Space-Based vs. Earth-Based Solar Power: Efficiency and Feasibility Comparison
JUL 22, 2025 |
As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and the need for sustainable energy sources, solar power has emerged as a viable solution. Traditionally harnessed from Earth, solar power technology is continuously evolving, with innovative concepts such as space-based solar power (SBSP) entering the conversation. This blog explores the efficiency and feasibility of space-based versus earth-based solar power, examining the pros and cons of each approach.
Harnessing Solar Power: Earth-Based Systems
Earth-based solar power systems have been in use for decades, providing renewable energy for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes. These systems capture sunlight using photovoltaic (PV) panels or concentrated solar power (CSP) systems.
Pros of Earth-Based Solar Power
1. **Proven Technology**: Earth-based solar power is a well-established, proven technology with extensive research and development behind it. The technology continues to improve, with advancements in panel efficiency, battery storage, and cost reduction.
2. **Accessibility and Scalability**: Solar panels can be installed in various locations, from rooftops to large solar farms, making them accessible to a wide range of users. The scalability of earth-based systems allows for gradual investment and expansion.
3. **Environmental Compatibility**: Solar panels produce no emissions during operation, significantly reducing the carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels. Moreover, they have minimal environmental impact when installed in non-sensitive areas.
Cons of Earth-Based Solar Power
1. **Intermittency and Weather Dependence**: Solar power generation is subject to weather conditions and diurnal cycles. Cloud cover, rain, and nighttime reduce the availability of sunlight, affecting energy production.
2. **Land Use**: Large solar farms require significant land areas, which can lead to habitat disruption and land-use conflicts, especially in densely populated regions.
Exploring Space-Based Solar Power
Space-based solar power involves placing solar panels in orbit to capture sunlight and transmit the energy back to Earth. While still in conceptual stages, SBSP offers intriguing possibilities for overcoming the limitations of earth-based systems.
Pros of Space-Based Solar Power
1. **Constant Solar Exposure**: Satellites in geostationary orbit can capture sunlight 24/7 without interference from weather or night cycles, offering a consistent and reliable energy source.
2. **Unobstructed Solar Access**: Space-based systems are unaffected by atmospheric absorption or scattering, allowing them to harness solar energy more efficiently than ground-based systems.
3. **Global Energy Distribution**: SBSP has the potential to provide energy to remote or underserved regions, bypassing the limitations of terrestrial infrastructure.
Cons of Space-Based Solar Power
1. **High Initial Costs**: Launching and maintaining solar satellites require significant investments, with high costs associated with space transportation and technology development.
2. **Technical Challenges**: The practical implementation of SBSP faces numerous technical hurdles, including the safe and efficient transmission of energy back to Earth, potential interference with satellite communications, and the durability of space-based systems.
3. **Regulatory and Safety Concerns**: The development of SBSP systems would require international cooperation and regulation to address issues of space debris, safety, and energy allocation.
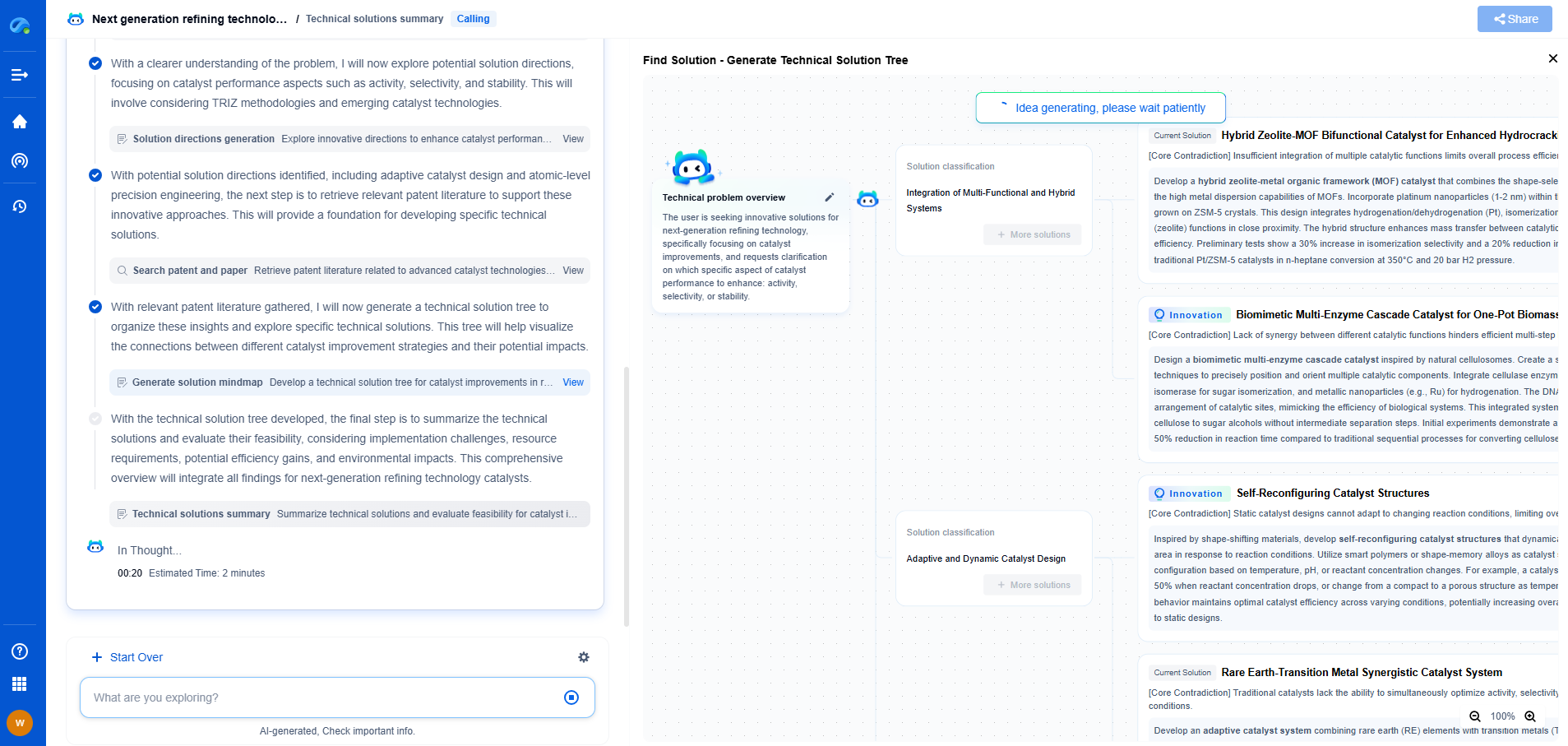
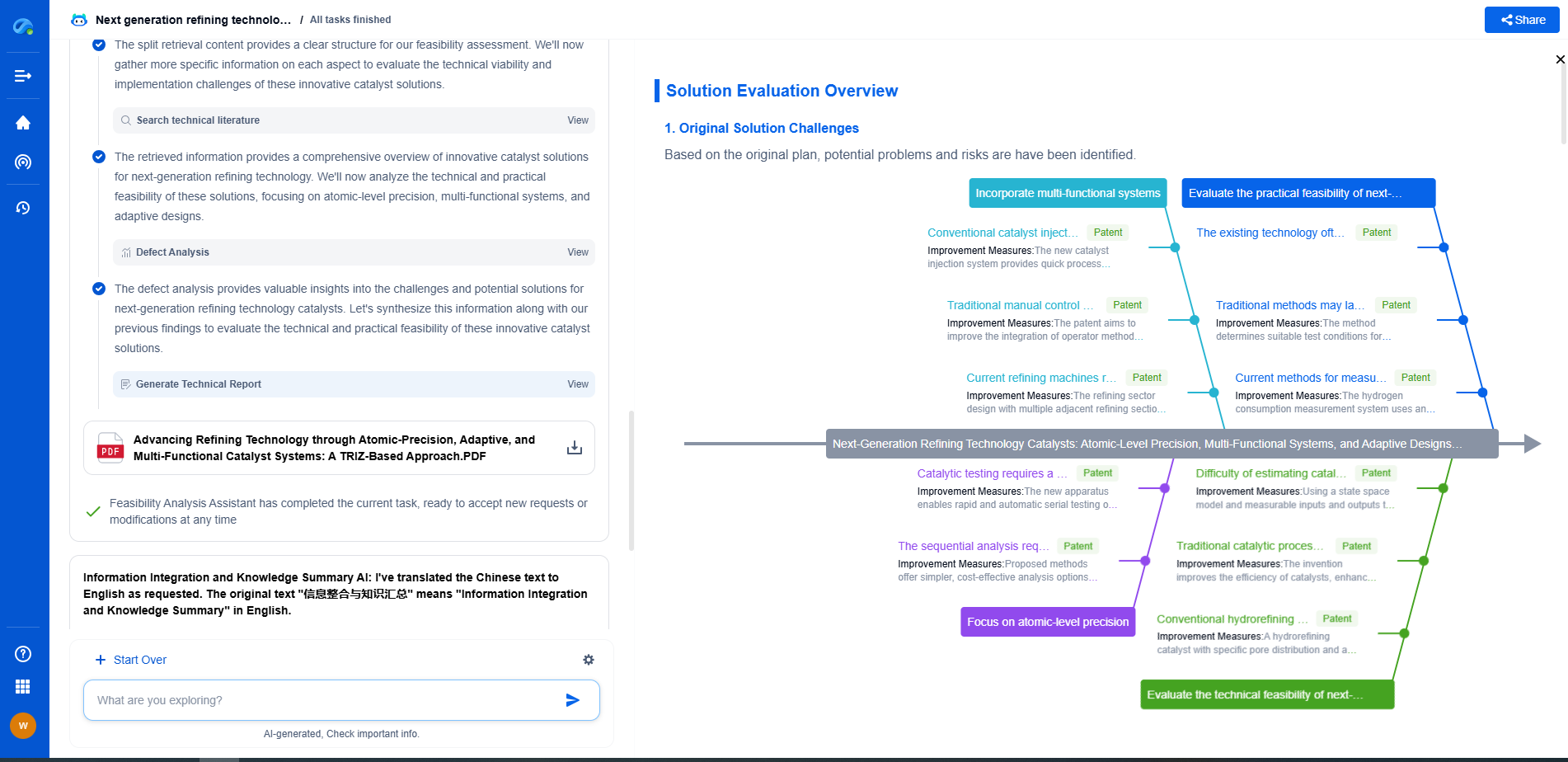
Efficiency and Feasibility Comparison
Comparing the efficiency and feasibility of space-based and earth-based solar power involves considering both current capabilities and future potential. Earth-based systems benefit from their established infrastructure and continual technological improvements, making them a practical choice for immediate and medium-term energy needs.
In contrast, space-based solar power represents a visionary approach with the potential to revolutionize global energy systems. However, its technical and financial challenges mean that significant advancements are needed before it can become a mainstream solution.
Conclusion
Both space-based and earth-based solar power systems offer distinct advantages and face unique challenges. While earth-based solar power continues to be a reliable and accessible energy source, the potential of space-based solar power as a future game-changer cannot be ignored. As technology progresses and investment in renewable energy grows, the balance between these two approaches may shift, shaping the future of global energy production.
As solar technology races ahead—from perovskite cells to tandem architectures, from anti-reflective coatings to transparent electrodes—staying on top of fast-moving innovation has become a strategic imperative.
Patsnap Eureka, our intelligent AI assistant built for R&D professionals in high-tech sectors, empowers you with real-time expert-level analysis, technology roadmap exploration, and strategic mapping of core patents—all within a seamless, user-friendly interface.
⚡ Ready to accelerate your solar innovation journey? Try Patsnap Eureka today and let AI help you harness the full power of the sun—and your IP strategy.
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com