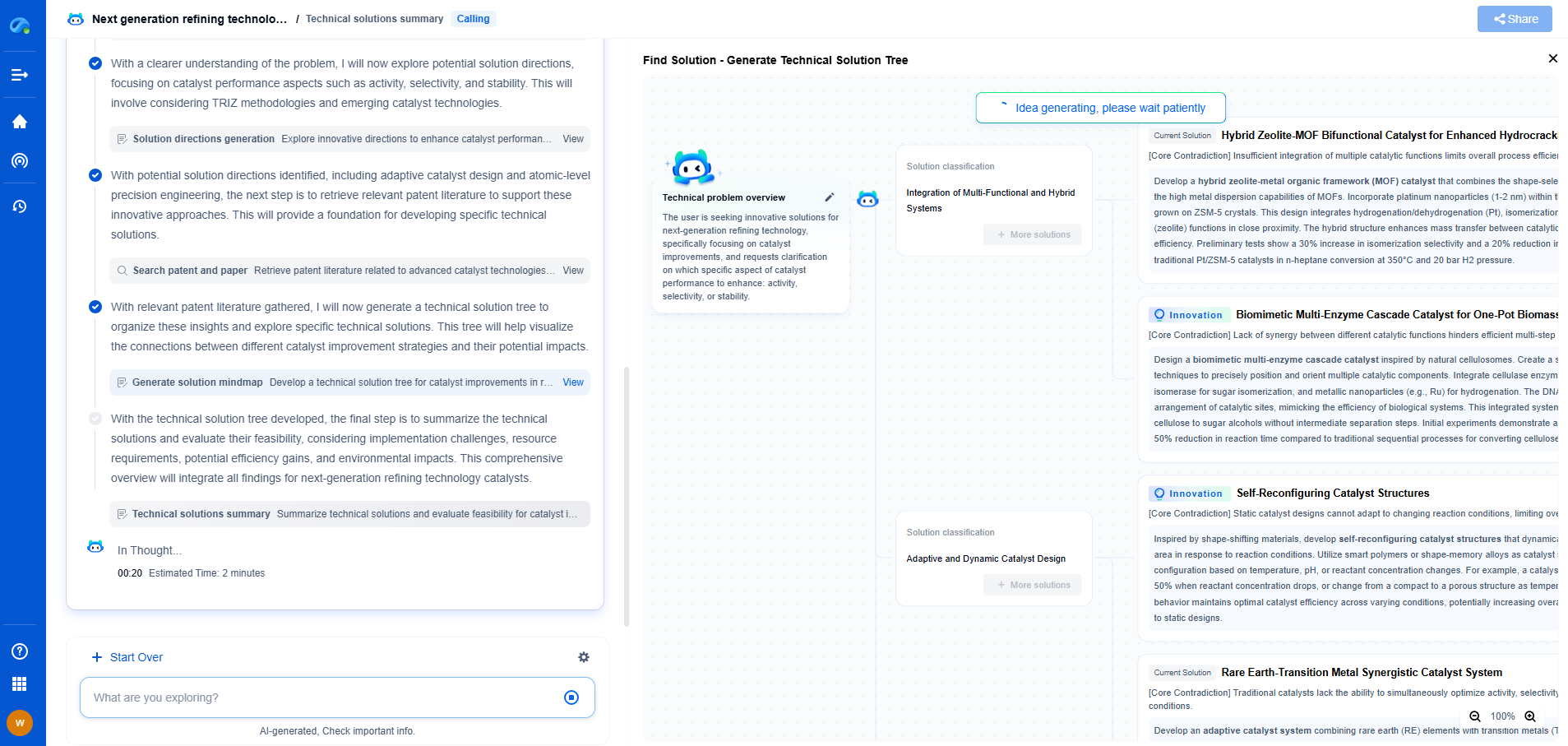
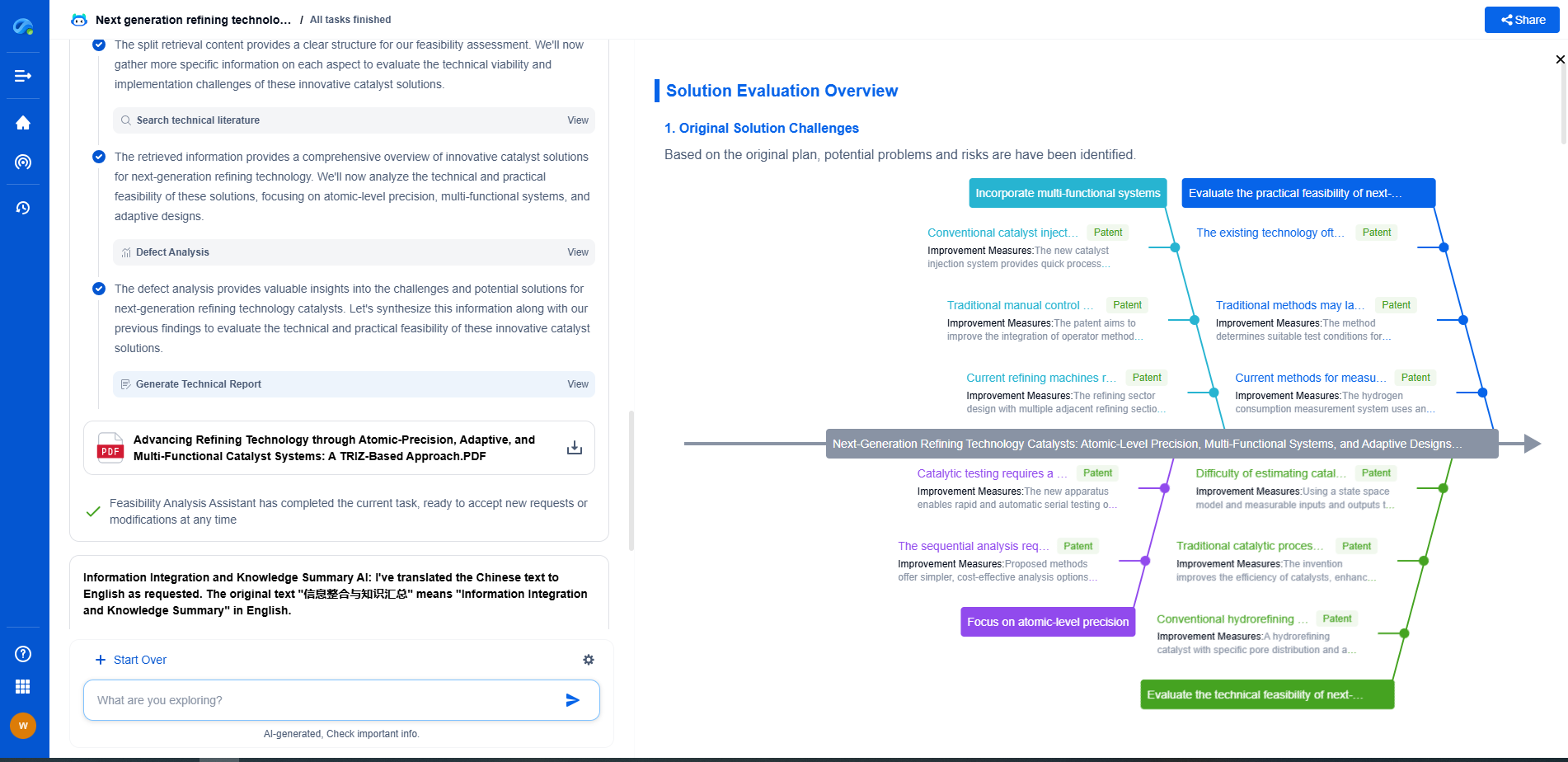
Self-Powered Wireless Sensors for Hard-to-Reach Industrial Locations
JUL 14, 2025 |
In the ever-evolving landscape of industrial operations, the demand for reliable and efficient monitoring systems is more pressing than ever. Industrial sites often encompass vast and complex infrastructures, with numerous hard-to-reach areas that are critical for operations. Traditional wired sensors can be challenging to deploy and maintain in such environments. Enter self-powered wireless sensors—a groundbreaking solution that promises to revolutionize how industries monitor and manage these difficult-to-access locations.
The Need for Self-Powered Wireless Sensors
Industries such as oil and gas, manufacturing, mining, and utilities often have remote or unreachable areas that require constant monitoring. Equipment located in these areas, such as pipelines, tanks, and heavy machinery, are critical to the operations but can be difficult and costly to monitor using traditional methods. Wired sensors require a network of cables, complicating installation and increasing maintenance efforts. Moreover, replacing batteries in wireless sensors located in inaccessible areas is often impractical.
Self-powered wireless sensors address these challenges by eliminating the need for external power sources or frequent battery replacements. These sensors leverage energy-harvesting technologies, such as solar, thermal, vibrational, or radio frequency energy, to power themselves. This allows for the deployment of sensors in harsh and remote environments, providing continuous and reliable data without the logistical hurdles of traditional systems.
Benefits of Self-Powered Wireless Sensors
1. Cost-Effectiveness: By eliminating the need for extensive wiring and reducing maintenance costs associated with battery replacements, self-powered sensors offer a cost-efficient solution over the long term. They enable more widespread monitoring, leading to better decision-making and resource allocation.
2. Enhanced Safety: Continuous monitoring of hard-to-reach industrial locations can preemptively identify issues before they escalate, ensuring the safety of personnel and reducing the risk of accidents. Real-time data can facilitate quicker responses to potential hazards.
3. Environmental Sustainability: Energy-harvesting technologies minimize dependence on external power sources, promoting a more sustainable approach to industrial monitoring. This aligns with global efforts to reduce carbon footprints and embrace greener technologies.
4. Longevity and Reliability: With the capability to harness energy from their surroundings, self-powered sensors can operate over extended periods, ensuring consistent and reliable data collection. This increases the lifespan of the sensors and enhances system reliability.
Applications in Industrial Settings
The versatility of self-powered wireless sensors makes them applicable across a wide range of industrial settings:
- Oil and Gas: Monitoring pipelines for leaks, corrosion, and pressure changes is crucial. Self-powered sensors can be deployed along extensive pipelines, ensuring data is consistently gathered irrespective of location.
- Manufacturing: In large-scale manufacturing plants, machinery health and environmental conditions such as temperature and humidity can be continuously monitored to enhance productivity and prevent equipment failure.
- Utilities: For power grids and water supply systems, self-powered sensors can track operational parameters in real-time, ensuring stability and efficiency in service delivery.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite their many advantages, self-powered wireless sensors face several challenges. The efficiency of energy-harvesting technologies can be impacted by environmental factors, and ensuring robust connectivity in remote areas remains a technical hurdle. Additionally, integrating these sensors into existing industrial systems can require significant upfront investment and technical expertise.
However, advancements in materials science, energy storage, and wireless communication technologies are poised to address these challenges. The ongoing development of more efficient energy harvesters and low-power sensor technologies will likely enhance the capability and appeal of self-powered sensors. As industries increasingly prioritize data-driven decision-making, the adoption of self-powered wireless sensors is expected to grow, driving innovation and efficiency in industrial operations.
Conclusion
Self-powered wireless sensors are transforming the way industries monitor and manage operations in hard-to-reach locations. By offering a sustainable, cost-effective, and reliable solution, these sensors are paving the way for more efficient and safe industrial practices. As technology continues to advance, the potential applications and benefits of self-powered sensors will expand, underscoring their critical role in the future of industrial monitoring.
From 5G NR to SDN and quantum-safe encryption, the digital communication landscape is evolving faster than ever. For R&D teams and IP professionals, tracking protocol shifts, understanding standards like 3GPP and IEEE 802, and monitoring the global patent race are now mission-critical.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
📡 Experience Patsnap Eureka today and unlock next-gen insights into digital communication infrastructure, before your competitors do.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com